From encrypted communications and digital signatures to IoT device authentication and secure email, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) forms the backbone of trust in digital ecosystems. But as compliance mandates like GDPR, HIPAA, eIDAS, FIPS 140-2, and SOX become more stringent, selecting the right PKI solution provider is no longer just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one.
Choosing a PKI provider for compliance involves more than comparing prices or scanning feature checklists. Organizations must evaluate providers on multiple fronts: security capabilities, scalability, compliance certifications, support services, automation, and cloud readiness. A misstep could lead to compliance violations, security breaches, or costly downtime.
This guide walks you through the key factors to consider when picking the best PKI solution provider for your regulatory needs in 2026 and beyond.
1. Understand Your Compliance Requirements
Choosing the best PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) solution provider starts with a clear understanding of your industry-specific compliance requirements. In today’s data-driven world, simply having encryption isn’t enough. Different industries are governed by regulatory frameworks that mandate specific cryptographic standards, certificate management practices, and audit capabilities. Failure to comply can result in data breaches, loss of trust, and severe legal penalties.
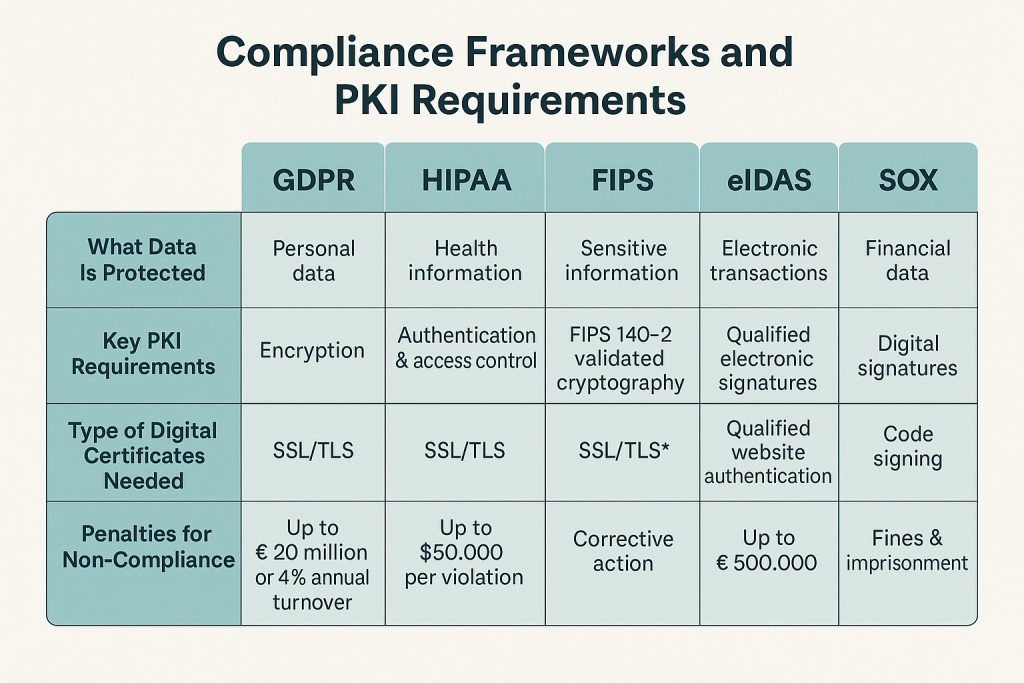
Before you evaluate a PKI provider, you must identify which regulatory standards apply to your organization and how a PKI solution can help you meet them. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most critical compliance frameworks and what they require from a PKI system:
1. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation – EU)
The GDPR mandates strong data protection measures for all entities handling personally identifiable information (PII) of EU citizens. One of the key components of GDPR compliance is the encryption and authentication of sensitive data, which PKI enables through digital certificates and secure key management.
-
✅ Requires encryption at rest and in transit
-
✅ Enforces strong identity verification (via certificates)
-
✅ Demands audit trails for data access and changes
-
✅ Penalties: Up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover
2. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act – USA)
For healthcare providers, insurers, and third-party vendors, HIPAA sets strict guidelines for protecting Protected Health Information (PHI). PKI helps enforce confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) by enabling secure communications, email encryption, and strong access control.
-
✅ Digital signatures ensure data integrity in medical records
-
✅ Secure messaging systems between healthcare providers
-
✅ Device authentication and secure portal access
3. eIDAS (Electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services – EU)
This EU regulation focuses on cross-border trust services and qualified electronic signatures. If your business operates in or with the EU, your PKI provider must support Qualified Trust Service Providers (QTSPs) and issue qualified digital certificates.
-
✅ Enables legally binding digital signatures
-
✅ Requires timestamping and certificate validation services
-
✅ Important for legal, finance, and cross-border transactions
4. FIPS 140-2 (Federal Information Processing Standard – USA)
FIPS 140-2 is a U.S. government standard that defines security requirements for cryptographic modules. Any organization dealing with federal contracts, defense, or classified data must ensure their PKI vendor uses FIPS 140-2 validated hardware and software.
-
✅ Ensures tamper-resistant hardware security modules (HSMs)
-
✅ Standard for encryption, hashing, and key management
-
✅ Often a baseline for high-security sectors including defense and aerospace
5. SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act – USA)
SOX mandates strict IT controls to ensure financial reporting accuracy and transparency. PKI solutions contribute by digitally signing financial documents, enforcing role-based access, and generating detailed audit logs for every transaction.
-
✅ Ensures document integrity through digital signing
-
✅ Enables secure access control for financial systems
-
✅ Supports audit trails for compliance audits
Key Takeaway:
Don’t assume that every PKI provider automatically complies with all standards. Ask direct questions such as:
-
“Do you offer GDPR- or HIPAA-compliant solutions out of the box?”
-
“Is your cryptographic module FIPS 140-2 validated?”
-
“Can you provide documentation of third-party audits or compliance certifications?”
The right provider should not only be aware of these regulations but also offer pre-configured templates, automated certificate management, and audit-ready logs tailored for your industry.
2. Evaluate PKI Core Capabilities
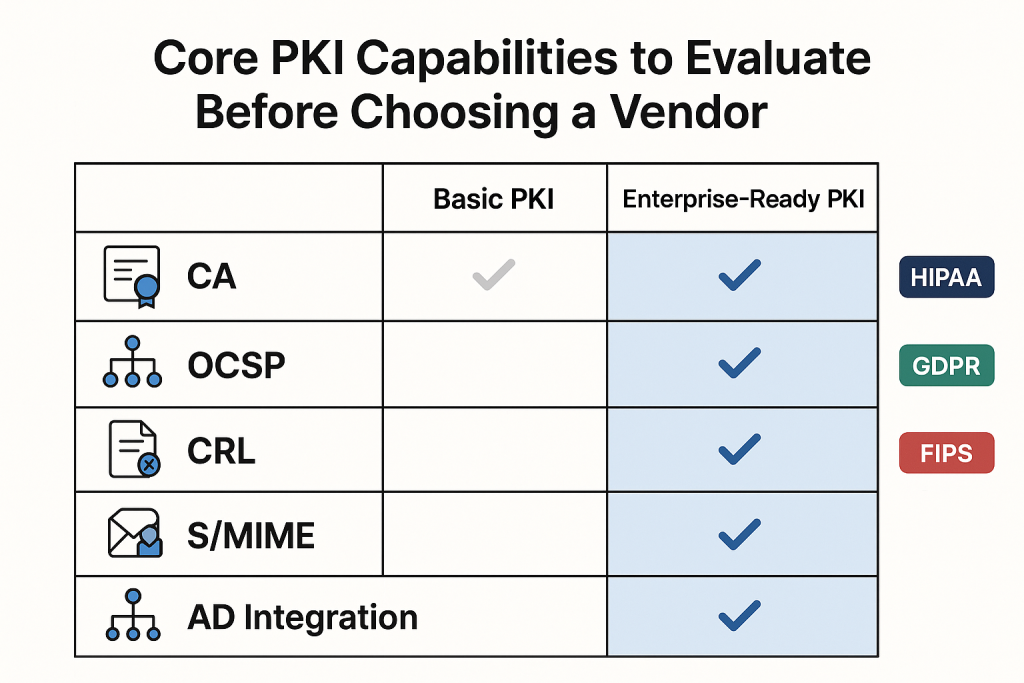
Once you’ve ensured that a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) provider aligns with your industry’s compliance frameworks, the next step is to evaluate their core technical capabilities. A robust PKI provider isn’t just compliant—it must also be technically equipped to support your organization’s current security needs and future growth.
At the heart of every PKI system lies a set of core components and functionalities that govern the issuance, validation, and management of digital certificates. These components ensure identity assurance, data confidentiality, and transaction integrity across networks, devices, applications, and users.
Below are the critical PKI features you should evaluate before choosing a solution provider:
Certificate Authority (CA) Hierarchy Support
The Certificate Authority is the cornerstone of trust in any PKI system. Look for providers that support a scalable CA hierarchy—including root CAs, intermediate CAs, and subordinate CAs. A flexible CA architecture allows you to:
-
Separate public-facing and internal certificate chains
-
Delegate certificate issuance across departments or regions
-
Improve security through role segregation and controlled trust anchors
Certificate Issuance and Revocation Policies
A reliable PKI provider must offer granular control over how certificates are issued, renewed, and revoked. These policies help enforce security standards and automate trust workflows.
Key features to look for:
-
Role-based access for certificate requests
-
Automated approval workflows
-
Scheduled renewal and revocation options
-
Policy enforcement for different certificate types (SSL, S/MIME, code signing)
OCSP and CRL Support (Real-Time Status Checking)
Timely revocation of compromised or expired certificates is critical to maintaining system security. Ensure that the PKI provider supports:
-
OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol) for real-time certificate validation
-
CRL (Certificate Revocation Lists) for batch verification when OCSP is not available
A modern PKI solution should include high-availability OCSP responders and allow for custom CRL publishing intervals to ensure uninterrupted service.
Support for S/MIME, TLS/SSL, Document Signing, Code Signing
Your PKI solution should be versatile enough to handle various use cases:
- S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) for email encryption and authentication
-
TLS/SSL certificates for securing websites and applications
-
Document signing to ensure content integrity and legal validity
-
Code signing certificates to verify software authenticity and prevent tampering
Support for these standards enables end-to-end digital trust, both internally and externally.
Integration with Active Directory, LDAP, Mobile and IoT Endpoints
Enterprises often operate across hybrid environments. Your PKI provider should offer out-of-the-box integration with:
- Active Directory or LDAP directories for identity-based certificate provisioning
-
MDM (Mobile Device Management) platforms for mobile endpoint trust
-
IoT security frameworks for securing embedded systems and connected medical devices
This enables automated enrollment, certificate-based authentication, and centralized policy enforcement across diverse endpoints.
Scalability and Lifecycle Management
Finally, evaluate whether the PKI platform can scale as your business grows. A modern PKI system should include:
- Automated certificate lifecycle management (CLM)
-
Dashboards for visibility into certificate status, expirations, and renewals
-
APIs for integration with DevOps pipelines, cloud-native apps, and security tools
A strong PKI solution should manage thousands of certificates across users, devices, and applications—with minimal manual intervention.
3. Check for Automation and Lifecycle Management
In 2026, manual certificate management is a high-risk liability. As organizations scale their digital infrastructure, managing hundreds—or even thousands—of certificates manually becomes impractical, error-prone, and non-compliant. A single expired certificate can bring down mission-critical systems, disrupt patient care (in healthcare), or compromise financial transactions (in banking and fintech). That’s why automation is no longer a luxury—it’s a core requirement for any modern PKI solution.
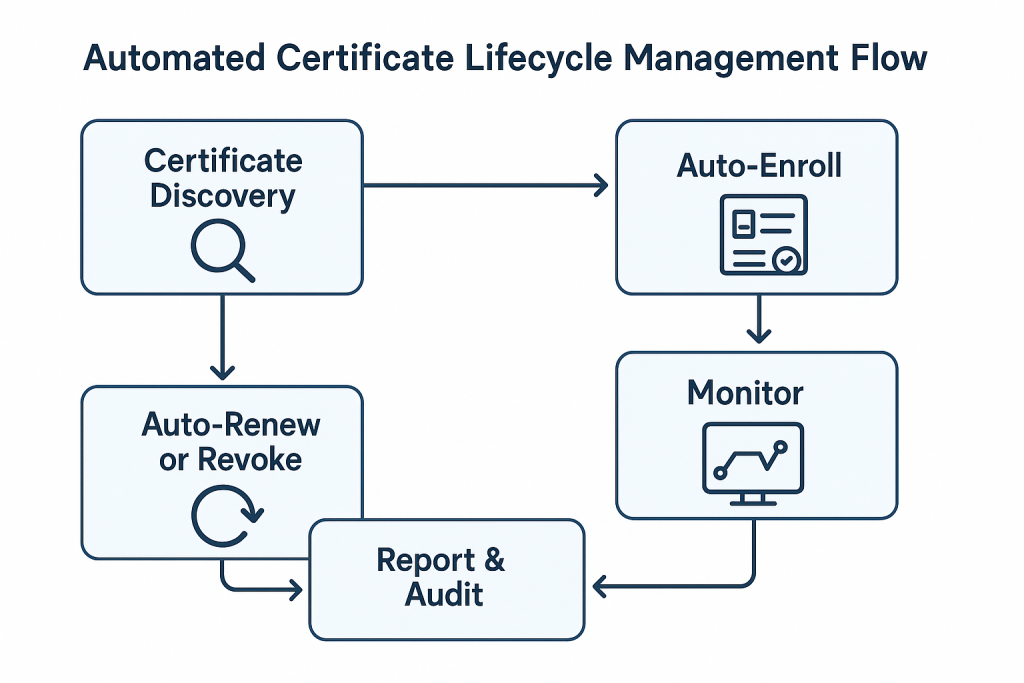
When choosing a PKI solution provider, look for end-to-end certificate lifecycle automation features that improve visibility, eliminate human error, and enable proactive compliance management.
Here’s what a fully automated PKI lifecycle management system should offer:
1. Discovery of Unmanaged and Shadow Certificates
Before you can manage certificates, you need to find them—especially those that were issued manually, by third-party tools, or by rogue internal systems. These “shadow certificates” pose serious risks if left unchecked.
A reliable PKI provider should offer:
-
Automated scanning of networks and endpoints for unmanaged certificates
-
Inventory mapping of all SSL/TLS, code signing, S/MIME, and device certificates
-
Reporting dashboards to visualize certificate usage across departments
2. Auto-Enrollment and Certificate Provisioning
Manual enrollment introduces delays, inconsistencies, and errors. Look for PKI solutions that support auto-enrollment protocols such as:
-
SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol)
-
EST (Enrollment over Secure Transport)
-
ACME (Automatic Certificate Management Environment)
These protocols automate certificate issuance for:
-
User identities via Active Directory
-
Mobile and BYOD devices via MDM solutions
-
IoT devices and servers at scale
3. Auto-Renewal and Revocation
Expired certificates are one of the leading causes of unplanned outages. A robust PKI platform should support automatic renewal of certificates before expiration and provide:
-
Pre-expiry notifications
-
Zero-downtime renewal processes
-
Granular revocation control in case of key compromise or policy violations
Automated revocation should be integrated with:
-
OCSP responders
-
CRL publishing mechanisms
-
SIEM tools for triggering alerts
4. Centralized Dashboard and Real-Time Alerts
A unified control panel is essential to manage the entire certificate lifecycle. The platform should provide:
-
Centralized visibility into issued, pending, expiring, and revoked certificates
-
Customizable alerts for expiry, misconfiguration, or unauthorized issuance
-
Audit trails and compliance reporting tools
This kind of certificate management dashboard helps security teams prevent disruptions and ensures that internal/external audits are met with confidence.
Why Automation Matters
✅ Improves Security: Eliminates certificate-based vulnerabilities
✅ Enables Scalability: Manage thousands of certificates across apps, devices, and teams
✅ Reduces Downtime: Prevents outages due to expired or misconfigured certificates
✅ Ensures Continuous Compliance: Meets HIPAA, GDPR, FIPS, SOX, and other regulatory requirements
✅ Saves Time and Resources: Reduces manual effort and human error
4. Review Security Infrastructure and Trust Models
In the world of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), security is non-negotiable. The integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of your entire digital environment depend on how well your PKI system is architected and protected. A weak or poorly configured PKI solution can be more dangerous than having no encryption at all—leaving you vulnerable to insider threats, supply chain attacks, and certificate misuse.
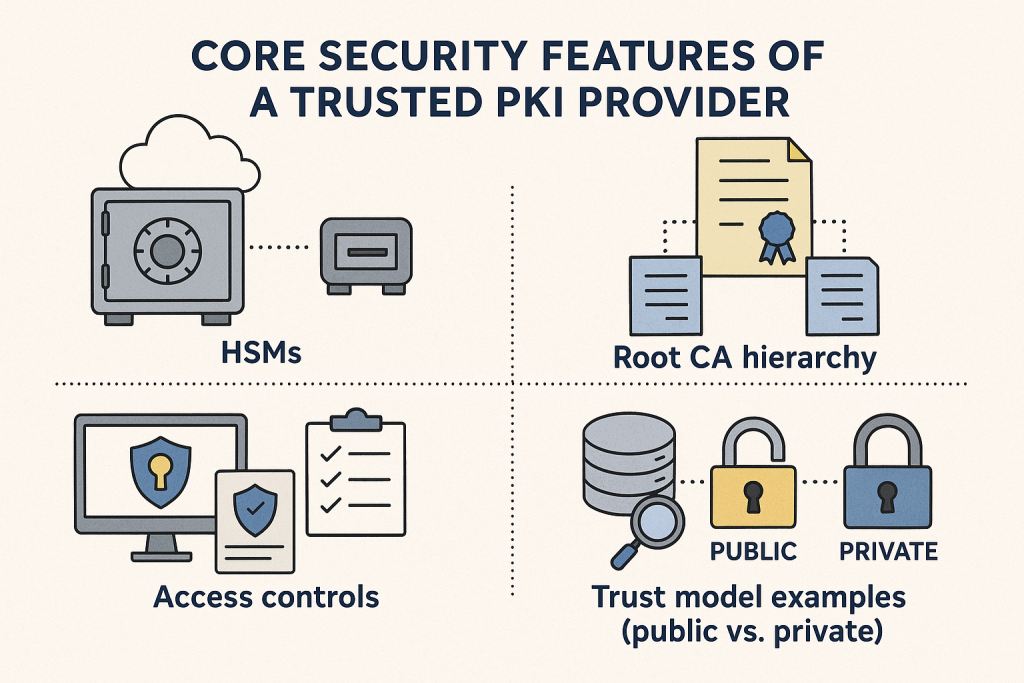
When choosing a PKI provider, it’s critical to evaluate the underlying security infrastructure, how cryptographic keys are stored and protected, and whether their trust models align with your use case—especially if you’re operating in regulated sectors like finance, healthcare, government, or defense.
Here are the key components to evaluate:
1. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) for Key Protection
HSMs are tamper-resistant hardware devices used to generate, store, and protect cryptographic keys. They ensure that private keys are never exposed, even to internal administrators. A trusted PKI provider should use:
-
FIPS 140-2 or FIPS 140-3 validated HSMs
-
Dedicated or multi-tenant HSM configurations
-
Cloud HSM options for scalable deployments
HSMs are essential for:
-
Digital certificate signing
-
Code signing and document signing
-
Key escrow and archival with regulatory compliance
2. Protection Against Insider and External Threats
A solid PKI architecture must account for both external attackers and malicious insiders. Ask your provider how they handle:
-
Role-based access control (RBAC) for CA administrators
-
Separation of duties (SoD) to reduce insider risks
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for administrative tasks
-
Logging of every key generation, issuance, and revocation event
Also inquire about physical security, secure cloud zones, and how they defend against DDoS attacks, CA compromise, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
3. Tamper-Proof Logging and Key Archival
Maintaining auditable logs is crucial for compliance and breach investigation. Your PKI provider should offer:
-
Immutable log storage for all certificate events
-
Cryptographically signed logs that cannot be altered post-fact
-
Secure key archival policies with backup encryption and retention settings
-
Time-stamping services for legal and forensic use cases
4. Use of Proven and Modern Cryptographic Algorithms
Make sure your provider uses only industry-standard, peer-reviewed cryptographic algorithms. Avoid vendors using outdated or proprietary encryption methods.
Best practices include:
-
RSA 2048/4096-bit or ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
-
SHA-2 or SHA-3 hashing (avoid SHA-1)
-
TLS 1.3 compatibility
-
Support for post-quantum cryptography (if future-proofing is required)
Your PKI system should also support algorithm agility—the ability to adapt to new cryptographic standards without major reengineering.
5. Root of Trust Model: Private vs. Publicly Trusted CAs
Your organization’s trust model determines how your certificates are recognized:
-
Private CA: Ideal for internal use (device authentication, internal services, intranet)
-
Public CA: Required for websites, customer-facing portals, or software distributed to third parties
Confirm whether the provider offers:
-
Publicly trusted root CA inclusion (e.g., in Microsoft, Mozilla, Apple stores)
-
Support for private CA setup with full control
-
Hybrid trust models for organizations that require both
FIPS 140-2 HSM: A Must for Compliance
If you’re in a regulated industry (healthcare, government, defense, finance), FIPS 140-2 or FIPS 140-3 validation is non-negotiable. Ask your provider for:
-
Validation certificates from NIST
-
Compliance reports or third-party audit results
-
Independent penetration testing outcomes
This ensures your cryptographic keys are secure, standards-compliant, and legally defensible during audits or breaches.
.
5. Look for Third-Party Audits and Certifications
In a digital ecosystem where trust is everything, third-party audits and industry certifications are your best assurance that a PKI solution provider follows globally accepted security practices. While any provider can claim to be secure and compliant, only independently verified certifications can prove that claim holds up under scrutiny.
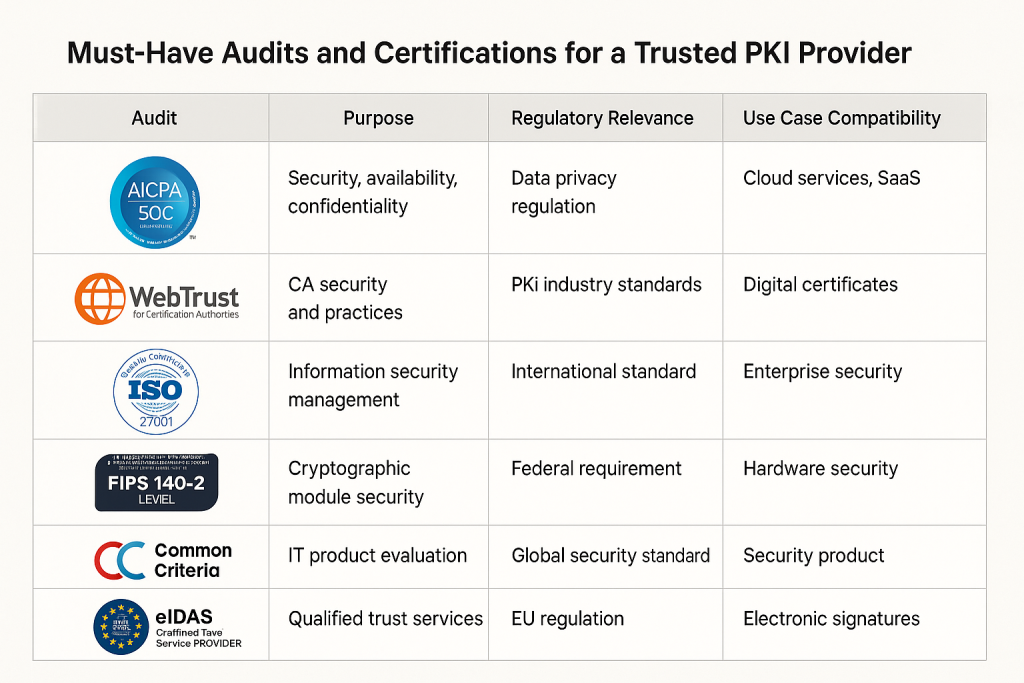
When evaluating PKI vendors, prioritize those who have undergone rigorous external audits and who hold certifications that demonstrate adherence to international standards in areas like data security, operational controls, cryptographic robustness, and compliance frameworks.
These certifications not only build credibility but are often mandatory for doing business in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, government, and defense.
Below are the essential audits and certifications to look for:
SOC 2 Type II — Operational Security & Data Handling Integrity
System and Organization Controls (SOC) 2 Type II is a widely recognized audit standard governed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). It evaluates how a provider stores, manages, and secures sensitive data over a set period—typically 6 to 12 months.
Key focus areas:
-
Security
-
Availability
-
Processing integrity
-
Confidentiality
-
Privacy
✅ Why it matters: Ensures the provider has proper internal controls, monitoring, and incident response procedures in place.
WebTrust Audit — Publicly Trusted CAs
If you’re purchasing certificates that must be trusted by browsers, operating systems, or mobile devices, your PKI provider must pass an annual WebTrust for Certification Authorities audit. Conducted by licensed CPA firms, this audit evaluates:
-
CA operations
-
Certificate issuance processes
-
Key management procedures
-
Compliance with CA/B Forum baseline requirements
✅ Why it matters: Only providers that pass WebTrust audits can issue public SSL/TLS certificates trusted by browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
ISO/IEC 27001 — Information Security Management Systems
ISO 27001 is a global standard for establishing and maintaining a risk-based information security management system (ISMS). If your provider is ISO 27001 certified, it means:
-
Security practices are formalized, documented, and continuously improved
-
Controls are in place to protect confidentiality, integrity, and availability
-
Internal audits and risk assessments are performed regularly
✅ Why it matters: Proves your PKI provider follows international best practices for data protection.
FIPS, Common Criteria, and eIDAS QTPS — Regulatory Trust Readiness
Depending on your industry or geography, you may also require:
✔ FIPS 140-2 or FIPS 140-3 (U.S. Federal Standard)
-
Validates cryptographic module security
-
Essential for healthcare, government, and military use
✔ Common Criteria (ISO/IEC 15408)
-
International standard for evaluating security of IT products
-
Accepted across 31 countries (CCRA member states)
✔ eIDAS Qualified Trust Service Provider (EU)
-
Required for issuing qualified digital certificates and eSignatures valid across EU borders
✅ Why it matters: These certifications provide the legal foundation for your organization’s encryption, authentication, and digital signature infrastructure.
Key Takeaway:
If your PKI provider lacks third-party certifications, you have no independent proof that they can be trusted to protect your data or issue certificates responsibly.
Always ask for:
-
Certification documents
-
Audit summaries
-
Frequency and scope of assessments
-
Who conducted the audit (must be a reputable, accredited body)
These certifications not only validate the technical robustness of the PKI provider but also confirm their ability to operate within legal frameworks across multiple jurisdictions.
.
6. Assess Vendor Reputation and Customer Support
Selecting a PKI provider isn’t just about checking off technical boxes or meeting compliance mandates—it’s about entering into a long-term trust relationship. Since compliance is not a one-time event but an ongoing process, your organization needs a partner who can grow with you, proactively support your evolving needs, and help you navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
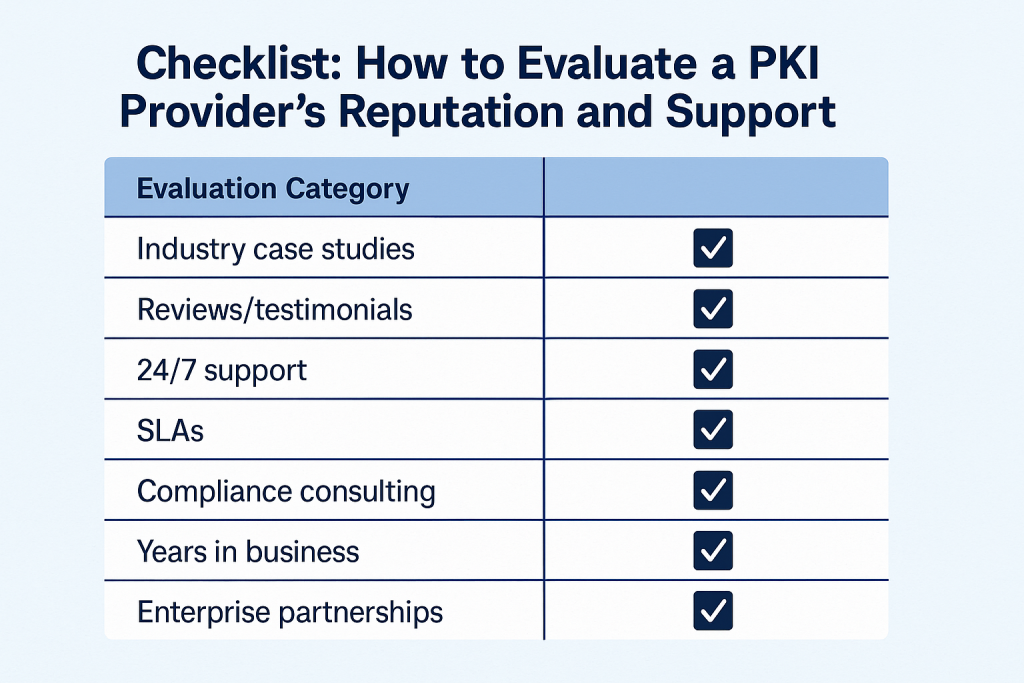
That’s why evaluating a PKI vendor’s market reputation, customer support capabilities, and long-term reliability is just as critical as evaluating their cryptographic tools.
Here’s how to assess whether a PKI provider is truly enterprise-ready and trustworthy:
1. Proven Case Studies in Your Industry
Look for PKI vendors who have demonstrated success in your specific sector—whether that’s healthcare, financial services, retail, defense, or government.
Ask for:
-
Industry-specific case studies or whitepapers
-
Client references or anonymized success stories
-
Use cases demonstrating how the provider helped meet compliance goals (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, FIPS)
Why it matters:
A vendor who understands your industry’s regulatory pressures and operational challenges is more likely to offer pre-configured templates, compliant deployment models, and quicker time-to-value.
2. Positive Customer Reviews and Testimonials
User reviews are a powerful indicator of real-world reliability. Check third-party platforms like:
-
G2
-
Capterra
-
TrustRadius
-
Gartner Peer Insights
Focus on:
-
Ease of deployment
-
Quality of customer service
-
Responsiveness to issues
-
Long-term performance
Why it matters:
Consistently positive reviews show that a vendor is trusted not just for the tech, but for the experience they offer.
3. 24/7 Customer Support with Guaranteed SLAs
In a world where certificate outages can shut down websites, block secure email, or crash applications, 24/7 support isn’t optional—it’s essential. Make sure your provider offers:
-
Round-the-clock support across time zones
-
Multiple support tiers (email, chat, phone)
-
Guaranteed SLAs (Service Level Agreements) for response and resolution times
-
Real-time incident alerts and escalation paths
Why it matters:
Downtime due to expired or revoked certificates can cost organizations millions in lost revenue and brand damage. Responsive support minimizes this risk.
4. Access to Dedicated Compliance Consultants
Choose a PKI provider that goes beyond technical support to offer strategic compliance guidance.
Look for:
-
Dedicated compliance experts or customer success managers
-
Advisory on implementing frameworks like NIST, HIPAA, SOX, eIDAS
-
Regular compliance check-ins and reporting tools
-
Proactive help with audit preparation and documentation
Why it matters:
A proactive compliance partner can help you avoid fines, pass audits faster, and reduce internal workload.
5. Vendor Longevity and Market Reliability
Lastly, consider how long the vendor has been in the industry and whether they are financially stable, growing, and investing in product innovation.
Check for:
-
Years in business
-
Global customer base
-
Enterprise clients and government partnerships
-
Investment in roadmap features like post-quantum cryptography, DevOps integration, etc.
Why it matters:
Long-term reliability ensures that your PKI provider will be around to support your future compliance needs—and won’t disappear or deprecate services mid-contract.
7. Compare Deployment Options (Cloud vs On-Premise)
Choosing the right deployment model for your PKI solution is a critical decision—one that depends heavily on your compliance requirements, IT infrastructure, risk tolerance, and resource availability. A one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work for enterprises with diverse needs. That’s why top-tier PKI vendors offer flexible deployment options, including cloud PKI, on-premise PKI, and hybrid models.
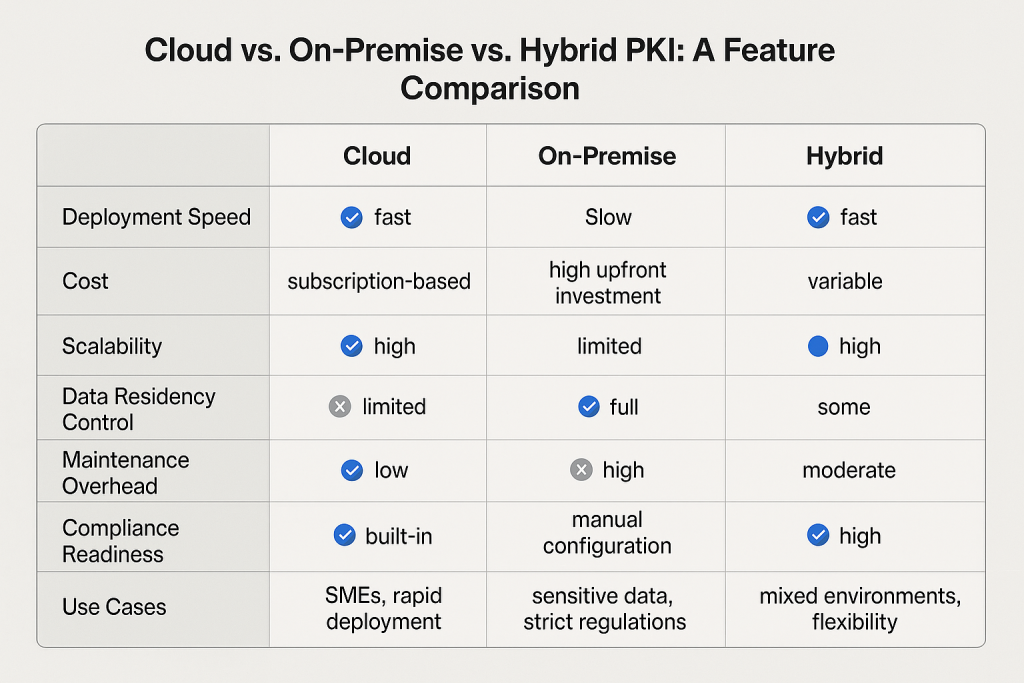
Let’s break down each deployment model and its advantages.
Cloud-Based PKI: Speed, Scalability, and Simplicity
Cloud PKI (also called PKI-as-a-Service or managed PKI) is hosted and managed by the vendor or a trusted third-party cloud platform. It is designed for speed of deployment, operational efficiency, and ease of management—especially beneficial for organizations with distributed teams or limited internal PKI expertise.
✅ Benefits:
-
Fast implementation with minimal upfront setup
-
Automatic updates, patching, and backups
-
Vendor-managed infrastructure and compliance monitoring
-
Highly scalable for dynamic environments (DevOps, IoT, remote work)
-
High availability and disaster recovery built-in
⚠️ Considerations:
-
Data residency concerns if hosted across borders
-
Dependency on vendor SLAs and access policies
-
Shared responsibility for compliance
On-Premise PKI: Full Control and Custom Compliance
On-premise PKI is hosted within your organization’s infrastructure—either physically or virtually. This model is ideal for enterprises with strict data sovereignty laws, classified environments, or custom integration requirements.
✅ Benefits:
-
Total control over hardware, keys, and certificate policies
-
Compliance with data localization regulations (e.g., in defense, government, and financial services)
-
Deeper customization and integration with legacy systems
-
Internal hosting for air-gapped or classified networks
⚠️ Considerations:
-
Requires internal PKI and cryptography expertise
-
Higher maintenance and operational costs
-
Longer deployment timelines
-
Responsibility for securing, updating, and auditing the system
Hybrid PKI: The Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid PKI combines the benefits of both cloud and on-premise models, allowing organizations to offload certificate issuance to the cloud while retaining control over root keys or sensitive systems on-premise.
✅ Benefits:
-
Cloud-powered scalability with local root-of-trust control
-
Ideal for multinational enterprises or regulated industries with global operations
-
Supports DevOps pipelines, IoT devices, and compliance-heavy systems simultaneously
-
Flexible integration with cloud-native platforms and legacy IT
Key Questions to Ask Your Provider
-
Do you offer all three deployment models—cloud, on-premise, and hybrid?
-
What security and compliance responsibilities are handled by your team vs. ours?
-
Can we migrate from one model to another in the future without data loss or revalidation?
-
Is your cloud PKI hosted in a region that satisfies our data residency requirements?
8. Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
When evaluating PKI solution providers, don’t stop at the price tag on the licensing agreement. While a low upfront cost may seem attractive, the true cost of PKI ownership includes much more than just software fees. The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) should factor in setup, integration, maintenance, renewal complexity, and even the risk of service disruptions due to expired certificates.
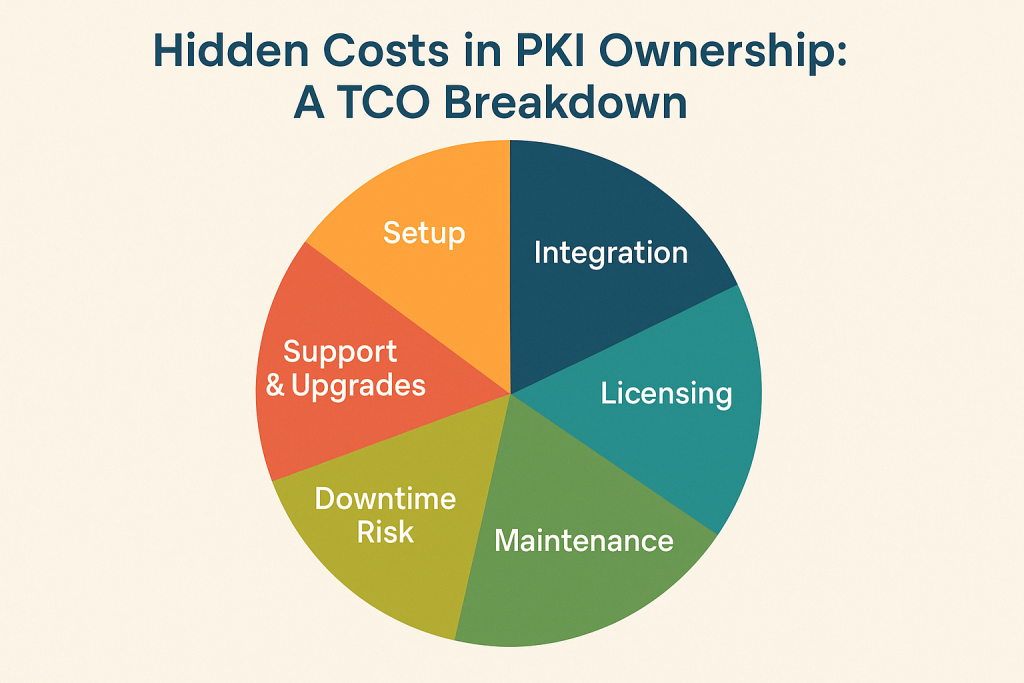
A provider offering lower upfront pricing may end up being more expensive in the long run if their solution requires intensive manual upkeep, lacks automation, or causes unplanned downtime.
Here’s how to assess the real cost of implementing and running a PKI solution:
1. Initial Setup and Onboarding
The cost of getting started can vary greatly depending on the provider and deployment model (cloud vs. on-premise).
Include:
-
Time and labor for installation, configuration, and CA hierarchy setup
-
Hardware costs (e.g., HSMs for on-premise PKI)
-
Consulting or professional services fees for implementation
-
Training for IT staff or administrators
2. Integration with Existing Infrastructure
A good PKI solution should integrate smoothly with your:
-
Active Directory / LDAP
-
Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP)
-
Email systems (for S/MIME)
-
DevOps tools (Kubernetes, CI/CD)
-
IoT or mobile device management systems
Cost factors include:
-
Custom connectors or APIs
-
Developer hours for integrations
-
Third-party tool licensing
3. Long-Term Maintenance and Certificate Renewals
Maintaining a PKI system is a continuous process that includes:
-
Regular patching, updates, and system monitoring
-
Certificate lifecycle management (issuance, renewal, revocation)
-
Staff time for audits, reporting, and compliance upkeep
Cloud-based PKI often includes these costs as part of the subscription, while on-premise solutions may require in-house security teams and system administrators.
4. Risk of Downtime from Expired Certificates
One of the most overlooked but costly elements of PKI ownership is the impact of expired certificates. Even a single outage can result in:
-
Revenue loss from inaccessible websites or apps
-
Reputation damage due to broken trust
-
Legal penalties for non-compliance
-
Increased IT workload to fix emergency issues
Automation can prevent these costs—but only if included in your vendor’s package.
5. Pricing Flexibility and Scalability
Some providers offer tiered pricing based on:
-
Number of certificates issued per year
-
Number of users or devices managed
-
Add-on services like timestamping, reporting, or HSM use
Choose a provider that allows you to:
-
Start small and scale easily
-
Avoid paying for unused volume
-
Predict costs through transparent pricing models
Key Takeaway:
The cheapest PKI solution on paper may cost the most in time, support, downtime, and compliance penalties over its lifecycle. A proper TCO analysis should always guide your final decision.
Conclusion
Choosing the best PKI solution provider for compliance involves more than checking off technical specs. It requires evaluating vendors across security infrastructure, compliance certifications, lifecycle automation, support, and long-term cost efficiency.
✅ Use this checklist:
- Does the provider meet your specific compliance standards (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR)?
- Do they offer full lifecycle management and automation?
- Are they independently audited and certified?
- Is their trust model and security infrastructure robust?
- Can they scale with your future needs?
By aligning your PKI strategy with compliance from the start, you’ll reduce audit risks, strengthen data protection, and position your organization for secure, compliant growth in 2026 and beyond.


