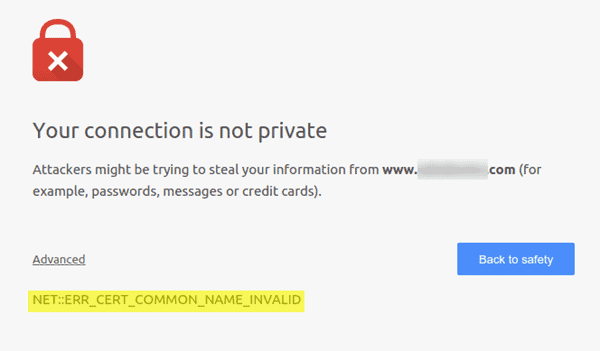
Protecting your online presence starts with securing your website with HTTPS. But even the best security measures can run into hiccups, like the dreaded “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error. Don’t worry, fixing it isn’t a cryptographic puzzle!
This error essentially means your website’s security credentials are misaligned. Imagine it like a password mismatch – your browser and the website are speaking different encryption languages. Although the solution depends on the specific cause, fear not, brave adventurer! We’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools to overcome this digital hurdle.
Google Chrome is concerned about security. When your browser tries to load a website, you may obtain a “ERR CERT COMMON NAME INVALID” error message. Learn what to do if this occurs.
When is the error “ERR CERT COMMON NAME INVALID” displayed?
This error signifies a discrepancy between the website’s domain and its security credentials – the SSL certificate. Think of it as a key mismatch. No matter how you try, the door to a secure connection remains locked.
The Suspects:
Several potential culprits lurk behind this error:
1. The Misconfigured Server:
- The Prime Suspect: This is the most common culprit. Imagine the server forgetting the correct “password” for the secure connection.
2. The Third-Party Extensions:
- Stealthy Interlopers: Some extensions can disrupt the SSL process, causing temporary glitches.
3. The Security Software:
- Overzealous Guardians: Antivirus and firewall programs can sometimes trigger the error due to overprotective measures.
4. The Domain Name Discrepancy:
- Identity Crisis: The common name on the SSL certificate might not match the actual domain name.
5. The Missing Certificate:
- Security Vacuum: Switching to HTTPS without installing an SSL certificate creates a vulnerability.
6. The Self-Signed Certificate:
- Unrecognized Credentials: Browsers might not trust self-signed certificates, requiring additional configuration.
Here’s what this problem looks like in the most popular clients on the web.
1. Chrome:

The “Your connection is not private” warning screen reigns supreme, accompanied by the specific code “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID”. This red flag alerts users of a potential security risk and may deter them from proceeding.
2. Firefox:

A shield icon with a red exclamation mark appears, accompanied by the message “The certificate is not trusted because its common name doesn’t match the website’s domain name.” This provides a more specific explanation, urging caution and potentially reducing user trust.
3. Safari:

The message “Safari can’t verify the identity of the website” or “Safari can’t open the page” appears, followed by the domain. This vague message, coupled with the lack of specific error codes, makes diagnosing the issue slightly harder.
4. Internet Explorer:

This browser takes a direct approach, stating “This site is not secure” and highlighting the untrustworthiness of the SSL certificate. It may also offer temporary solutions, such as adding or removing “www” from the URL, but emphasizes the need for a permanent fix.
How to Fix NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID
1. Verifying Your SSL Certificate
The “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error often arises when there’s a discrepancy between your website’s domain name and the “common name” listed on its SSL certificate. Think of it like a door – if the key (domain name) doesn’t match the lock (certificate), the door remains locked, leading to the error message.
To investigate this issue, Google Chrome offers a simple way to analyze the certificate and identify the potential mismatch. Here’s how to do it:
1. Access the Certificate Information:
- Click on the “Not Secure” warning in the URL bar.
- In the menu that appears, select “Certificate (Invalid)”.
This opens a window displaying details about the certificate.
2. Analyze the Common Name:
- Look for the “General” section.
- Under “Subject”, you’ll find the “Common Name” field. This is the crucial information.
- Compare the “Common Name” with your actual website domain name (both www and non-www versions).
3. Identify the Mismatch:
If the “Common Name” doesn’t match your domain name exactly, you’ve found the source of the error. Mismatches can occur due to:
- Typos: Errors during certificate purchase can lead to discrepancies.
- Self-Signed Certificates: Browsers might not recognize them as valid.
- Incorrect Redirects: Improper configuration between HTTP and HTTPS versions can cause conflicts.
Taking Action:
Once you identify the mismatch, you can take the following steps to fix the error:
- Correct Typos: Carefully review and update the certificate configuration.
- Obtain a Valid Certificate: Acquire a trusted certificate from a reliable Certificate Authority (CA).
- Configure Redirects: Ensure proper transitions between HTTP and HTTPS versions of your website
2. Detecting Misconfigured Redirects
The “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can also arise due to misconfigured redirects on your website. Imagine a maze with conflicting paths – browsers get confused and trigger the error message.
Here’s how to investigate potential redirect issues:
1. Identify Redirect Types:
There are two primary types of redirects to consider:
- HTTP to HTTPS: These redirects ensure secure connections by moving from unencrypted (HTTP) to encrypted (HTTPS) versions of your website.
- Domain Redirects: These redirects might point from one domain name to another, such as redirecting from your non-www version (http://example.com) to your www version (https://www.example.com).
2. Analyze Redirect Configuration:
Your website’s server settings or .htaccess file likely contain redirect rules. Here’s how to access them:
- Server Settings: Consult your web hosting provider’s documentation to understand how to manage redirect rules on your server.
- .htaccess File: This file typically resides in your website’s root directory. You can access and edit it using FTP clients or cPanel file manager.
3. Look for Conflicts:
Carefully review the redirect rules and look for any potential conflicts. Common issues include:
- Duplicated Redirects: Multiple redirects leading to the same destination can cause confusion.
- Redirect Loop: Endless cycles of redirects trap browsers and trigger the error.
- Incorrect Target URL: Redirecting to the wrong URL can lead to certificate mismatches.
4. Test and Fix:
Once you identify conflicting redirects, it’s time to fix them. Here are some suggestions:
- Remove unnecessary redirects: Simplify your redirect configuration and streamline the user journey.
- Break redirect loops: Identify and remove any loops causing endless cycles.
- Update target URLs: Ensure redirects point to the correct and intended destination.
Tools like online redirect checkers can help visualize and identify problematic redirects. Additionally, testing your website on different browsers and devices can ensure smooth transitions and prevent potential errors.
3. Aligning WordPress Address and Site Address
The “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can also arise due to mismatched WordPress Address and Site Address settings within your WordPress installation. Imagine your website as a building with two entrances – if the addresses listed on the signs don’t match, visitors might get confused and lost.

Here’s how to investigate and fix this issue:
1. Locate the Settings:
- Login to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Settings > General.
2. Analyze the Addresses:
- Look for the “WordPress Address (URL)” and “Site Address (URL)” fields.
- These fields should match your website’s domain name (both www and non-www versions).
3. Identify the Mismatch:
If the WordPress Address and Site Address don’t match exactly, you’ve found the source of the error. Mismatches can occur due to:
- Manual Errors: Accidental typos during configuration can lead to inconsistencies.
- Plugin Conflicts: Certain plugins might alter these settings unintentionally.
- Incorrect Migrations: Moving your website to a new domain can leave behind conflicting address settings.
4. Take Action:
Once you identify the mismatch, it’s time to correct it. Here’s what you can do:
- Update the Address Fields: Ensure both fields match your website’s domain name exactly.
- Deactivate Plugins: If you suspect a plugin is causing the conflict, try deactivating them one by one to identify the culprit.
- Check for Migration Leftovers: If you migrated your website, search for any leftover settings or configurations that might still be pointing to the old domain name.
5. Test and Verify:
After correcting the mismatch, it’s crucial to test and verify the changes. Here are some steps:
- Clear your browser cache and cookies.
- Open your website in a different browser or device.
- Check if the error message persists.
4. Identifying Self-Signed Certificates
The “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can sometimes be caused by using a self-signed SSL certificate on your website. Think of it like using your own house key on someone else’s door – it may not work and might raise security concerns.
Here’s how to determine if your site uses a self-signed certificate:
1. Check the Certificate Information:
- In your browser, click on the “Not Secure” warning in the URL bar for your website.
- Select “Certificate (Invalid)” to open the certificate details.
2. Analyze the Issuer:
- Look for the “Issued By” or “Issuer” field.
- If it displays the name of your website or a similar domain, it’s likely a self-signed certificate.
3. Identify the Risks:
Self-signed certificates have limitations:
- Browser Warnings: Browsers might display warning messages, discouraging visitors from accessing your website.
- Security Concerns: Browsers might not trust self-signed certificates, increasing security risks.
- Limited Compatibility: Some devices and applications might not recognize self-signed certificates, restricting access.
4. Consider Alternatives:
For optimal security and compatibility, it’s best to obtain a trusted SSL certificate from a reputable Certificate Authority (CA). CAs verify your identity and issue certificates recognized by most browsers and devices.
5. Take Action:
If you identify a self-signed certificate as the culprit, consider the following:
- Obtain a Trusted Certificate: Purchase a certificate from a trusted CA like DigiCert, Comodo, or Let’s Encrypt.
- Install the Certificate: Follow your web hosting provider’s instructions to install the certificate on your server.
- Update Configuration: Ensure your server and website configuration references the new certificate.
By replacing a self-signed certificate with a trusted one, you can eliminate the “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error and create a secure and trustworthy online experience for your visitors.
5. Clearing Your SSL State and Browser Cache
The “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can sometimes be caused by corrupt temporary data stored in your browser’s cache or related to SSL connections. Imagine it like a cluttered workspace – having too much old information can lead to confusion and errors.

Here’s how to clear this data and potentially resolve the error:
1. Clear Browser Cache and Cookies:
- Each browser has its own method for clearing browsing data. Here are some general steps:
- Chrome: Open Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data.
- Firefox: Open History > Clear Recent History.
- Safari: Open Preferences > Privacy > Manage Website Data > Remove All.
- Internet Explorer: Open Settings > Internet Options > Browsing history > Delete.
2. Clear SSL State:
- This removes cached information related to SSL connections.
- Chrome: Go to Settings > Advanced > Change proxy settings (under “Network”). Click the “Content” tab and click “Clear SSL state”.
- Firefox: Open Advanced > Network > Security > Clear SSL State.
- Safari: No specific option available. Clearing browser cache and cookies may help.
- Internet Explorer: Open Internet Options > Content > Clear SSL state.
3. Restart Your Browser:
- After clearing the data, restart your browser for the changes to take effect.
4. Test and Verify:
- Open your website again and check if the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error persists.
5. Consider Additional Measures:
- If clearing the cache and SSL state doesn’t resolve the error, try the following:
- Update your browser to the latest version.
- Disable any browser extensions that might be interfering with SSL connections.
- Reset your browser settings to default.
By cleaning up your browser’s temporary data, you can eliminate potential conflicts and ensure a smooth and secure connection to your website.
6. Assessing Your Proxy Settings
The “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can sometimes be caused by misconfigured proxy settings on your computer. Imagine navigating a maze with a faulty map – you might end up in the wrong place or encounter unexpected obstacles.

Here’s how to assess your proxy settings and ensure they don’t contribute to the error:
1. Identify Proxy Usage:
- Check if you’re using a proxy server to connect to the internet. This is often used for security or accessing geo-restricted content.
2. Analyze Proxy Configuration:
- Open your system settings and navigate to the proxy configuration options.
- Verify that the proxy details are accurate and correspond to your intended connection.
- If you’re not sure about the correct settings, consult your network administrator or internet service provider for assistance.
3. Consider Temporarily Disabling Proxy:
- To isolate the proxy as a potential cause of the error, try temporarily disabling it.
- Follow the instructions based on your operating system and browser to disable the proxy.
- Open your website again and check if the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error persists.
4. Identify Potential Conflicts:
- If disabling the proxy resolves the error, it suggests that there might be a conflict between your proxy settings and your website’s SSL certificate.
- Review the certificate details and compare the domain name with your proxy configuration.
- Ensure that your proxy allows connections to secure sites and doesn’t interfere with encryption processes.
5. Take Action:
- If you identify any conflicts or misconfigurations in your proxy settings, you need to take action:
- Update your proxy settings to ensure they are correct and compatible with your website’s SSL certificate.
- Contact your network administrator or internet service provider for assistance with configuring your proxy settings.
- Consider using a different proxy server if the current one is causing issues.
By ensuring your proxy settings are accurate and don’t interfere with secure connections, you can prevent the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error and maintain a smooth and secure online experience.
7. Troubleshooting Browser Extension Conflicts
The “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can sometimes be triggered by browser extensions interfering with secure connections. Imagine having too many cooks in the kitchen, each trying to control the ingredients and recipe, leading to confusion and unforeseen results.
Here’s how to investigate and resolve potential browser extension conflicts:
1. Identify Suspicious Extensions:
Certain extensions known to interfere with SSL connections include:
- Proxy extensions
- Ad blocker extensions
- Security and privacy extensions
- Download managers
2. Disable All Extensions:
The most effective way to identify a conflicting extension is to disable them all temporarily. Here’s how:
- Chrome: Open Settings > More tools > Extensions. Toggle off all extensions.
- Firefox: Open Add-ons and Themes > Extensions. Click the disable button for each extension.
- Safari: Open Safari > Preferences > Extensions. Uncheck the box for each extension.
- Internet Explorer: Open Internet Explorer > Tools > Manage Add-ons. Select “All Add-ons” and click “Disable” for each extension.
3. Re-Enable Extensions One by One:
With all extensions disabled, reload your website and see if the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error persists. If the error disappears, it confirms an extension conflict.
Re-enable your extensions one by one, opening your website after each activation. This helps identify the specific extension causing the conflict.
4. Remove the Culprit Extension:
Once you identify the conflicting extension, it’s best to remove it. This ensures it doesn’t interfere with secure connections and cause the error again.
- Chrome: Click the “Remove” button next to the extension in the Extensions settings.
- Firefox: Click the “Remove” button next to the extension in the Add-ons and Themes manager.
- Safari: Click the “Uninstall” button next to the extension in the Extensions settings.
- Internet Explorer: Select the extension and click “Disable” followed by “More” > “Remove.”
5. Consider Alternatives:
If the conflicting extension offers valuable functionality, consider searching for alternative extensions that don’t interfere with SSL connections. This ensures you can enjoy both the features and a secure browsing experience.
By troubleshooting potential browser extension conflicts and taking appropriate action, you can eliminate the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error and maintain a safe and secure connection to your website.
8. Modifying Antivirus Software Settings
The “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can sometimes arise due to overprotective antivirus software settings interfering with secure connections. Imagine a security guard who’s so vigilant that they block even legitimate visitors, preventing access and causing disruptions.
Here’s how to investigate and adjust your antivirus software settings to ensure they don’t contribute to the error:
1. Identify Antivirus Software:
Check which antivirus software is installed on your computer. Different software has different settings and configuration options.
2. Review Antivirus Settings:
- Open your antivirus software and navigate to its settings.
- Look for sections related to internet security, web protection, or HTTPS scanning.
- Some software might have a dedicated “SSL/TLS” settings section.
3. Analyze HTTPS Scanning:
- Verify whether HTTPS scanning is enabled. Some antivirus software might scan and intercept encrypted connections, potentially causing conflicts.
- Consider temporarily disabling HTTPS scanning to isolate it as a potential cause of the error.
4. Review Certificate Exception Lists:
- Some antivirus software allows adding websites to an exception list, exempting them from specific security checks.
- Consider adding your website’s domain name to the exception list if it’s not already included.
5. Test and Verify:
- After making changes to your antivirus software settings, restart your computer and open your website again.
- Check if the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error persists.
6. Consult Antivirus Documentation:
- If you’re unsure about specific settings or how to configure HTTPS scanning, consult your antivirus software’s official documentation or support resources.
- Their website or knowledge base might offer detailed instructions and troubleshooting steps.
7. Consider Alternative Software:
- If you still encounter the error after adjusting your antivirus software settings, consider switching to a different antivirus program with less aggressive HTTPS scanning features.
- Research and compare different options to find one that offers optimal security while ensuring compatibility with secure connections.
By understanding how your antivirus software might impact secure connections and taking appropriate action to adjust its settings, you can eliminate the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error and enjoy a safe and secure online experience.
9. Updating Your Browser and Operating System (OS)
The “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error can sometimes be caused by outdated browsers and operating systems struggling to interpret modern encryption standards. Imagine trying to open a high-tech door with an old key – it simply won’t work, leading to frustration and access denied.
Here’s how updating your browser and operating system can help resolve this error:
1. Identify Your Current Versions:
- Check your browser and operating system versions.
- You can usually find this information in the settings or about sections of your applications.
2. Update Your Browser:
- Download and install the latest version of your browser.
- Most browsers automatically check for updates, but you can also manually initiate the update process.
3. Update Your Operating System:
- Download and install the latest updates for your operating system.
- The process for updating your operating system varies depending on your platform (Windows, Mac, Linux).
4. Restart Your Device:
- After updating your browser and operating system, restart your computer or device.
- This ensures the updates are applied correctly and take effect.
5. Test and Verify:
- Once your system is updated, open your website again.
- Check if the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error persists.
6. Consider Additional Updates:
- In addition to your browser and operating system, ensure your antivirus software and other security applications are also updated to the latest versions.
- This helps maintain an overall secure environment and prevents potential conflicts.
Benefits of Updating:
- Updating your browser and operating system offers numerous benefits beyond resolving the “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error:
- Improved security: Updates often address security vulnerabilities and patch known issues.
- Enhanced performance: Updates can optimize performance and improve the overall user experience.
- Access to new features: Updates introduce new features and functionalities to your applications.
- Increased compatibility: Updates ensure compatibility with the latest websites and online services.
By keeping your browser and operating system updated, you can ensure a smoother and more secure online experience, eliminating potential errors like “ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” and enjoying the latest features and functionalities.