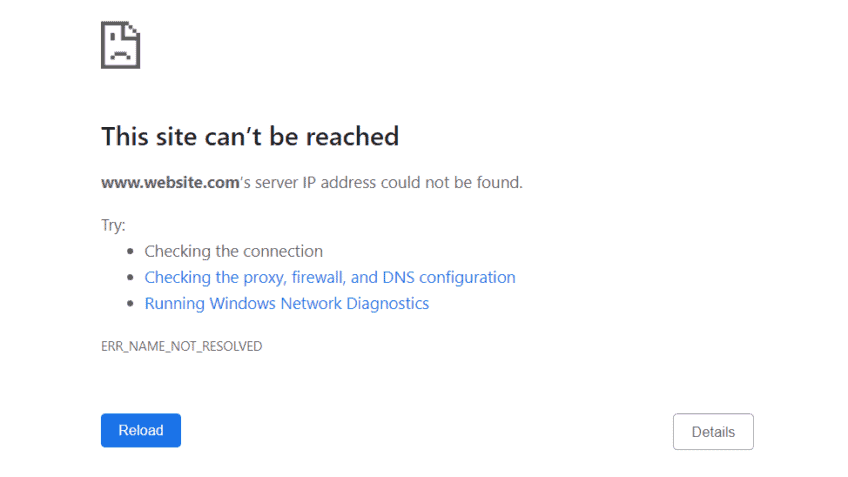
The internet allows you access to an almost infinite number of different websites. To access a certain online project, all you need is an internet browser and the project’s domain name. To represent the page’s numerical IP address, you type the domain name into your browser’s address bar. Domain name resolution is the automatic translation that DNS servers (Domain Name System) handle. You will certainly experience errors if the domain name cannot be resolved, preventing you from accessing the website. When this happens, the error message “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” appears in the Google Chrome browser.
You’ll learn more about what causes DNS domain name resolution issues in the sections below. We’ll also show you how to fix the Chrome browser problem “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” with the best troubleshooting options.
What does “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” indicate in terms of an error message?
Chrome says it couldn’t locate an IP address that matches the website domain name you specified when you see the “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” error message. Because the IP address is required to establish a connection with the web server, you will be unable to access the website if this occurs. This problem can occur whether you’re using Chrome on a desktop computer (Windows, macOS, or Linux) or on a mobile device (Android or iOS). This problem is not limited to the Chrome browser; it can also occur in other browsers such as Firefox or Safari. If the DNS fails to resolve the domain name when trying to access a website, they will display a different error message than Google Chrome.
The “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” error could have several reasons.
A DNS domain name resolution can fail for a variety of reasons. The DNS server is (temporarily) unavailable is one of the most typical reasons. In this case, the DNS will be unable to resolve the domain name if there are no entries for the website you are trying to access in your browser cache or your operating system’s DNS cache. The “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” problem in Chrome might also be caused by the previously listed address entries. This error can arise, for example, if the browser tries to respond to a DNS query using a cached address while the IP address has since changed.
Router issues, wrongly configured internet settings, Chrome’s prediction service for faster page loading, malware, and defective security software are all probable reasons of this message.
How to Fix Chrome’s ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED Error
There is no universal answer because there are so many distinct reasons why you can be having DNS issues. If you insist on tackling the “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” error message on your own, we’ll go over the remedies that have the best chance of succeeding in the sections below.
· First, restart the router.
Before you start playing with Chrome or your operating system’s settings, make sure the router that connects your device to the internet is working properly. Even if it appears that your internet connection is working properly, this may not be the case. As a result, you should restart the network device to see if the “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” error may be resolved quickly and easily. Disconnect the power supply for at least 30 seconds to restart the device by removing the power cable. Connect the router to the power supply after that.
Note
It will take some time for the router to fully restart operation once you have momentarily unplugged it from the power source. Wait for the internet/DSL indicator to turn green before restarting the router to see if the DNS problem has been resolved.
Solution 2: clear your browsing history
Chrome automatically saves data from all previous websites you’ve visited. This cached data makes refreshing pages faster and auto-completes addresses as you input. This function, as handy as it is, can quickly become a problem, resulting in the “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” error on Android, Windows, and other platforms. As a result, deleting all of your browser data could be a viable option. To do so, use the three-dot icon to enter the Chrome menu and select “More tools.” After that, select “Clear browsing data.”
Google Chrome’s menu icon is a three-dot icon.
You won’t find the “Clear browsing data” option under “More tools” if you’re using Chrome on a mobile device (Android or iOS). You’ll find it in the “History” menu option instead.
Choose which categories of browser data Chrome should remove from the cache, with “Browser history” and “Cookies and other site data” being required. Make sure that the “All time” option is selected under “Time range“; otherwise, it will only remove your most recent browser history. After you’ve made your choice, click “Clear data.”
Menu “Clear browsing data” in Google Chrome
Many websites will load slower than usual the next time you access them after you erase your browser cache.
Solution 3: Delete the DNS cache in your operating system.
Cached web addresses are frequently associated with the browser as the user interface for accessing the internet. Web address books are built into conventional operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux, and they automatically cache DNS entries for websites you’ve visited before. The DNS cache, like the browser cache, can cause problems like Chrome’s “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” message when the stored entry for an address is erroneous or out of current. In this case, clearing the cache, also known as a DNS flush, is also a viable option.
A DNS flush on Windows 10 is as simple as typing a single command into the command prompt window. To get started, go to the Start menu. Then select “Command Prompt” from the drop-down menu. You may also use the search function to locate it. To clear the DNS cache, open the command prompt window and type the following command:
/flushdns ipconfig
If the operation was successful, you will receive a notification stating that the cache has been emptied after a few seconds.
Using the command prompt window in Windows 10, perform a DNS flush.
On Windows, you don’t require administrator privileges to do a DNS flush.
Our article on how to flush your computer’s DNS contains more thorough information regarding the DNS cache as well as instructions on how to empty the DNS memory cache on different operating systems.
Solution 4. Reset the Winsock catalog
If the “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” problem was not caused by the browser cache or DNS cache, Windows users should investigate the Winsock interface and system application (also known as Windows Sockets). Winsock allows programs to communicate across TCP/IP by creating entries for each connection formed. Resetting the Winsock catalog may be a solution to connection problems in the Chrome browser because this data can also block a website from being accessible. This reset can be done via the command prompt window, just as the DNS flush. However, in this case, you must run the command as an administrator, as seen below:
By clicking the Windows symbol, you can access the Start menu.
Depending on your operating system version, look for the “Command Prompt” icon under “Accessories” or “Windows System.”
Select “Run as Administrator” from the context menu of “Command Prompt.”
The “Command Prompt” icon in the Start menu in Windows 10
Without administrator rights, you can’t operate Windows services like the Command Prompt as an administrator.
To reset the Winsock catalog, open the Windows command prompt window and type the following command:
reset winsock netsh
To run the command, press the Enter key. The system should then be restarted to complete the reset.
Solution 5: Change the DNS server
There isn’t much you can do if the “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” error message appears in Chrome because the responsible DNS server isn’t working. However, by configuring your DNS address settings to use the IPv4 or IPv6 protocol, you can change your DNS server. Cloudflare’s public DNS servers, for example, are a viable option. The IPv4 addresses 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1, as well as the IPv6 addresses 2606:4700:4700::1111 and 2606:4700:4700::1001, are available.
These DNS servers, which are meant to be quick and safe, can be set as the default option on Windows by following the procedures below:
- From the Start menu, select Control Panel.
- “Network and Sharing Center” should be selected (in the icon view).
- After that, select “Change Adapter Settings.”
- Select “Properties” from the context menu of the network adapter that links you to the internet.
- “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” or “Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)” should be double-clicked.
- For the preferred and alternate servers, enter the above-mentioned addresses under “Use the following DNS server addresses.”
- Click “OK” to confirm the changes.
Tip
On macOS, iOS, and Android, as well as previous versions of Windows, the Digital Guide explains how to change the DNS server.
Solution 6: Turn off Chrome’s predictive text.
The prediction function was created by Google Chrome to give faster loading speeds in the long run. To accomplish this, the function collects information about any links on the currently open webpage in order to reduce the time it takes for those linked pages to load if you happen to click on one of them. However, because this prediction service has been known to cause problems like ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED, deactivating it in Chrome may solve your DNS issue.
To disable the prediction feature, go to the Chrome menu and select the three-dot icon. Then choose “Settings.” Scroll all the way down the following menu and select “Show advanced settings.” Move the slider to the left for the option “Preload pages for faster browsing and searching” under “Privacy and security.”
Google Chrome’s “Privacy and Security” menu
When preloading is enabled in Google Chrome, the browser uses more system resources automatically.
Solution 7: turn off security software for a while
On Android, Windows, and other platforms, any security software you may have installed can trigger the Chrome “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” problem. Antivirus software or a firewall, for example, can block access to particular websites, causing the browser to display an error message. By temporarily stopping the programs you’re using, you can simply see if they’re producing issues like this. If the domain name can then be resolved, you’ve found the cause of the problem. If this is the case, you have two options: contact the publisher of the problematic software or replace it with a suitable alternative.
Solution 8: Check for malware
Malicious software on your computer, like with many other computer problems, could be the source of the “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” message. Malware, for example, can alter DNS server configurations, corrupt your browser history, or prevent the domain name from being resolved in any way. If the procedures indicated above do not work, it is critical to verify your system for a possible malware infestation. Perform a scan with your security software or Microsoft’s Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT). The MSRT is only available for Windows users, and it can only be used with administrator privileges.
We trust that this article will prove informative. Until next time, stay secure!!!