In today’s hyper-connected digital economy, cloud security refers to the strategies, technologies, and policies used to protect data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in cloud environments. This includes safeguarding against threats like unauthorized access, misconfiguration, data leaks, and ransomware within platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and hybrid clouds.
As more organizations accelerate digital transformation, cloud adoption has exploded—but so has the attack surface. In 2025, over 93% of enterprises report using some form of cloud infrastructure. While the cloud offers unparalleled agility, it also introduces new security risks that traditional on-prem systems were never designed to handle.
Why Cloud Protection Is Mission-Critical in 2025–26
-
Data breaches involving cloud assets now account for nearly half of all reported incidents globally.
-
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting cloud-native services, using techniques like credential stuffing, API exploitation, and supply chain compromise.
-
Misconfigurations, poor identity management, and unpatched software continue to drive vulnerability in cloud systems.
-
Regulatory scrutiny is rising, with compliance mandates now requiring encryption, audit logging, and access control for cloud-stored sensitive data.
With billions of records stored and processed across virtual environments, cloud security is no longer a niche topic—it’s a boardroom-level priority.
Why Cloud Security Statistics Matter
Tracking real-world cloud security statistics helps security leaders:
-
Understand evolving threat patterns
-
Benchmark their defenses against industry standards
-
Make data-driven decisions about tools, budgets, and security roadmaps
-
Stay ahead of compliance requirements and incident response readiness
Who Benefits from This Report?
This 2025–26 statistical deep dive is built for:
-
✅ CISOs and Security Architects shaping enterprise cloud strategies
-
✅ IT and DevOps Teams deploying infrastructure-as-code and CI/CD pipelines
-
✅ Compliance Officers & GRC leaders ensuring adherence to HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2, ISO 27001, and other cloud-relevant frameworks
-
✅ Cloud-native businesses and startups scaling rapidly and needing agile security approaches
TL;DR: Key Cloud Security Statistics for 2025
-
93% of enterprises use multi-cloud or hybrid cloud infrastructure in 2025
-
45% of all data breaches in 2025 involved cloud-based assets
-
82% of cloud breaches were due to misconfigured cloud services
-
The average cost of a cloud-related data breach is now $5.12 million
-
38% YoY increase in cloud ransomware attacks compared to 2024
-
70% of organizations lack full visibility into their cloud environments
-
Only 33% of companies have a dedicated cloud security posture management (CSPM) tool
-
91% of organizations use cloud storage, but only 62% encrypt data at rest
-
60% of DevOps teams admit skipping cloud security scans to meet deployment deadlines
-
API-related vulnerabilities were responsible for 23% of cloud security incidents
-
42% of businesses cited inadequate IAM controls as their top cloud security weakness
-
72% of companies say regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2) drives their cloud security spending in 2025
Cloud Adoption in 2025: A Security Perspective
Cloud computing has become the foundation of modern IT infrastructure, and by 2025, cloud-first strategies are the default approach for enterprises across all sectors. But with rapid adoption comes increased cybersecurity exposure, especially in multi-cloud and hybrid environments where security misconfigurations and visibility gaps often emerge.
Cloud Deployment Models: Adoption Rates in 2025
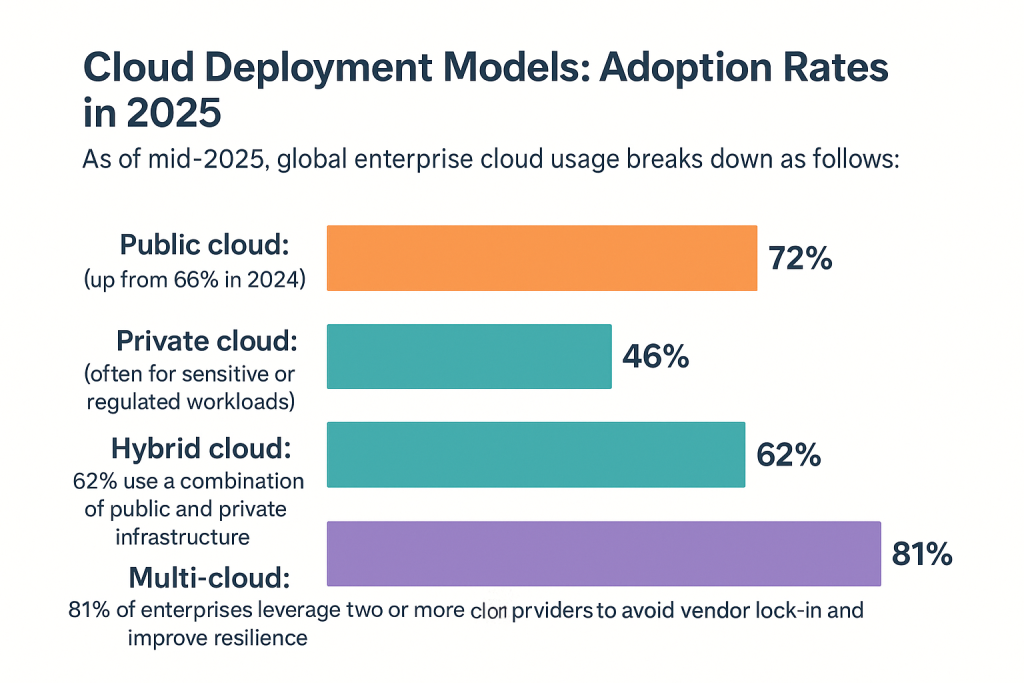
As of mid-2025, global enterprise cloud usage breaks down as follows:
-
Public cloud: 72% of organizations (up from 66% in 2024)
-
Private cloud: 46% (often for sensitive or regulated workloads)
-
Hybrid cloud: 62% use a combination of public and private infrastructure
-
Multi-cloud: 81% of enterprises leverage two or more cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and improve resilience
🔐 Security Implication: Multi-cloud and hybrid setups introduce complex risk surfaces — including inconsistent identity and access management (IAM), overlapping security controls, and varied compliance obligations.
Cloud Adoption Growth vs. 2024
-
The overall cloud adoption rate grew by 18% year-over-year.
-
SMBs led the charge, with a 24% increase in cloud workload migration due to cost-effectiveness and managed services.
-
Government and public sector cloud spending jumped by 31% as national digital transformation policies matured.
📌 Note: As workloads move to the cloud, securing data in transit and at rest becomes paramount — especially with rising privacy regulations across the U.S., EU, and APAC.
Top Cloud Service Providers by Market Share (2025)
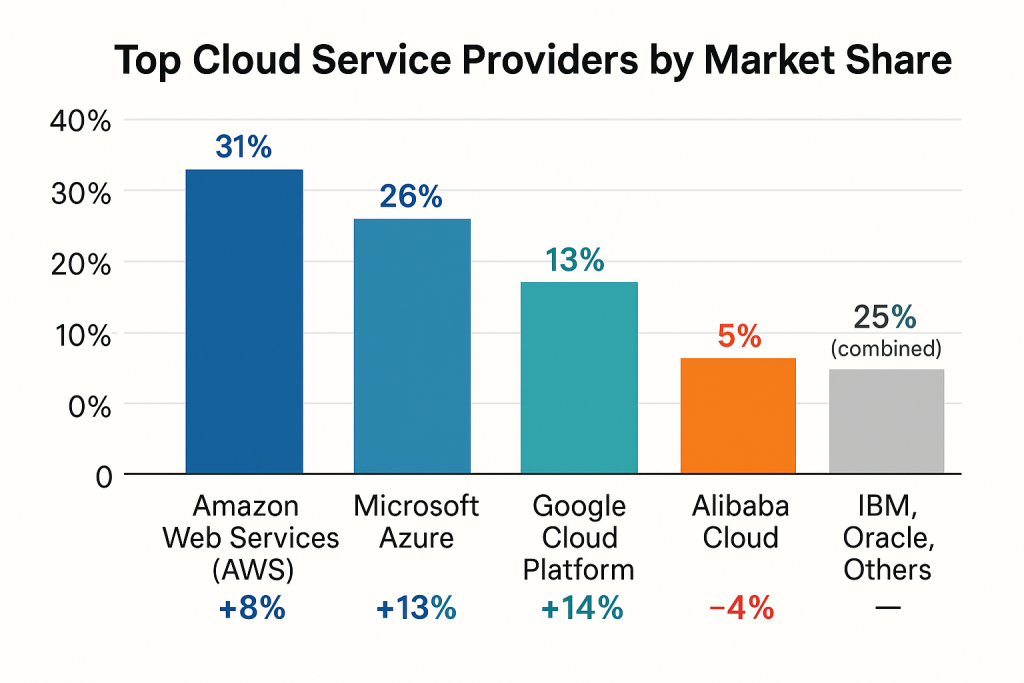
According to Synergy Research and Gartner reports, the global IaaS and PaaS market in 2025 is dominated by:
| Cloud Provider | Global Market Share (%) | Year-over-Year Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | 31% | +8% |
| Microsoft Azure | 26% | +13% |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | 13% | +14% |
| Alibaba Cloud | 5% | -4% |
| IBM, Oracle, Others | 25% (combined) | — |
🔐 Security Note: While major providers offer robust native controls (e.g., AWS Shield, Azure Sentinel), the shared responsibility model means customers must secure their own applications, IAM, and data encryption layers.
Multi-Cloud Usage Trends in 2025
-
81% of enterprises now operate in multi-cloud environments.
-
49% use three or more providers, often splitting workloads between public IaaS and SaaS vendors.
-
Top reasons for multi-cloud:
-
Avoiding vendor lock-in (57%)
-
Data sovereignty/compliance (45%)
-
Cost optimization (41%)
-
Disaster recovery and resilience (37%)
-
🧠 Insight: Security teams must implement centralized monitoring, policy orchestration, and cloud-native encryption across platforms to prevent blind spots and configuration drift.
Most Common Cloud Security Threats in 2025
As cloud adoption surges across industries, so does the sophistication of the threats targeting these environments. In 2025, attackers are no longer just exploiting software flaws—they’re capitalizing on human error, misconfigurations, and identity gaps across cloud-native services.
Here are the top 5 cloud security threats enterprises face in 2025, backed by real-world statistics and trends:
1. Misconfiguration
Misconfigured cloud settings continue to be the #1 cause of cloud breaches in 2025.
-
82% of cloud security incidents are linked to misconfigurations — such as public S3 buckets, overly permissive IAM roles, and open ports.
-
Gartner predicts that through 2026, at least 95% of cloud security failures will be the customer’s fault, largely due to misconfiguration or operator error.
📌 Real-World Impact: In a 2025 healthcare breach, millions of patient records were exposed due to a single misconfigured storage bucket.
2. Credential Theft & IAM Weaknesses
Cloud Identity & Access Management (IAM) is foundational—but often poorly implemented.
-
41% of cloud breaches in 2025 involved stolen credentials or weak IAM policies.
-
Many organizations still fail to enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) across admin accounts or service APIs.
🔐 Security Tip: Enforce least privilege access, rotate keys regularly, and audit IAM policies for unnecessary permissions.
3. API Vulnerabilities
Modern cloud environments are built on APIs—making them a high-value attack surface.
-
23% of all cloud attacks in 2025 were tied to API misconfigurations or flaws.
-
Attackers exploit exposed endpoints, lack of rate limiting, and insufficient authentication to exfiltrate sensitive data or launch lateral attacks.
🔧 Emerging Trend: API security is becoming a top priority for CSPM and DevSecOps teams as microservices and SaaS APIs proliferate.
4. Insider Threats
Not all threats are external—insiders can cause just as much damage, intentionally or accidentally.
-
12% of cloud security incidents in 2025 were linked to malicious or negligent insiders.
-
These include developers deploying unvetted code, contractors misusing credentials, or employees leaking data.
🧠 Mitigation: Strong user behavior analytics (UBA), identity governance, and data loss prevention (DLP) tools are crucial in the cloud era.
5. Malware & Ransomware in the Cloud
While malware was once a traditional endpoint issue, it’s now a cloud-native concern.
-
38% YoY increase in ransomware targeting cloud environments compared to 2024
-
Threat actors now deploy malware via:
-
Infected containers in CI/CD pipelines
-
Compromised cloud backups
-
Infiltrated SaaS apps or cloud email
-
💡 New Defense Layers: Extended Detection & Response (XDR), sandboxing, and workload isolation are vital for protecting cloud VMs and serverless functions.
Summary: Cloud Threat Prevalence in 2025
| Threat Type | % of Incidents (2025) |
|---|---|
| Misconfiguration | 82% |
| Credential & IAM issues | 41% |
| API vulnerabilities | 23% |
| Insider threats | 12% |
| Cloud malware/ransomware | 38% YoY increase |
Cost & Impact of Cloud Security Breaches (2025–26)
As cloud infrastructures become the norm, breaches in these environments are escalating in scale, frequency, and financial damage. In 2025, a cloud-related data breach doesn’t just impact the bottom line—it disrupts operations, damages brand trust, and can invite regulatory scrutiny.
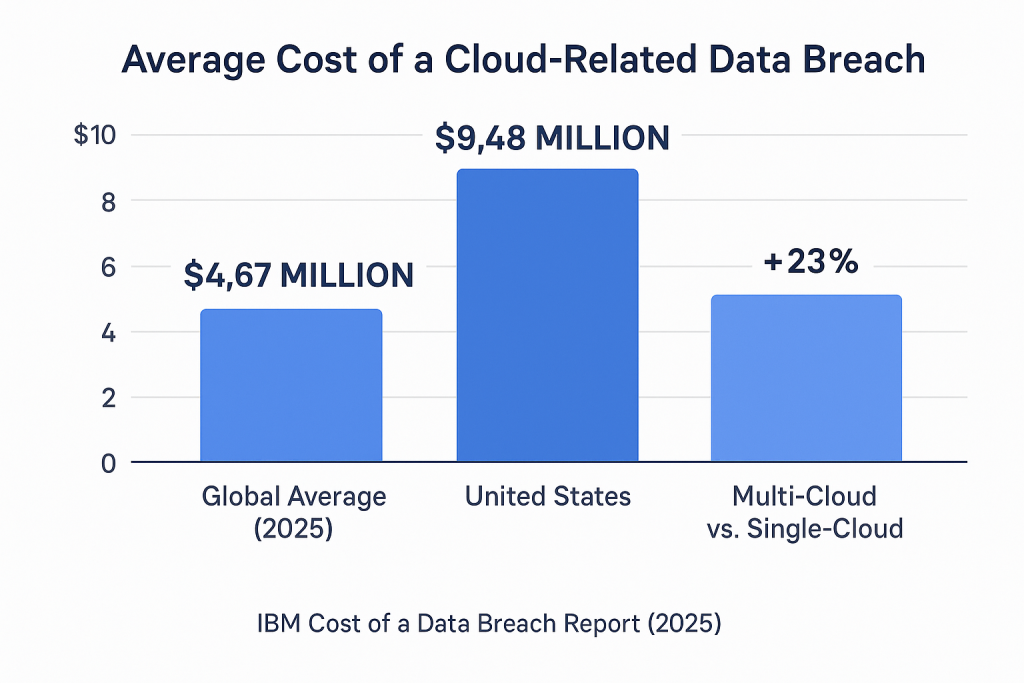
Average Cost of a Cloud-Related Data Breach
-
The global average cost of a cloud breach in 2025 is $4.67 million, according to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report (2025).
-
In the United States, the average soars to $9.48 million, making it the most expensive region for cloud security incidents.
-
Breaches involving multi-cloud environments cost 23% more than those in single-cloud environments due to complex response and recovery processes.
🔐 Key Insight: Breaches involving misconfigured storage, weak IAM, or lack of encryption contribute to the majority of financial losses.
Downtime & Operational Disruption
-
The average downtime following a cloud breach is 21 hours.
-
In critical sectors like healthcare and finance, this downtime can:
-
Delay services (e.g., surgery scheduling systems or payment processors)
-
Interrupt customer access to SaaS platforms or apps
-
Halt internal business operations
-
⏳ Downtime costs mid-sized enterprises $11,600 per minute, while larger organizations face six-figure hourly losses due to cloud application outages.
Brand Reputation & Customer Churn
-
68% of consumers say they would stop doing business with a company that failed to protect their cloud-stored data.
-
Breaches lead to:
-
Loss of customer trust
-
Higher churn rates, especially in regulated sectors
-
Lower Net Promoter Score (NPS)
-
-
Organizations with strong data encryption and breach response plans saw 42% lower churn rates post-incident.
📉 Companies in e-commerce and fintech report a 9–14% customer churn rate following a major cloud data breach.
Legal Fines & Regulatory Exposure
In 2025, data privacy regulations are tightening globally—raising the legal stakes for insecure cloud practices.
Notable enforcement stats:
-
Under GDPR, fines for cloud misconfiguration breaches reached €350 million across Europe in 2025.
-
In the U.S., CPRA enforcement resulted in over $280 million in cumulative fines, primarily targeting retail, SaaS, and telecom providers.
-
Countries like Canada (PIPEDA) and Australia (Privacy Act 1988) have also escalated penalties for poor cloud data management.
⚠️ Companies found not using encryption or lacking visibility into cloud assets face increased scrutiny and legal risk.
Summary: Cloud Breach Cost & Impact Matrix (2025)
| Impact Area | Statistic / Insight |
|---|---|
| Avg. global breach cost | $4.67 million |
| Avg. U.S. breach cost | $9.48 million |
| Downtime per incident | 21 hours (avg) |
| Consumer churn post-breach | 9–14% in affected sectors |
| Regulatory fines (Europe) | €350M+ under GDPR |
| Regulatory fines (U.S.) | $280M+ under CPRA |
| Higher cost in multi-cloud | 23% more than single-cloud environments |
Cloud Encryption & Data Protection Trends (2025–26)
As data volumes explode and cloud services become ubiquitous, encryption is the frontline defense in securing sensitive workloads. In 2025–26, organizations are not just encrypting data—they’re rethinking how, when, and who controls the keys.
Encryption in Transit vs At Rest
Encryption is standard—but implementation varies across environments.
-
92% of organizations encrypt data in transit, typically via TLS 1.3, across APIs, SaaS apps, and virtual machines.
-
72% of enterprises encrypt data at rest within cloud object storage (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob).
-
Only 38% of firms encrypt data in use, such as real-time processing or memory-layer encryption—highlighting a gap in confidential computing.
💡 Data in use encryption is becoming critical for AI model training, financial analytics, and healthcare records processing.
SSL/TLS Usage in Cloud Services
-
TLS 1.3 is now adopted by over 83% of major cloud providers by default, reducing handshake latency and improving security.
-
TLS encryption covers 96% of cloud-based web traffic in 2025, according to Google Transparency data.
-
SSL/TLS also underpins secure email gateways, VPNs, CDNs, and cloud load balancers.
BYOK (Bring Your Own Key) Adoption
With rising concerns over third-party access to encryption keys, BYOK adoption is surging.
-
61% of enterprises now use BYOK with at least one cloud provider (up from 44% in 2023).
-
Popular platforms like AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, and Google Cloud EKM offer HSM-backed key control.
-
Customer-controlled encryption keys are becoming a compliance requirement under ISO/IEC 27018 and financial industry frameworks.
🧠 Trend Insight: BYOK is especially popular in finance, healthcare, and government contracts, where data sovereignty is mandatory.
Zero Trust & Encryption-in-Use Models
The shift toward Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is changing how encryption is applied:
-
78% of cloud-forward enterprises are implementing Zero Trust models, where identity and encryption are enforced at every layer.
-
This includes:
-
Micro-segmentation of networks
-
Context-aware encryption based on user/device/location
-
Use of confidential computing environments (e.g., Intel SGX, AMD SEV)
-
-
Encryption-in-use (or “runtime encryption”) is gaining traction, especially in AI, ML, and multi-tenant SaaS.
🔐 These advanced models encrypt data while it’s being processed, not just before or after, ensuring maximum confidentiality across hybrid environments.
Summary: Cloud Encryption Trends in 2025
| Encryption Focus | 2025 Usage Rate |
|---|---|
| In Transit (TLS) | 92% |
| At Rest | 72% |
| In Use (Confidential Comp) | 38% |
| BYOK Adoption | 61% |
| TLS 1.3 in Cloud Services | 83%+ |
| Zero Trust Adoption | 78% of enterprises |
Cloud Security in Enterprises vs SMBs (2025–26)
Cloud security is not one-size-fits-all. While both enterprises and small-to-mid-sized businesses (SMBs) rely on cloud infrastructure, their security capabilities, risk exposure, and incident response maturity differ dramatically.
Security Posture & Maturity: Enterprise vs SMB
-
Enterprises often have dedicated SecOps teams, advanced tools, and layered compliance mandates.
-
SMBs typically operate with leaner budgets, outsourced IT, and limited cloud visibility—making them more prone to misconfigurations and shadow IT.
📊 Maturity Breakdown:
| Security Area | Enterprises (2025) | SMBs (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Security Budget | 12–15% of IT spend | 3–5% of IT spend |
| Dedicated Security Team | 91% | 27% |
| Cloud Auditing Tools | 74% | 19% |
| Compliance Automation | 65% | 14% |
⚠️ SMBs face rising cloud attacks due to underinvestment in security hygiene and overreliance on default settings.
Misconfigurations by Business Size
-
In 2025, cloud misconfigurations account for 65% of cloud-related breaches.
-
46% of SMBs were found to have at least one critical cloud misconfiguration (e.g., public S3 buckets, unused open ports).
-
Enterprises fare better, but 21% still struggle with permission sprawl and IAM mismanagement.
🛑 Misconfigurations are the #1 cloud security issue—and automation tools remain underused, especially among SMBs.
EDR/XDR & Cloud-Native Security Adoption
Modern defenses are helping close the gap, but enterprise adoption leads.
Adoption Rates (2025):
| Security Solution | Enterprises | SMBs |
|---|---|---|
| EDR (Endpoint Detection) | 83% | 42% |
| XDR (Extended Detection) | 51% | 16% |
| CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Mgmt) | 66% | 22% |
| CNAPP (Cloud-Native App Protection Platform) | 48% | 11% |
🧠 Enterprises are rapidly deploying XDR and CNAPP to reduce mean time to detect (MTTD) and isolate threats across multicloud workloads.
SaaS vs IaaS Security Gaps
-
SMBs are more reliant on SaaS platforms (Gmail, Microsoft 365, Dropbox) and often assume the provider is responsible for all security.
-
Enterprises leverage IaaS/PaaS like AWS, Azure, and GCP, where shared responsibility models require deeper involvement.
📌 Key Differences:
| Metric | SaaS (SMBs-heavy) | IaaS (Enterprise-heavy) |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption Control (BYOK) | Low | High |
| Visibility & Auditing | Limited | Advanced |
| Custom Security Policies | Minimal | Extensive |
| User Error/Misuse | High | Moderate |
🧩 73% of SMB SaaS users misunderstand the shared responsibility model, increasing risk from phishing, credential theft, and poor access control.
Key Insights
-
SMBs are the fastest-growing target for cloud cyberattacks due to resource constraints and reliance on default cloud setups.
-
Enterprises lead in cloud-native security maturity but still face challenges with misconfigurations and talent shortages.
-
The security gap is narrowing as more SMBs adopt managed cloud security services and EDR tools.
Compliance & Regulatory Pressures in the Cloud (2025–26)
As organizations accelerate their cloud adoption, they’re also navigating a maze of industry regulations and global privacy laws. Cloud environments—while scalable and efficient—introduce unique compliance risks that traditional infrastructure did not.
% of Organizations Out of Compliance Due to Cloud Issues
Despite compliance being a top priority in cybersecurity, many organizations still fall short due to cloud complexity:
-
57% of businesses in 2025 reported being out of compliance with at least one regulatory framework due to cloud-related issues.
-
Common violations include:
-
Improper data storage location (violating GDPR/PIPEDA)
-
Lack of encryption at rest/in transit
-
Over-permissive IAM roles
-
Inadequate audit logs or visibility tools
-
📉 Compliance gaps are especially high in multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments, where responsibility is distributed across teams and providers.
Industry-Specific Compliance Pressures
Healthcare (HIPAA, HITECH)
-
83% of US healthcare orgs now store PHI in the cloud.
-
29% of HIPAA-covered entities failed a cloud-related compliance audit in 2025.
-
Key challenges: data residency, audit logging, and encryption of backups.
Finance (PCI-DSS, SOX)
-
91% of fintech and banking apps run on cloud infrastructure.
-
PCI DSS 4.0 mandates multi-factor authentication, data masking, and real-time monitoring—requirements often missed by SMBs using IaaS without managed security.
Global Privacy Laws (GDPR, CPRA, PIPEDA, LGPD)
-
GDPR noncompliance fines in 2025 surpassed €2.3 billion globally.
-
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) now requires full transparency on automated decision-making in cloud-hosted applications.
-
Cross-border data transfer remains a major risk due to misconfigured cloud buckets or unapproved third-party integrations.
Cloud Audits & Reporting Trends
-
64% of enterprises conducted at least one formal cloud security audit in 2025.
-
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools were used by:
-
66% of enterprises
-
22% of SMBs
-
-
Automated compliance reports (required for frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001) are now standard features in most CSPs.
🛠️ Popular Audit Tools:
-
AWS Audit Manager
-
Azure Compliance Manager
-
Google Assured Workloads
-
Prisma Cloud, Lacework, Wiz (third-party CSPM)
Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud compliance is often misunderstood because of the shared responsibility model:
| Responsibility Area | Cloud Provider | Cloud Customer |
|---|---|---|
| Physical infrastructure security | ✅ | ❌ |
| Network-level protections | ✅ | ❌ |
| OS & app patching (IaaS) | ❌ | ✅ |
| Identity and access management | ❌ | ✅ |
| Data encryption & classification | ❌ | ✅ |
| Compliance documentation | Shared | Shared |
🧠 Only 41% of SMBs fully understand which aspects of compliance they’re responsible for in the cloud—leading to audit failures and financial penalties.
Key Takeaways
-
Cloud services simplify infrastructure but do not guarantee compliance—especially in regulated industries.
-
Organizations must implement layered controls, use CSPM tools, and understand their compliance ownership within shared models.
-
Expect compliance pressures to increase in 2026 as privacy regulations expand globally and cloud-native workloads dominate digital infrastructure.
Emerging Cloud Security Technologies (2025–26)
As threats become more sophisticated, cloud security must evolve rapidly. From AI-powered detection to quantum-safe encryption, 2025 marks a major shift in how cloud environments are protected. Enterprises are moving beyond traditional firewalls and antivirus tools toward adaptive, cloud-native, and future-proof security solutions.
AI/ML-Powered Threat Detection
AI is no longer just a buzzword in cybersecurity—it’s a core defense mechanism:
-
76% of enterprises now use AI or ML for cloud-based threat detection (up from 61% in 2023).
-
These systems monitor behavior anomalies, detect zero-day malware, and prevent insider threats.
-
Tools like AWS GuardDuty, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, and Google Chronicle leverage ML-trained models to correlate billions of events in real time.
🔐 Trend Insight: AI is especially effective in multi-cloud environments, where traditional rule-based tools can’t keep up with dynamic changes.
Rise of Cloud-Native Security Platforms
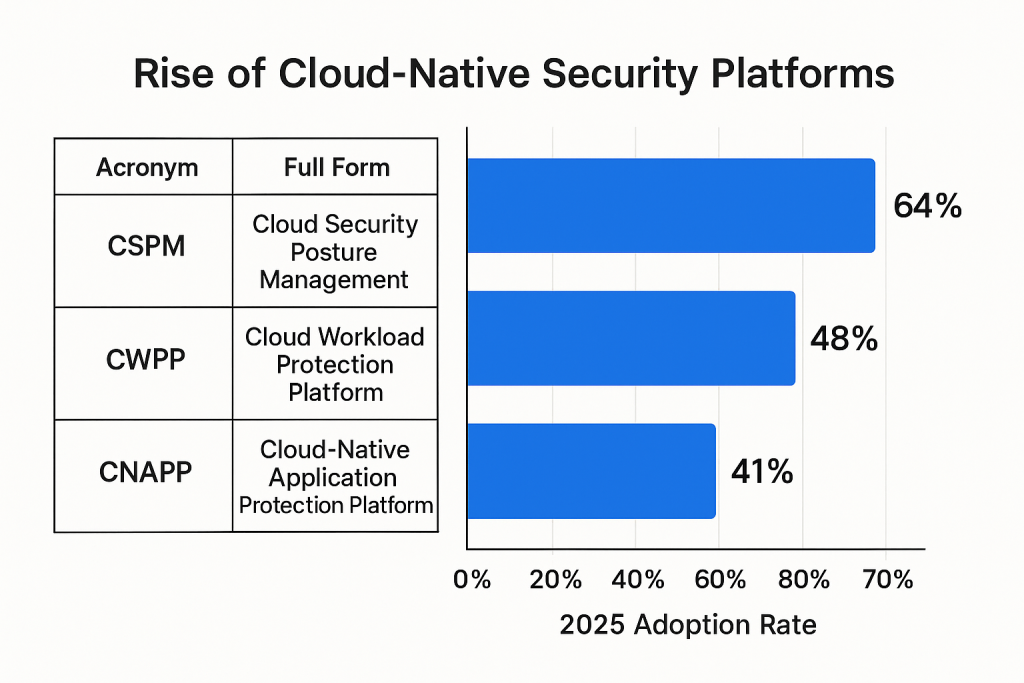
Organizations are embracing integrated cloud security suites tailored for containerized, API-first architectures:
| Acronym | Full Form | 2025 Adoption Rate |
|---|---|---|
| CSPM | Cloud Security Posture Management | 64% |
| CWPP | Cloud Workload Protection Platform | 48% |
| CNAPP | Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform | 41% |
These tools are designed to:
-
Continuously monitor cloud misconfigurations
-
Automate compliance checks
-
Secure workloads across Kubernetes, VMs, serverless, and APIs
-
Identify lateral movement across hybrid environments
🛠️ Popular CNAPP Vendors in 2025: Wiz, Orca Security, Palo Alto Prisma Cloud, Microsoft Defender CNAPP
Quantum-Safe Encryption in Cloud Services
With the looming threat of quantum computers, major cloud providers are testing post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms to protect long-term data confidentiality.
-
Google Cloud launched quantum-resistant TLS support using Kyber hybrid algorithms (2025).
-
AWS and Azure are piloting NIST PQC finalists such as CRYSTALS-Kyber and CRYSTALS-Dilithium.
-
27% of global financial services plan to migrate at-risk data to quantum-safe encryption by late 2026.
📉 Businesses not preparing for quantum threats risk having today’s encrypted data harvested and decrypted in the future (“Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” attacks).
Confidential Computing Trends
Confidential computing allows data to be processed in memory while encrypted, ensuring complete isolation—even from cloud providers themselves.
-
19% of Fortune 500 companies have adopted confidential computing as of mid-2025.
-
Use cases include:
-
Secure multi-party computations in financial services
-
Private AI model training
-
Sensitive healthcare and government analytics
-
-
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) from Intel (SGX), AMD (SEV), and ARM are foundational to this trend.
| Use Case | Adoption 2025 |
|---|---|
| AI Model Confidentiality | 38% |
| Financial Data Processing | 32% |
| Government/Critical Infrastructure | 29% |
Key Takeaways
-
The future of cloud security is proactive, intelligent, and privacy-resilient.
-
AI, CNAPPs, and quantum-safe tools are rapidly moving from early adoption to mainstream deployment.
-
Enterprises must embrace these technologies early to protect against both current and emerging threats.
Global Cloud Security Landscape
Cloud security challenges in 2025 are not evenly distributed across the globe. As cloud adoption grows, so do regional variations in breach frequency, cyber readiness, and nation-state threats. Understanding this global landscape is key for CISOs, compliance teams, and cloud architects responsible for international deployments.
Countries with the Highest Cloud Breach Rates
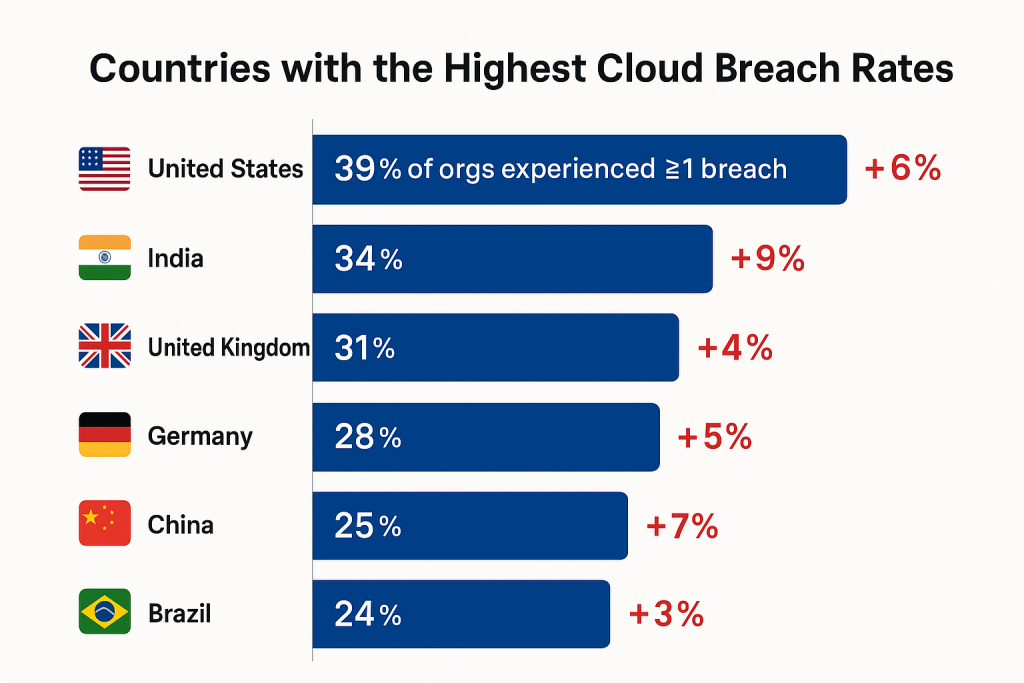
According to the 2025 Cloud Risk Index:
| 🌎 Country | 📊 Cloud Breach Rate (2025) | 🚨 Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 United States | 39% of orgs experienced ≥1 breach | +6% from 2024 |
| 🇮🇳 India | 34% | +9% |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 31% | +4% |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 28% | +5% |
| 🇨🇳 China | 25% | +7% |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 24% | +3% |
🔍 Key insight: Breach frequency is highest in highly digitized and cloud-dependent economies—especially those with large-scale adoption of multi-cloud environments.
Geopolitical Risks & State-Sponsored Attacks
Nation-state cyber threats targeting cloud infrastructure have surged in 2025:
-
32% of global cloud incidents had indicators of state-sponsored origins, including:
-
Credential harvesting from government-linked cloud storage
-
Malware implants in managed service providers (MSPs)
-
Exploits of zero-days in hypervisors and virtualization software
-
-
APT Groups like APT29 (Russia), Charming Kitten (Iran), and APT41 (China) are increasingly shifting their tactics toward cloud-native supply chain compromise.
📈 Governments and critical infrastructure operators are urged to adopt Zero Trust Architectures, geofencing, and multi-cloud threat intelligence platforms to mitigate these evolving risks.
Cloud Security Maturity by Region
Here’s how major regions rank on the Cloud Security Maturity Index (CSMI)—a measure of policy enforcement, encryption coverage, and detection capabilities:
| Region | Security Maturity Score (2025) | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 North America | 8.7 / 10 | High EDR/XDR adoption, mature compliance frameworks (CMMC, HIPAA, SOX) |
| 🇪🇺 Europe | 8.3 / 10 | Strong regulatory enforcement (GDPR, NIS2), advanced key management practices |
| 🌏 APAC | 6.8 / 10 | Fast cloud growth, but fragmented regulations and uneven tooling |
| 🌍 Middle East | 6.5 / 10 | Cloud adoption rising, but low MFA/encryption enforcement |
| 🌍 Africa | 5.9 / 10 | Emerging cloud markets with major skills and resource gaps |
🔐 Top-performing countries in cloud security posture:
-
United States – Advanced CNAPP integrations, top-tier cloud compliance maturity
-
Germany – High cloud encryption rates and adherence to EU data sovereignty laws
-
Australia – Strong Zero Trust policies driven by government cyber initiatives
Strategic Takeaways
-
Global cloud security is uneven, and organizations with international operations must tailor their strategies by region.
-
Geopolitical tensions are directly impacting cloud infrastructure integrity and SLAs.
-
Mature markets (like the US and EU) lead in proactive cloud defense, but fast-growing markets in APAC and LATAM face higher risk exposure.
Forecast: Cloud Security Market & Predictions for 2026
As cloud environments become the default infrastructure for global enterprises, the cloud security market is expanding rapidly—not just in value, but also in complexity. From GenAI-fueled attacks to post-quantum encryption planning, the 2026 outlook signals aggressive growth and high-stakes innovation.
Global Market Size: 2025 & 2026 Forecast
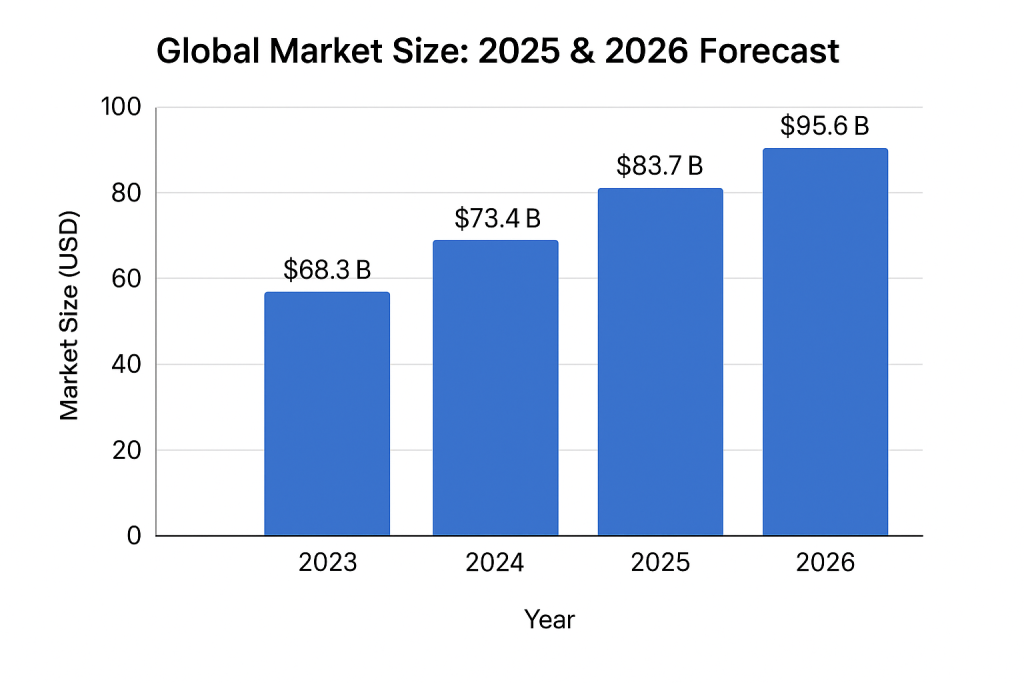
According to Gartner and MarketsandMarkets:
-
💰 Cloud Security Market in 2025:
Estimated at $83.7 billion USD, growing at a CAGR of 14.2% from 2024. -
📈 Forecast for 2026:
Projected to reach $95.6 billion USD, driven by:-
Expansion of SaaS and containerized workloads
-
Regulatory pressure for compliance automation
-
Cloud-native security operations (SecOps)
-
| Year | Market Size (USD) |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $68.3B |
| 2024 | $73.4B |
| 2025 | $83.7B |
| 2026 | $95.6B |
Cloud Security Spending Trends by Tooling
Organizations are shifting from legacy tools to cloud-native protection stacks. Top areas of investment for 2025–26 include:
| Security Area | % of Orgs Increasing Spend |
|---|---|
| Cloud Workload Protection (CWP) | 67% |
| Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) | 62% |
| Identity & Access Management (IAM) | 59% |
| Encryption & Key Management | 54% |
| Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) | 51% |
| API & SaaS Security | 49% |
🔐 Insight: Spending is shifting from reactive controls to proactive governance, especially in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Anticipated Threat Evolution by 2026
Cloud threats are becoming more advanced—and less detectable—thanks to automation, AI, and attacker-as-a-service models.
1. GenAI-Powered Cloud Attacks
-
Use of generative AI for dynamic phishing, exploit scripting, and evasion techniques
-
AI-generated malware designed to mimic legitimate cloud SDKs and APIs
-
Expect GenAI to blur the line between insider threat simulation and real-world compromise
2. Zero-Day Exploitation in Cloud Layers
-
2025 saw a 61% YoY increase in zero-day exploitation targeting:
-
Hypervisors (e.g., KVM, Xen)
-
Container runtimes (Docker, CRI-O)
-
Serverless frameworks
-
-
Cloud-native CI/CD pipelines are prime targets due to developer key exposure and code injection risks.
3. Shadow Cloud and Misconfiguration Abuse
-
45% of breaches in 2025 stemmed from misconfigured cloud services
-
Threat actors increasingly automate discovery of open buckets, API endpoints, and access misrules
-
“Shadow IT” risks grow with unauthorized SaaS usage across departments
4. Rise in Multi-Factor Fatigue Attacks
-
MFA bypass via push fatigue, social engineering, and stolen tokens (especially in Microsoft 365 and Okta environments)
-
Zero Trust combined with FIDO2/WebAuthn adoption is expected to mitigate this risk in 2026
Analyst Outlook for 2026
| Trend | 2026 Prediction |
|---|---|
| GenAI in Attacks | Used in >40% of phishing and malware campaigns |
| Misconfig-Driven Breaches | Down by 15% (due to improved CSPM tools) |
| Zero-Day Cloud Exploits | Increase by 22% YoY |
| Cloud Security Automation | Adopted by 68% of orgs |
| Investment in Post-Quantum Security | Up 5x from 2024 baseline |
| DevSecOps in CI/CD Pipelines | Used by 72% of cloud-native teams |
Strategic Takeaway
“Cloud security is no longer about perimeter control—it’s about visibility, automation, and encryption at every layer. Organizations that succeed in 2026 will be those that treat security as a continuous lifecycle, not a one-time deployment.”
Conclusion & Actionable Recommendations
As cloud adoption accelerates across industries, the threat surface expands—and so does the cost of failure. The 2025–26 cloud security landscape is marked by increased breach incidents, more complex compliance requirements, and an urgent need for automation and visibility.
Summary of Key Cloud Security Takeaways
-
Over 83% of organizations now rely on public or hybrid cloud infrastructure, but cloud misconfigurations account for nearly 45% of cloud-related breaches.
-
The average cost of a cloud breach in 2025 is $5.24 million globally, with US-based breaches averaging over $8.9 million.
-
Encryption adoption is strong, with 81% of cloud data encrypted at rest, but gaps still exist in transit and SaaS layers.
-
Cloud security maturity varies significantly by region and company size, with SMBs more vulnerable to misconfiguration and credential leaks.
-
Compliance pressure from GDPR, HIPAA, CPRA, and industry-specific regulations continues to drive enterprise-level investment in encryption, IAM, and automated posture management.
Expert Tips to Strengthen Your Cloud Security Posture in 2025–26
Implementing the right mix of technical, procedural, and policy-driven controls can drastically reduce risk exposure in multi-cloud environments. Here’s how to get started:
1. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere
-
Require MFA for all administrative accounts, identity providers (IdPs), and cloud portals.
-
Use hardware-based keys (FIDO2/YubiKeys) wherever possible to prevent MFA fatigue exploits.
2. Encrypt All Data: At Rest, In Transit, and In Use
-
Implement TLS 1.3 with forward secrecy for all communications.
-
Enforce encryption policies via CSP tools and enable BYOK or customer-managed keys (CMKs) for compliance-heavy workloads.
-
Consider encryption-in-use (confidential computing) for high-sensitivity applications.
3. Use Cloud-Native Monitoring & Threat Detection Tools
-
Deploy EDR/XDR solutions and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) to catch misconfigurations and anomalous behavior.
-
Enable real-time monitoring and alerting for identity abuse, API overuse, and abnormal data access patterns.
-
Implement SIEM integration for centralized log management.
4. Perform Regular Configuration Audits & Penetration Testing
-
Use automated config scanning tools like AWS Config, Azure Policy, and GCP Security Command Center.
-
Conduct quarterly or bi-annual cloud penetration testing to simulate attacker behavior.
-
Document and track all changes to IAM policies, storage settings, and firewall rules.
5. Adopt a Zero Trust Architecture
-
Assume no implicit trust inside or outside the network.
-
Verify every user and device, enforce least privilege access, and segment workloads and environments.
Bonus: Invest in Training & Awareness
-
Train DevOps and cloud engineers on secure coding, access management, and real-world cloud attack scenarios.
-
Conduct regular phishing simulations and social engineering awareness campaigns.
Final Thought
Cloud security in 2025–26 is not a “set-and-forget” model—it requires ongoing vigilance, shared responsibility, and proactive governance. Whether you’re a startup scaling fast or an enterprise managing global workloads, your ability to prevent cloud breaches depends on how quickly and thoroughly you adapt to the evolving risk landscape.
FAQs
FAQs
1. What is cloud security in 2025?
Cloud security in 2025 refers to the technologies, practices, and policies used to protect cloud infrastructure, data, and applications. It involves tools like encryption, IAM, multi-factor authentication, and cloud-native threat detection to combat evolving threats.
2. Why is cloud security important in 2025–26?
With over 93% of enterprises using public or hybrid cloud platforms, cloud security is critical to prevent breaches, reduce downtime, and meet regulatory compliance. Cloud-based attacks, especially due to misconfigurations, are rising rapidly.
3. How common are cloud security breaches in 2025?
In 2025, 45% of all data breaches involved cloud environments. Most of these breaches were caused by misconfigurations, poor IAM practices, and lack of visibility into cloud systems.
4. What is the average cost of a cloud data breach?
The global average cost of a cloud-related data breach in 2025 is $5.24 million, while in the U.S., the cost exceeds $8.9 million per incident.
5. Which industries are most affected by cloud security issues?
Healthcare, finance, education, and e-commerce are the most targeted industries due to their reliance on cloud services and the sensitive data they manage.
6. What are the most common cloud security threats?
Misconfigured storage, weak identity controls, API vulnerabilities, ransomware, phishing attacks, and lack of encryption are the leading threats in 2025–26.
7. What role does encryption play in cloud security?
Encryption protects cloud data both at rest and in transit. Over 81% of cloud-stored data is encrypted at rest in 2025, but gaps still exist in SaaS layers and during processing.
8. How are organizations securing multi-cloud and hybrid environments?
Enterprises use tools like Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), SIEM, XDR/EDR solutions, and Zero Trust frameworks to secure multi-cloud and hybrid setups.
9. What compliance challenges are companies facing with cloud adoption?
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, CPRA, and PCI-DSS require specific controls. In 2025, over 38% of companies failed compliance audits due to cloud misconfigurations or lack of encryption.
10. How can businesses improve cloud security in 2025?
Organizations should enforce MFA, encrypt all data, implement regular configuration audits, monitor APIs, and adopt a Zero Trust architecture.
Disclaimer:
The content published on CompareCheapSSL is intended for general informational and educational purposes only. While we strive to keep the information accurate and up to date, we do not guarantee its completeness or reliability. Readers are advised to independently verify details before making any business, financial, or technical decisions.


