Cybersecurity spending in 2026 has surged to unprecedented heights, driven by escalating ransomware incidents, AI-driven cybercrime, global regulatory pressure, digital transformation, and the expansion of hybrid workforces. Organizations across all industries increased investments in detection, response, identity security, cloud protection, and encryption technologies. The rise of sophisticated adversaries — from professional ransomware cartels to AI-enabled cybercriminals — has forced enterprises, governments, and SMEs to rethink their defensive budgets.
The cybersecurity market in 2026 is no longer defined simply by endpoint solutions or firewalls. Instead, spending is shaped by:
-
Zero Trust adoption
-
Cloud-native security
-
Identity-first security models
-
API and application protection
-
Quantum-resilient encryption planning
-
Mobile and IoT ecosystem protection
-
Cyber insurance requirements
-
Dark web monitoring and threat intelligence
With the continued global shift toward digital operations and increased dependence on cloud workloads, cybersecurity spending has become one of the fastest-growing enterprise technology segments.
-
Total Global Cybersecurity Investment: Global cybersecurity spending is expected to reach $240–$250 billion in 2026, driven by escalating ransomware, supply-chain attacks, and AI-powered threats. This level of investment positions cybersecurity as one of the fastest-growing segments of global IT spending, with growth rates far exceeding overall enterprise technology budgets.
-
Cybercrime Pressure on Budgets: As cybercrime damages approach $10.5 trillion annually, organizations are forced to increase security budgets to offset financial, legal, and operational risks. On average, enterprises now dedicate 8–12% of their total IT budgets to cybersecurity, compared to less than 6% just four years ago.
-
Cost of Breaches vs Security Spend: The average global data breach cost of $4.44 million continues to shape cybersecurity investment strategies. In high-regulation markets such as the U.S., where average breach costs exceed $10.22 million, organizations are prioritizing preventative controls and faster detection to reduce long-term financial exposure.
-
Ransomware-Led Investment Growth: Ransomware incidents now influence nearly half of cybersecurity budget decisions. In 2026, organizations are allocating increased spending toward ransomware-resilient infrastructure, including immutable backups, Zero Trust network segmentation, and incident response retainers. Even without ransom payment, recovery costs average $5.08 million per event.
-
Security Spending Allocation Trends: Approximately 40% of cybersecurity budgets in 2026 are directed toward security software and platforms, including SIEM modernization, XDR, cloud workload protection, and identity security. Spending on managed security services continues to rise as companies struggle with skill shortages and 24×7 monitoring requirements.
-
Attack Volume Driving Continuous Investment: Cyberattacks occur at near-constant frequency, with global organizations facing tens of thousands of attack attempts daily. The sustained volume of threats has shifted spending away from one-time tools toward continuous monitoring, automation, and real-time response capabilities.
-
Industry-Specific Spending Patterns: Healthcare and financial services remain the highest cybersecurity spenders due to regulatory exposure and sensitive data handling. Manufacturing cybersecurity budgets have surged following a 61% year-over-year rise in ransomware attacks targeting industrial and operational technology systems.
-
Geographic Budget Variations: Cybersecurity spending is highest in North America, followed by Europe and the Middle East. Middle Eastern organizations have significantly increased investment in AI-driven defenses, contributing to lower breach growth rates despite rising threat activity. Asia-Pacific markets show the fastest budget expansion as digital adoption accelerates.
-
AI-Driven Security Investments: In response to AI-enabled cyber threats, organizations are rapidly increasing investment in security automation. Companies deploying AI-powered defenses reduce breach response times by up to 80 days and lower incident costs by approximately $1.9 million, reinforcing automation as a core budget priority for 2026.
What Are Cybersecurity Spending Statistics?
Cybersecurity spending statistics are quantifiable measures that track how much organizations, industries, and governments invest in protecting digital systems, data, and infrastructure. They answer questions such as: How much do companies spend on cybersecurity each year? Which security categories receive the largest budgets? How fast are cybersecurity investments growing compared to overall IT spending? These figures are compiled from enterprise surveys, market research firms, financial disclosures, and global security reports to measure how organizations respond financially to cyber risk.
At a high level, cybersecurity spending statistics reflect the economic response to digital threats. As cyberattacks become more frequent, costly, and disruptive, organizations adjust their budgets accordingly. Analysts track metrics such as total global cybersecurity spend, year-over-year growth rates, budget allocation by security category, and spending differences across industries and regions. Together, these numbers reveal where organizations feel the most pressure and where security priorities are shifting.
For example, global market tracking shows that cybersecurity spending is projected to exceed $240–$250 billion in 2026, growing at a 17–22% annual rate, far outpacing general IT budget growth. Enterprise surveys consistently report that organizations now allocate 8–12% of total IT budgets to cybersecurity, up from single-digit levels earlier in the decade. This shift highlights how cybersecurity has moved from a support function to a core business investment.
Cybersecurity spending statistics also help explain how budgets are used. Industry data breaks spending into categories such as security software and platforms, managed security services, cloud and identity protection, network security, and incident response. For instance, security software alone accounts for roughly 40% of total cybersecurity budgets, while managed security services continue to grow as talent shortages make in-house monitoring difficult to sustain.
In simpler terms, cybersecurity spending statistics act like a financial dashboard for digital risk. Just as a company tracks revenue, operating costs, and margins, it also tracks how much it must invest to prevent breaches, reduce downtime, and meet regulatory requirements. When data shows that ransomware-driven incidents cost organizations an average of $5 million+ per event, companies respond by increasing investment in backups, Zero Trust architectures, and response automation.
These statistics matter because they guide strategic decisions. If spending data shows that AI-driven security reduces breach costs by $1.9 million per incident, organizations know where to prioritize future budgets. If certain industries or regions are increasing spending faster than others, it signals rising threat exposure or regulatory pressure. In short, cybersecurity spending statistics transform abstract cyber risk into measurable financial decisions, helping leaders understand not just how dangerous the threat landscape is—but how much protection truly costs in 2026.
Why Cybersecurity Spending Matters in 2026
Organizations that underinvest in cybersecurity face:
-
Higher breach probability
-
Larger financial damages
-
Business continuity crises
-
Regulatory violations
-
Long-lasting reputation damage
-
Increased insurance premiums or denial of coverage
As attacks surge across multiple threat vectors — cloud, mobile, identity, APIs, IoT, and supply chain — cybersecurity budgets are growing aggressively to address new digital risks.
Cybersecurity spending statistics help businesses:
-
Benchmark their security maturity
-
Justify budget increases
-
Identify the most important investment areas
-
Understand where competitors and industries are focusing
-
Prepare for upcoming compliance obligations
Global Cybersecurity Market Size in 2026
The cybersecurity market in 2026 is expanding faster than ever. Fueled by geopolitical tensions, data breaches, ransomware growth, AI-driven threats, and cloud adoption, worldwide security spending continues to accelerate.
In 2026, cybersecurity spending entered a decisive phase marked by record investment levels, accelerated budget growth, and tighter alignment with business risk. Cybersecurity is no longer treated as a defensive IT cost but as a core economic safeguard against financial loss, regulatory exposure, and operational disruption. The global picture shows organizations increasing security budgets faster than overall IT spend as threats continue to scale in volume, sophistication, and financial impact.
Below is a snapshot comparing key cybersecurity spending and investment indicators from 2025 vs 2026, highlighting how priorities are shifting year over year.
| Metric | 2025 | 2026 (Est.) | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total global cybersecurity spending | ~$205B | $240–$250B | +17–22% YoY growth |
| Share of IT budgets allocated to security | ~7–9% | 8–12% | Rising board-level priority |
| Security software & platforms spend | ~$80B | ~$95–$100B | Largest budget category (~40%) |
| Managed security services (MSSP) | ~$70B | ~$85B | Strong growth due to talent shortages |
| Cloud & identity security investment | ~$55B | ~$70B | Driven by cloud & hybrid work |
| AI-driven security & automation spend | ~$18–20B | $28–32B | Fastest-growing segment |
| Average breach cost influencing budgets | $4.44M | $4.5M+ | Spending tied to loss prevention |
| Cyber insurance market size | ~$24–25B | ~$30B | Rising premiums drive security spend |
| Unfilled cybersecurity roles | ~4.8M | ~5M+ | Sustains outsourcing demand |
What the Numbers Signal
The data shows a clear shift from reactive security purchases to strategic, long-term investment planning. Organizations are not only spending more, but spending differently—prioritizing automation, managed services, and identity-centric defenses over isolated point solutions. The fastest budget growth is occurring where tools reduce breach lifecycle time, staffing pressure, and regulatory risk.
In practical terms, cybersecurity spending statistics in 2026 illustrate how financial risk, operational resilience, and digital trust are converging. Enterprises that fail to scale security investment in line with threat growth face disproportionate losses, while those aligning budgets with real-world risk metrics are achieving measurable reductions in breach costs and recovery time.
Global Cybersecurity Spending (2026 Estimate)
$212–$225 billion, depending on sector classification
YoY Growth Rate (2025 → 2026):
≈ +17% to +22%
This represents one of the highest year-over-year increases in cybersecurity history.
3-Year Compound Annual Growth Rate (2024–2026):
≈ 15–17% CAGR
Forecast for 2027:
The global cybersecurity market is projected to hit
$250–$270 billion by 2027.
Industry Segments Driving the Most Spending in 2026
Cybersecurity spending is not distributed evenly. Sectors facing heavy regulation or high-value data continue to invest the most.
Top Spending Industries (2026):
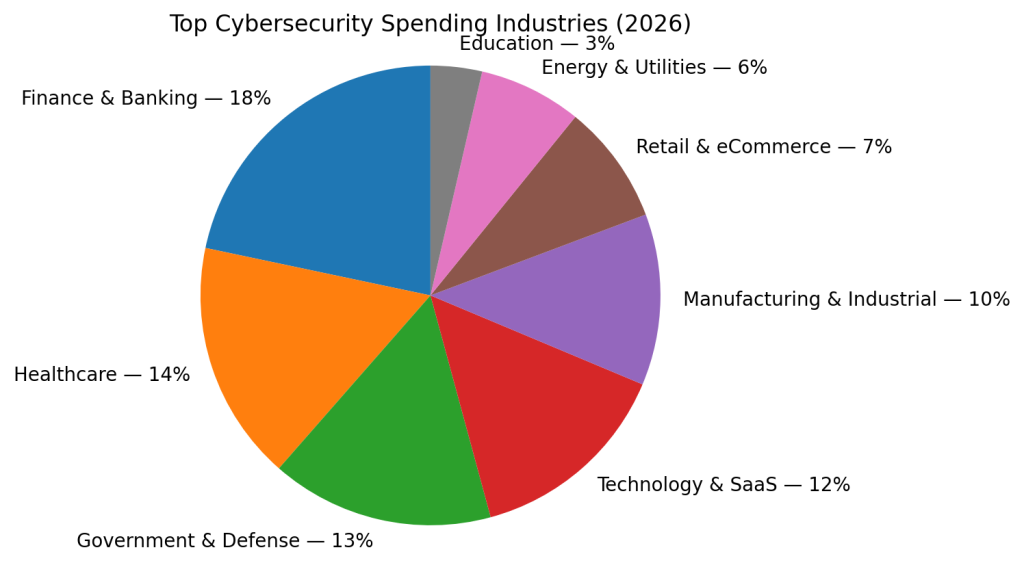
- Finance and banking account for the largest share of global cybersecurity spending at approximately 18%. Financial institutions invest heavily in security due to constant exposure to fraud, ransomware, data theft, and strict regulatory requirements governing customer data and transaction integrity.
- Healthcare represents around 14% of worldwide cybersecurity expenditure, driven by the high value of patient data, frequent ransomware attacks, and regulatory mandates such as HIPAA. The sector consistently reports the highest average breach costs, making proactive security investment unavoidable.
- Government and defense organizations contribute about 13% of total cybersecurity spending, reflecting the critical need to protect national infrastructure, defense systems, and sensitive citizen data from state-sponsored and advanced persistent threats.
- Technology and SaaS companies make up roughly 12% of global cybersecurity budgets, as they safeguard cloud platforms, customer data, APIs, and software supply chains. Security spending in this sector is closely tied to uptime, customer trust, and compliance obligations.
- Manufacturing and industrial enterprises account for approximately 10% of cybersecurity spending, fueled by a sharp rise in ransomware and operational technology (OT) attacks that disrupt production lines, supply chains, and industrial control systems.
- Retail and eCommerce businesses represent about 7% of global cybersecurity investment, focusing primarily on payment security, customer data protection, fraud prevention, and defending high-traffic digital storefronts from attacks.
- Energy and utilities organizations allocate around 6% of cybersecurity spending, prioritizing the protection of critical infrastructure, smart grids, and energy distribution systems against disruption and sabotage.
- Education accounts for roughly 3% of global cybersecurity spend, reflecting lower budgets but growing investment as schools and universities face increasing ransomware attacks and data exposure risks.
Fastest Growing Sectors (2026 YoY):
- Healthcare: Cybersecurity spending grew +26% YoY in 2026, the fastest across all industries.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing cybersecurity budgets increased +22% YoY, reflecting rising OT and ransomware exposure.
- Retail & eCommerce: Retail and eCommerce security spending rose +19% YoY amid elevated fraud and breach activity.
- Government: Government cybersecurity investment expanded +18% YoY as public-sector threat levels increased.
- SaaS & Technology: SaaS and technology firms saw cybersecurity spending grow +17% YoY in 2026.
Largest Cybersecurity Investment Categories in 2026
Organizations are shifting how they spend money. Traditional perimeter tools are declining while modern identity and cloud-centric tools dominate.
Top Security Categories by Spending (2026):
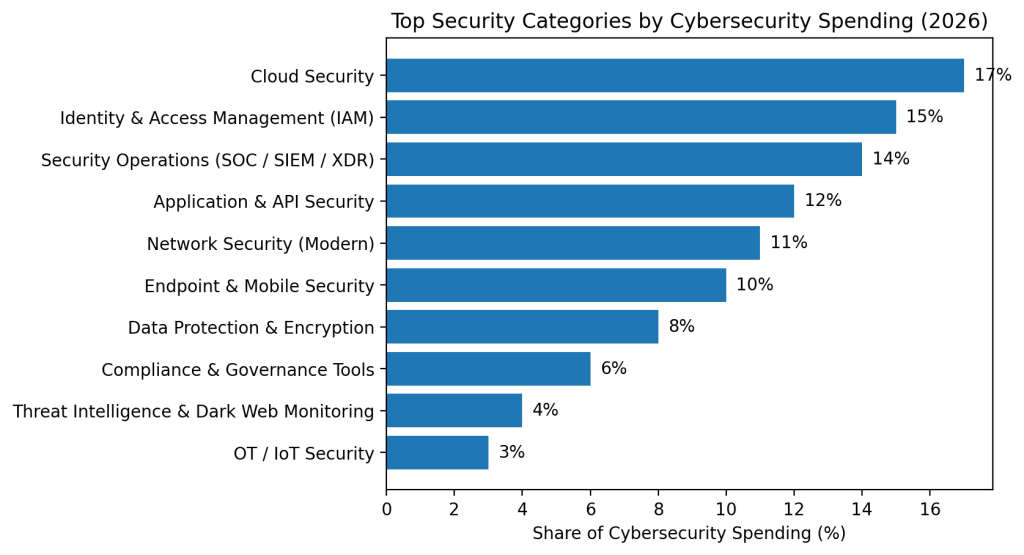
- Cloud security accounts for the largest share of cybersecurity spending at approximately 17% in 2026. As organizations accelerate cloud adoption and operate across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, protecting cloud workloads, configurations, and access layers has become a top investment priority.
- Identity and access management (IAM) represents around 15% of total cybersecurity spend, reflecting the industry’s shift toward identity-centric security models. Zero Trust architectures, privileged access management, and identity governance tools are driving sustained budget growth in this category.
- Security operations, including SOC platforms, SIEM, and XDR, make up roughly 14% of cybersecurity spending. Organizations are investing heavily in centralized visibility, faster threat detection, and automated response as attack volumes continue to scale beyond manual monitoring capabilities.
- Application and API security captures about 12% of global cybersecurity budgets, fueled by the expansion of web applications, SaaS platforms, and API-driven ecosystems. Vulnerability management, runtime protection, and API abuse prevention are now core security requirements.
- Modern network security solutions account for approximately 11% of total spending, as traditional perimeter defenses are replaced by software-defined networking, secure access service edge (SASE), and microsegmentation technologies.
- Endpoint and mobile security represents around 10% of cybersecurity investment, driven by hybrid work, BYOD policies, and the growing attack surface created by laptops, mobile devices, and unmanaged endpoints.
- Data protection and encryption tools make up about 8% of cybersecurity spending, with organizations prioritizing data-at-rest and data-in-transit protection to meet regulatory requirements and reduce breach impact.
- Compliance and governance tools account for roughly 6% of security budgets, supporting audit readiness, regulatory reporting, risk management, and policy enforcement across complex IT environments.
- Threat intelligence and dark web monitoring represent around 4% of total spending, helping organizations detect early indicators of compromise, credential leaks, and emerging attack campaigns before they escalate.
- Operational technology (OT) and IoT security accounts for approximately 3% of cybersecurity spending, a smaller but rapidly growing category as industries work to secure industrial control systems, smart devices, and critical infrastructure.
Growth Rates by Category (YoY):
-
Cloud Security: Cybersecurity spending increased 28% year over year in 2026.
-
Identity Security: Identity and access security budgets grew 31% YoY.
-
Application & API Security: Spending on application and API security rose 27% YoY.
-
XDR / SOC Modernization: Security operations and XDR investments expanded 33% YoY, the highest growth rate.
-
Mobile Security: Mobile and endpoint security spending increased 21% YoY.
-
IoT Security: IoT and connected device security budgets grew 22% YoY.
Cloud, API, and identity security are the fastest-growing categories in 2026 due to cloud-native application adoption and the global reliance on SaaS platforms.
Drivers Behind the Surge in Cybersecurity Investments (2026)
1. Rise of AI-Driven Threats
AI tools are:
-
Automating phishing
-
Writing malware
-
Bypassing authentication
-
Generating deepfake voices
-
Performing large-scale credential validation
Organizations are forced to increase investment in AI-powered detection, behavior analytics, and deception technologies to keep pace.
2. Increasing Volume of Data Breaches
With more breaches exposing billions of records, companies are spending heavily on:
-
Encryption
-
Tokenization
-
Data loss prevention
-
Dark web monitoring
-
Real-time detection
3. Ransomware Financial Losses
Ransomware now accounts for a huge share of breach costs:
-
Average ransomware payment: +35% YoY
-
Average downtime after ransomware: ~20–30 days
-
RaaS adoption: ~78% of attacks
Organizations now budget specifically for ransomware prevention, backup modernization, and incident response.
4. Transition to Zero Trust Architectures
Zero Trust requires:
-
Continuous authentication
-
Device posture checks
-
Micro-segmentation
-
Identity-first controls
These investments significantly increase cybersecurity spending across identity, API security, and network segmentation tools.
5. Cloud Migration & SaaS Adoption
Cloud workloads require new tools:
-
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
-
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM)
-
Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
-
API monitoring and token management
This is one of the top three spending categories in 2026.
6. Cyber Insurance Requirements
Cyber insurers now demand:
-
MFA
-
Data encryption
-
Zero Trust
-
EDR/XDR
-
Patch compliance
-
Backup & DR plans
Companies failing to meet baseline security controls face:
-
Higher premiums
-
Deductibles
-
Policy rejection
This forces mandatory cybersecurity investments.
SMB Cybersecurity Spending Trends in 2026
Small and medium businesses (SMBs) represent the fastest-growing adopter group.
2026 SMB Spending Metrics:
-
SMB cybersecurity budgets grew 21% year over year in 2026.
-
About 72% of SMBs increased cybersecurity spending in 2026.
-
Approximately 64% of SMBs adopted cloud-native security tools.
-
Nearly 58% of SMBs deployed MDM or endpoint protection solutions.
-
An estimated 43% of SMBs were targeted by cyberattacks.
SMBs are now preferred targets because:
-
They store valuable data
-
They often lack experienced security staff
-
They are dependent on SaaS platforms
-
They have limited breach response capability
The dark web’s sale of SMB access credentials further increases attack risk.
Global Cybersecurity Spending Distribution by Region (2026)
Cybersecurity budgets vary significantly across regions due to differences in digital infrastructure maturity, regulatory pressure, cyberattack frequency, and IT investment priorities. In 2026, every major region increased cybersecurity spending — but some regions invested far more aggressively than others.
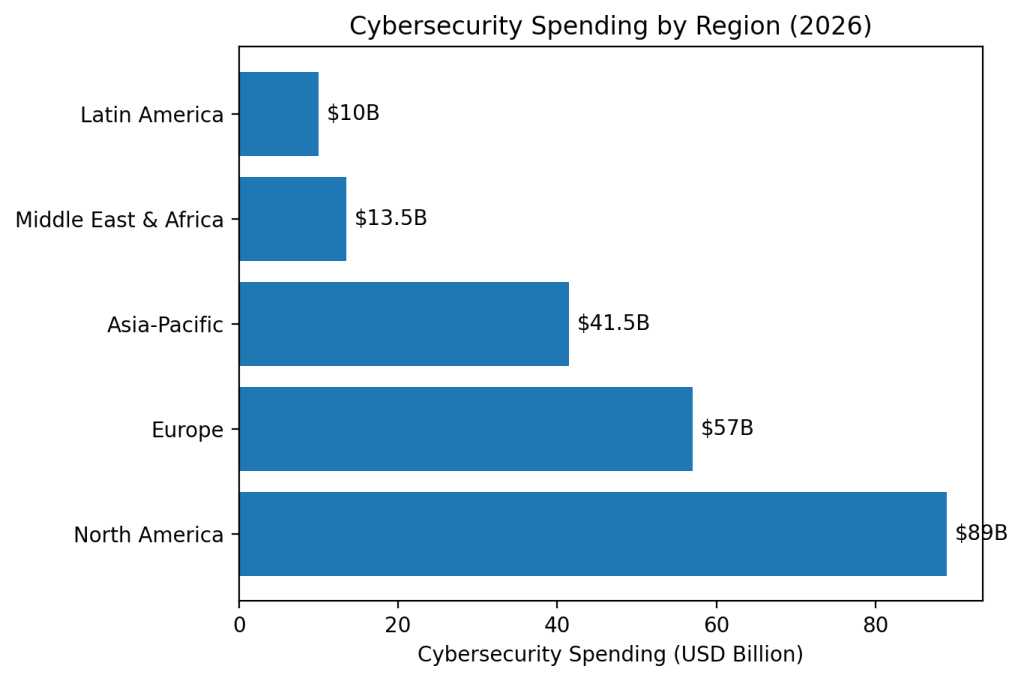
1. North America (U.S. & Canada)
North America remains the world’s largest cybersecurity market.
2026 Spending Estimate:
$86–$92 billion
(~40% of global cybersecurity spend)
YoY Growth:
+18%
Key Investment Drivers in 2026:
-
Surge in ransomware attacks targeting financial institutions
-
Zero Trust mandates across enterprise environments
-
Growth in SOC modernization & XDR deployment
-
Increase in AI-powered detection and automated response
-
Cyber insurance requirements becoming stricter
Sectors spending the most:
-
Finance
-
Healthcare
-
Government defense contractors
-
SaaS & cloud service providers
North America leads the adoption of identity-centric security frameworks, advanced analytics, and cloud-native controls.
2. Europe (EU, UK, Nordics)
Europe’s cybersecurity posture strengthened due to new regulatory frameworks and increased cross-border cyber threats.
2026 Spending Estimate:
$54–$60 billion
YoY Growth:
+16%
Top Spending Drivers:
-
GDPR fines and enforcement tightening
-
Rise in ransomware targeting hospitals and education systems
-
Government investment in critical infrastructure security
-
Increased adoption of supply-chain risk mitigation tools
-
Expansion of endpoint and mobile security for remote workforces
Western Europe leads cloud security adoption, while Eastern Europe shows fastest overall budget growth.
3. Asia-Pacific (APAC)
APAC is the fastest-growing cybersecurity market in 2026 due to rapid digital transformation across emerging economies.
2026 Spending Estimate:
$38–$45 billion
YoY Growth:
+24%
Key Investment Drivers:
-
Massive adoption of mobile and cloud-first environments
-
High ransomware impact on manufacturing and finance
-
Growing fintech markets requiring encryption and fraud prevention
-
Rising cybercrime syndicates operating across Southeast Asia
-
National cybersecurity initiatives in India, Singapore, Japan & Australia
APAC enterprises invest heavily in mobile, API, and cloud security — areas where attacks are growing fastest.
4. Middle East & Africa (MEA)
MEA saw some of the most aggressive YoY spending increases.
2026 Spending Estimate:
$12–$15 billion
YoY Growth:
+22%
Key Drivers:
-
Saudi Arabia & UAE cybersecurity mega-projects
-
National digital transformation in finance & government
-
Growth in critical infrastructure (oil & energy) cyber protection
-
Increased ransomware targeting public and private sectors
-
Workforce identity modernization and Zero Trust initiatives
MEA is becoming a high-priority region for cybersecurity vendors due to rapid digital expansion.
5. Latin America (LATAM)
LATAM’s cybersecurity market accelerated sharply due to rising fraud and ransomware targeting retail, logistics, and finance.
2026 Spending Estimate:
$9–$11 billion
YoY Growth:
+19%
Digital payment adoption and increased cloud workloads are major spending catalysts.
Enterprise vs SMB Cybersecurity Spending (2026 Update)
Cybersecurity budgets differ dramatically between large enterprises and small-to-medium businesses (SMBs). Yet both segments increased investments in 2026.
Enterprise Cybersecurity Spending Trends (2026)
Large Enterprise Budget Growth:
+20% YoY
Average Enterprise Cybersecurity Budget:
$8M–$14M per year, depending on industry
Key Focus Areas:
-
Zero Trust implementation
-
XDR & automated SOC systems
-
Cloud workload protection
-
Identity governance & privileged access
-
Secure SDLC & API testing
-
Encryption modernization
-
Threat intelligence & dark web monitoring
Enterprise Challenges:
-
Expanding attack surfaces (mobile, IoT, multi-cloud)
-
Integration complexity
-
High cost of skilled security professionals
-
Legacy infrastructure modernization
SMB Cybersecurity Spending Trends (2026)
SMB Budget Growth:
+21% YoY
Average SMB Cybersecurity Budget:
$18,000–$200,000 annually, depending on company size
Key Spending Drivers:
-
Increasing attacks on small businesses
-
Mandatory insurance requirements
-
Migration to SaaS platforms
-
Supply-chain compliance needs
-
Identity and endpoint protection
SMB Weaknesses:
-
Understaffed IT & security teams
-
Slow patching cycles
-
Overreliance on SaaS without proper security controls
-
Lack of incident-response readiness
SMBs spend less, but their risk exposure is disproportionately high.
Cybersecurity Budget Allocation Trends in 2026
Organizations are reallocating budgets to reflect new threats and tech adoption patterns.
Below is the most realistic 2026 allocation breakdown for cybersecurity spending.
1. Identity & Access Management (IAM) — 2026 Focus
IAM spending surged due to the rise of credential theft, MFA fatigue attacks, SSO vulnerabilities, and workforce mobility.
IAM Spending Growth:
+31% YoY
IAM Allocation Share (2026):
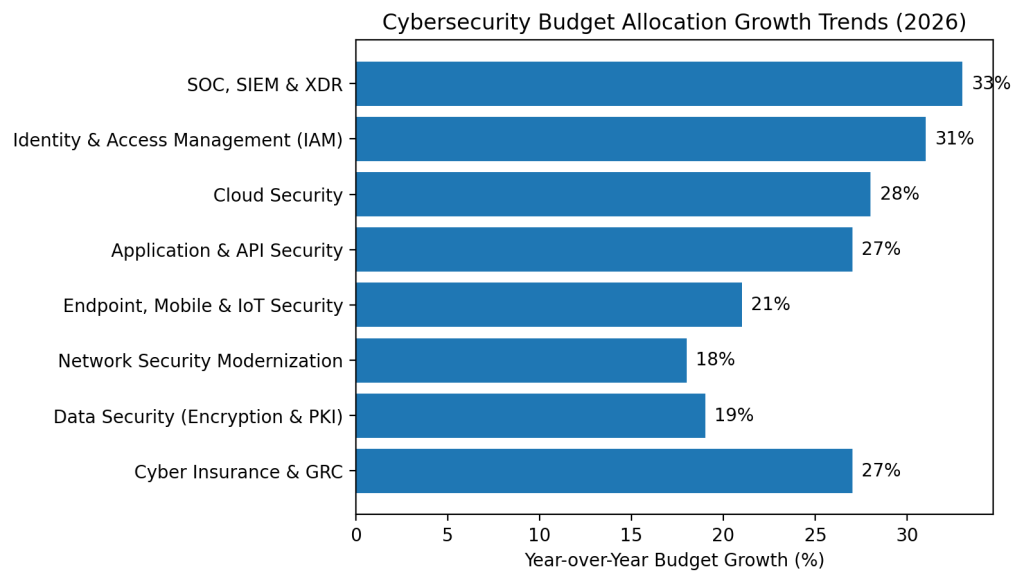
≈ 15% of total cybersecurity budgets
Top IAM investment areas:
-
Passwordless authentication
-
Multi-factor authentication (biometrics, app-based)
-
Privileged access management
-
Identity governance
-
SSO security hardening
-
Device-bound identity verification
2026 is the first year where identity security surpasses endpoint security as a spending priority.
2. Cloud Security Spending in 2026
As workloads migrate to AWS, Azure, GCP, and multi-cloud environments, cloud security became the fastest-growing segment.
Cloud Security Spend:
≈ 17% of global budget
Cloud Security Growth YoY:
+28%
Primary Investments:
-
CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management)
-
CWPP (Cloud Workload Protection Platforms)
-
CIEM (Cloud Entitlements Management)
-
Cloud firewalls & micro-segmentation
-
API Gateway & token enforcement
-
Serverless security
Misconfigurations remain the #1 cause of cloud breaches, fueling demand for continuous monitoring.
3. Application & API Security Spending (2026)
API-driven ecosystems are now the backbone of SaaS, mobile, fintech, and eCommerce.
API Security Spending Growth:
+27% YoY
Share of overall budgets:
≈ 12%
Top investments include:
-
Runtime API protection
-
API threat detection
-
Secure code review
-
Application security testing (DAST, SAST, IAST)
-
Bot mitigation
-
WAAP (Web Application & API Protection) platforms
API abuse is expected to remain a major attack vector through 2027.
4. Endpoint, Mobile & IoT Security Spending
Endpoints remain critical due to ransomware and malware proliferation.
Endpoint/Mobile Security Growth:
+21% YoY
Share of security budgets:
≈ 10%
Key categories:
-
EDR/XDR
-
Mobile Threat Defense (MTD)
-
Device encryption & MDM
-
IoT network segmentation
-
OT/ICS endpoint monitoring
IoT security spending is growing at +22% YoY, fueled by industrial automation and smart devices.
5. Network Security Modernization
Legacy firewalls are being replaced by modern solutions:
-
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
-
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
-
SD-WAN + security bundles
Network Security Growth YoY:
+18%
Budget Share:
≈ 11%
Despite cloud adoption, network-layer security remains a core spend.
6. SOC, SIEM & XDR Modernization
Security Operations budgets continue to grow significantly as organizations seek faster detection and response.
SOC & SIEM Growth:
+33% YoY
Top spending categories:
-
XDR platforms
-
Automated threat detection
-
AI/ML-based SOC tooling
-
SOAR automation
-
Log analytics modernization
-
Threat intelligence integration
Organizations are consolidating tools to reduce complexity and improve response time.
7. Encryption, PKI & Data Security Spending
Data protection spending is rising due to compliance, cloud adoption, and ransomware.
Data Security Spend YoY:
+19%
Key spending areas:
-
TLS/SSL certificate lifecycle automation
-
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
-
Tokenization & anonymization
-
DLP solutions
-
Encrypted backups
-
Post-quantum cryptographic readiness
Post-quantum planning saw +23% YoY spending growth.
8. Cyber Insurance & Governance Spending in 2026
Cyber insurance is reshaping cybersecurity budgets.
Cyber Insurance Premium Increase:
+27% YoY
As a result, companies must invest more in:
-
MFA enforcement
-
EDR deployment
-
Patch compliance
-
Incident response planning
-
Backup validation
-
Vendor risk assessments
Governance, Risk, Compliance (GRC) Spending:
≈ 6% of total cybersecurity budget
+17% YoY growth
Security Operations (SOC) Investments & Automation Trends in 2026
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) are undergoing massive transformation in 2026. Traditional SOCs are struggling with alert overload, skill shortages, slow incident response, and fragmented tooling. As a result, organizations are aggressively modernizing their SOC infrastructure through automation, consolidation, and AI-driven analytics.
SOC Spending Growth in 2026
-
SOC modernization spending increased 33% year over year, reflecting accelerated investment in detection and response capabilities.
-
Approximately 64% of organizations upgraded their SOC tooling to improve visibility and operational efficiency.
-
Around 57% of enterprises adopted AI-driven SOC automation to reduce alert fatigue and response times.
-
Nearly 49% of companies moved from SIEM-only setups to combined SIEM and XDR platforms.
-
About 41% of organizations adopted outsourced or co-managed SOC models to address skills and staffing gaps.
Modern SOCs now depend heavily on:
-
Extended Detection & Response (XDR)
-
Automated incident response
-
Machine learning threat models
-
Unified security dashboards
-
Cloud-native analytics
-
Behavioral detection engines
-
Threat intelligence enrichment
The goal is simple: reduce detection time, reduce response time, and reduce analyst fatigue.
Why SOC Spending Spiked in 2026
1. AI-Driven Threats Increased Alert Volume
AI-generated polymorphic malware, automated phishing, and credential-stuffing bots create tens of thousands of signals per day.
SOC teams cannot manually triage this volume anymore.
2. Ransomware Attacks Became Faster and More Targeted
Ransomware attacks now move from initial access → encryption in as little as 25 minutes.
Organizations need faster detection and automated response.
3. Cloud Environments Create New Blind Spots
Cloud workloads, containers, microservices, and serverless functions generate complex traffic patterns that require advanced monitoring.
4. SOC Teams Face Analyst Shortage
SOC analysts remain one of the hardest roles to hire, pushing organizations to invest in automation.
Threat Intelligence & Dark Web Monitoring Spending (2026 Update)
Threat intelligence spending grew dramatically as organizations recognized the need to monitor:
-
Stolen credentials
-
Corporate access brokers
-
Data leaks
-
Brand impersonation kits
-
Ransomware group activities
-
Zero-day exploit markets
-
Dark web chatter targeting specific industries
2026 Threat Intelligence Spending Metrics
-
Threat intelligence spending grew 28% year over year, reflecting increased demand for proactive threat detection.
-
Approximately 62% of organizations subscribed to external threat intelligence feeds to enhance security awareness.
-
Nearly 49% of companies conducted dark web monitoring on a regular basis to detect leaked credentials.
-
Around 44% of enterprises integrated threat intelligence directly into SOC automation workflows.
-
About 53% of organizations used threat intelligence to detect and prevent identity fraud attempts.
Most Requested TI Categories in 2026
-
Credential exposure monitoring
-
Ransomware group tracking
-
Zero-day chatter analysis
-
Supply-chain threat alerts
-
Executive identity protection
-
Payment fraud monitoring
Threat intelligence is no longer optional — it’s essential for proactive security.
Impact of Ransomware on Cybersecurity Budgets (2026)
Ransomware remains the biggest budget driver for cybersecurity teams in 2026. Attacks have become:
-
Faster
-
More automated
-
More expensive
-
More destructive
-
More targeted
-
More persistent
Ransomware Impact Stats (2026)
-
Ransomware incidents increased 35% year over year, continuing a multi-year acceleration across industries.
-
The average ransom demanded grew by approximately 35% YoY, increasing financial pressure on victim organizations.
-
Average ransomware-related downtime now ranges between 20 and 30 days, extending operational disruption.
-
About 58% of ransomware attacks specifically targeted backups, aiming to disable recovery options.
-
Roughly 21% of ransomware victims were attacked again within 12 months, indicating repeat targeting risk.
-
Approximately 67% of organizations budgeted for ransomware-specific security tools in 2026.
Budget categories influenced by ransomware:
1. Backup & Disaster Recovery Modernization
-
Immutable backups
-
Offsite backups
-
Air-gapped architecture
-
Cloud DRaaS
2. Identity & Access Security
-
Privileged access management
-
Strong MFA
-
Passwordless authentication
3. Endpoint/XDR Security
-
Behavioral detection
-
Automated ransomware rollback
4. Network Segmentation
-
Reduce lateral movement
5. Incident Response Investments
-
Retainer contracts
-
Forensics teams
-
Ransom negotiation consulting
Ransomware remains the largest financial pressure forcing budget increases.
Cybersecurity Workforce Shortage & MDR Adoption (2026)
The cybersecurity talent shortage has reached a critical level globally.
Cybersecurity Workforce Gap in 2026
Impact on Spending:
Because companies cannot hire enough experts, they invest in:
-
Managed Detection & Response (MDR)
-
Co-managed SOC services
-
Outsourced incident response
-
Cloud-managed security platforms
-
Automation-first tooling
MDR (Managed Detection & Response) Growth in 2026
MDR Adoption Stats:
MDR is now a standard component of cybersecurity programs, especially for businesses that lack a fully staffed SOC.
Security Tool Consolidation Trends in 2026
Organizations have reached a breaking point with fragmented, overly complex security stacks. The average enterprise previously used:
-
75–95+ security tools
-
15–20 overlapping vendors
This caused:
-
Alert overload
-
Integration challenges
-
Higher total cost
-
Lower visibility
-
Operational strain
2026 Consolidation Statistics
-
Around 58% of organizations reduced the number of security tools to simplify operations and lower management overhead.
-
The average number of security tools declined by about 14% year over year, reflecting platform consolidation trends.
-
Approximately 49% of enterprises adopted unified security platforms such as SASE, XDR, or CNAPP.
-
Nearly 44% of companies reduced their security vendor count to improve integration and cost efficiency.
Consolidation Trends Include:
1. XDR replacing multiple endpoint & SIEM tools
A single platform for endpoint, network, identity, and cloud telemetry.
2. CNAPP replacing cloud tool fragmentation
Combining CSPM + CWPP + CIEM into one platform.
3. SASE replacing firewalls, VPNs & SD-WAN
Centralized identity-based access.
4. Vendor consolidation for cost optimization
Enterprises negotiate multi-product deals to reduce cost by 20–30%.
Consolidation improves detection accuracy, reduces alert fatigue, and lowers operational complexity — major goals for 2026 security leaders.
Cloud-Native Budget Restructuring in 2026
Cloud adoption is now the backbone of cybersecurity budgeting.
Cloud-Specific Budget Metrics
-
Around 74% of organizations increased cloud security budgets as cloud exposure and attack surfaces expanded.
-
Approximately 61% of companies now operate multi-cloud environments, increasing complexity and security investment needs.
-
Cloud security spending recorded 28% year-over-year growth, making it one of the fastest-growing security categories.
-
Nearly 17% of total cybersecurity budgets are allocated to cloud security, reflecting its strategic importance.
-
About 32% of organizations experienced breaches caused by cloud misconfigurations, driving preventive spending.
Top Cloud Security Investments in 2026
1. CSPM — Posture Management
Monitors misconfigurations and compliance drift.
2. CWPP — Workload Protection
Protects containers, microservices, Kubernetes, serverless.
3. CIEM — Entitlement Management
Prevents identity sprawl in cloud environments.
4. API Gateways & Token Security
API abuse became a top-three attack vector in 2026.
5. Cloud-native SIEM / XDR
Built for high-volume telemetry.
6. Cloud-based data encryption & HSM services
Essential for regulated sectors.
Cybersecurity Spending Forecast for 2027
Spending in 2026 reached historic highs, but projections show even stronger growth in 2027 as organizations expand cloud adoption, enforce Zero Trust, modernize SOC operations, integrate AI into security, and prepare for post-quantum cryptographic transitions.
Global Cybersecurity Spending Forecast (2027)
Estimated $250–$270 billion, fueled by:
-
Rapid AI-driven cyberattack escalation
-
Higher ransomware financial impact
-
Expansion of remote work and cloud-native environments
-
Increased regulatory pressure
-
Rising need for encrypted communication across mobile & IoT
-
Growth in digital payments, fintech and identity fraud
Projected YoY Spending Growth (2026 → 2027):
+16% to +22%, depending on sector and region.
Why Spending Continues Rising in 2027
-
AI-powered threats surpass human-scale defense capabilities.
-
Ransomware continues increasing in both severity and automation.
-
Credential theft is now the dominant attack technique globally.
-
Cloud ecosystem complexity outpaces security team capacity.
-
Cyber insurance policies enforce stricter security requirements.
Cybersecurity Technologies Expected to Dominate 2027 Budgets
Below are the areas predicted to see the largest budget increases in 2027.
1. AI-Powered Security Tools
Expected Growth: +32% YoY
AI/ML is now essential for:
-
Threat detection
-
SOC automation
-
Identity analytics
-
Attack path mapping
-
Behavioral analysis
By 2027, nearly every enterprise security stack will include AI-driven components.
2. Identity Security & Passwordless Authentication
Expected Growth: +28% YoY
Identity-first security becomes standard due to:
-
Credential theft explosion
-
MFA fatigue attacks
-
Increased phishing sophistication
-
Cloud access risk expansion
Passwordless authentication adoption is projected to exceed 55% of enterprises.
3. Cloud-Native Security: CNAPP, CSPM, CWPP, CIEM
Expected Growth: +30% YoY
Drivers include:
-
Multi-cloud deployments
-
Rapid growth of microservices
-
Serverless adoption
-
Cloud misconfiguration breaches
Organizations are consolidating cloud tools under CNAPP platforms.
4. API Security Investments
Expected Growth: +27% YoY
API attacks now rank among the top three vectors for enterprise breaches.
Investments focus on:
-
API discovery
-
Runtime protection
-
Authentication hardening
-
Abuse detection
-
Token security
5. Data Security & Post-Quantum Cryptography Planning
Expected Growth: +24% YoY
As quantum computing advances, organizations prepare by:
-
Updating PKI
-
Adopting hybrid encryption
-
Upgrading TLS policies
-
Strengthening certificate lifecycle automation
Financial, government, and healthcare sectors will lead early adoption.
6. Ransomware Defense & Incident Response Investment
Expected Growth: +25% YoY
Top focus areas:
-
Immutable backups
-
Automated containment
-
DRaaS
-
Threat intel integration
-
Rapid forensic tooling
-
MDR services
Ransomware remains the single biggest catalyst for budget increases.
Security Recommendations for 2026–27
Based on current threat trends and spending patterns, the following recommendations are essential for both enterprises and SMBs.
1. Move Toward a Full Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust should include:
-
Identity-first access
-
Device compliance checks
-
Context-aware policies
-
Micro-segmentation
-
Certificate-based authentication
-
Continuous user verification
Organizations implementing Zero Trust reduce breach probability significantly.
2. Prioritize Identity Security
Identity is the new perimeter.
Invest in:
-
Passwordless authentication
-
Strong MFA
-
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
-
Identity Governance & Administration (IGA)
-
Behavior-based authentication
Credential attacks are rising too fast to rely on passwords.
3. Modernize Cloud Security Architecture
Cloud-native environments require:
-
CSPM for continuous misconfiguration monitoring
-
CIEM for entitlement visibility
-
CWPP for workload security
-
CNAPP for unified cloud posture and workload protection
-
API protection tools
Cloud breaches increasingly come from misconfigurations and identity flaws.
4. Enhance SOC Capabilities With Automation & AI
Security operations must include:
-
Automated playbooks
-
AI-enabled triage
-
XDR for unified detection
-
SOAR platforms
-
Threat-intel-driven enrichment
Automation reduces response time and analyst burnout dramatically.
5. Harden TLS/SSL & Encryption Practices
Organizations must ensure:
-
TLS 1.2 or 1.3 everywhere
-
No deprecated cipher suites
-
No certificate bypasses
-
Automated certificate management
-
Certificate pinning for critical apps
-
Encryption of sensitive cloud workloads
Encryption hygiene is one of the highest ROI security investments.
6. Deploy Continuous Dark Web Monitoring
Dark web intelligence helps organizations track:
-
Exposed employee credentials
-
Brand impersonation kits
-
Listings targeting company networks
-
Ransomware actor chatter
-
Fresh breach dumps
This enables early incident response before attackers exploit leaked data.
7. Invest Strongly in Ransomware Defense
Key controls include:
-
Zero Trust identity
-
EDR/XDR
-
Immutable backups
-
DR testing
-
Network segmentation
-
SOC modernization
-
Rapid-response retainers
Ransomware disruptions remain financially devastating.
8. Build a Cyber-Resilient Culture
Human error still drives over 70% of breaches.
Organizations must:
-
Train employees continuously
-
Teach phishing and smishing recognition
-
Address MFA fatigue exploitation
-
Encourage secure mobile and cloud usage
-
Build strong incident reporting culture
Security awareness is not optional anymore.
Conclusion: Cybersecurity Spending in 2026 Signals a New Era of Digital Defense
Cybersecurity spending in 2026 reflects a fundamental shift:
Organizations are no longer investing reactively. They are building long-term resilience, preparing for AI-driven threats, cloud complexity, identity-focused attacks, and a rapidly expanding attack surface across mobile, IoT, and APIs.
Key takeaways:
-
Global spending reached $212–$225 billion in 2026
-
Cloud, identity, XDR, and Zero Trust dominated budgets
-
Ransomware remained the largest financial risk
-
SOC automation and MDR adoption surged due to workforce shortages
-
SMB cybersecurity spending grew faster than enterprise spending
-
2027 spending will exceed $250 billion
Cybersecurity is now a board-level priority and a core requirement for digital transformation. Organizations that delay modernizing their security stack will face greater operational, financial, and reputational risks as cyber threats continue evolving.
FAQ
1. How much is the global cybersecurity market worth in 2026?
Approximately $212–$225 billion, depending on industry classification.
2. Which regions spent the most on cybersecurity in 2026?
North America leads, followed by Europe and APAC — which is the fastest-growing region.
3. What industries invested the most in cybersecurity?
Finance, healthcare, government, SaaS/technology, and manufacturing.
4. What category grew the fastest in 2026?
Cloud security, identity security, XDR/SOC modernization, and API protection.
5. Why did ransomware significantly influence budgets?
Ransomware attacks increased ~35% YoY and caused severe downtime and financial losses.
6. How are SMBs approaching cybersecurity budgets?
SMBs increased their security spending by ~21% due to rising attacks and insurance requirements.
7. What is the role of AI in cybersecurity spending?
AI drives both attacks and defenses, leading to a sharp increase in AI-powered SOC, analytics, and identity tools.
8. What will cybersecurity spending look like in 2027?
Projected to reach $250–$270B, driven by AI threats, cloud adoption, and Zero Trust expansion.
REFERENCE
The content in this report is based on aggregated insights from:
-
Global cybersecurity market forecasts (2024–2025)
-
Industry financial reports on IT and security spending
-
Ransomware incident response trend reports
-
Cloud security posture management insights
-
Identity and access management adoption surveys
-
Threat intelligence vendor annual overviews
-
SOC modernization and automation research
-
Public analyses of cyber insurance requirements
-
Workforce shortage data from international cybersecurity workforce studies
-
Dark web marketplace monitoring and credential exposure analyses
Disclaimer:
The content published on CompareCheapSSL is intended for general informational and educational purposes only. While we strive to keep the information accurate and up to date, we do not guarantee its completeness or reliability. Readers are advised to independently verify details before making any business, financial, or technical decisions.


