Generative AI has moved from experimental to essential in just a few short years. In 2025, it’s no longer a futuristic concept—it’s powering everything from personalized marketing and automated code generation to synthetic media, customer service, and product design. As adoption surges across industries, generative AI is reshaping workflows, business models, and even regulatory frameworks.
The global conversation is no longer just about what generative AI can do, but how it’s being used right now—and what that means for productivity, ethics, jobs, and innovation.
Generative AI is a form of artificial intelligence that creates new content—such as text, images, videos, or code—based on the data it has learned from. Examples include ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Sora.
In this post, we break down the most important generative AI statistics for 2025—covering growth trends, adoption rates, industry-specific insights, cost savings, and risks. Whether you’re a tech leader, marketer, developer, or investor, these numbers tell the real story of where GenAI stands today—and where it’s heading.
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content—such as text, images, audio, video, and code—based on the data it has been trained on. Instead of just analyzing or categorizing information, generative AI produces original outputs that mimic human creativity and language.
Examples of Generative AI Tools
Here are some of the most popular generative AI systems in use today:
-
ChatGPT – generates human-like responses to text prompts (e.g., conversations, writing, analysis)
-
DALL·E – creates detailed images and art from written descriptions
-
Sora – generates short, realistic video clips from text prompts
-
GitHub Copilot – helps developers write code with AI suggestions
-
Runway – used by video editors and designers to generate or enhance visual content
How Is Generative AI Different from Traditional AI?
| Traditional AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|
| Analyzes existing data | Creates new content from patterns in data |
| Classifies, predicts, or recommends | Writes, draws, designs, codes, or talks |
| Example: fraud detection, product recommendations | Example: writing articles, designing images, generating videos |
Traditional AI focuses on decision-making and automation based on predefined rules or data patterns, while generative AI is about creation and innovation, often with outputs that appear to be human-made.
Common Use Cases of Generative AI (2025)
Generative AI is now used across nearly every industry. Key applications include:
-
Content Creation: blog writing, social media posts, marketing copy
-
Coding & Development: auto-completing code, debugging, documentation
-
Customer Support: AI chatbots that handle complex queries with context-aware responses
-
Design & Media: creating logos, UI designs, promotional videos, game assets
-
Education: tutoring, lesson planning, content summarization
-
Entertainment: script writing, character generation, voiceovers
Key Generative AI Stats You Should Know (2025)
Generative AI has gone from hype to hard numbers. In 2025, adoption has accelerated across sectors, delivering measurable gains in productivity, speed, and cost-efficiency. These statistics illustrate just how deeply generative AI is transforming business operations and workflows worldwide.
1. Business Adoption of Generative AI
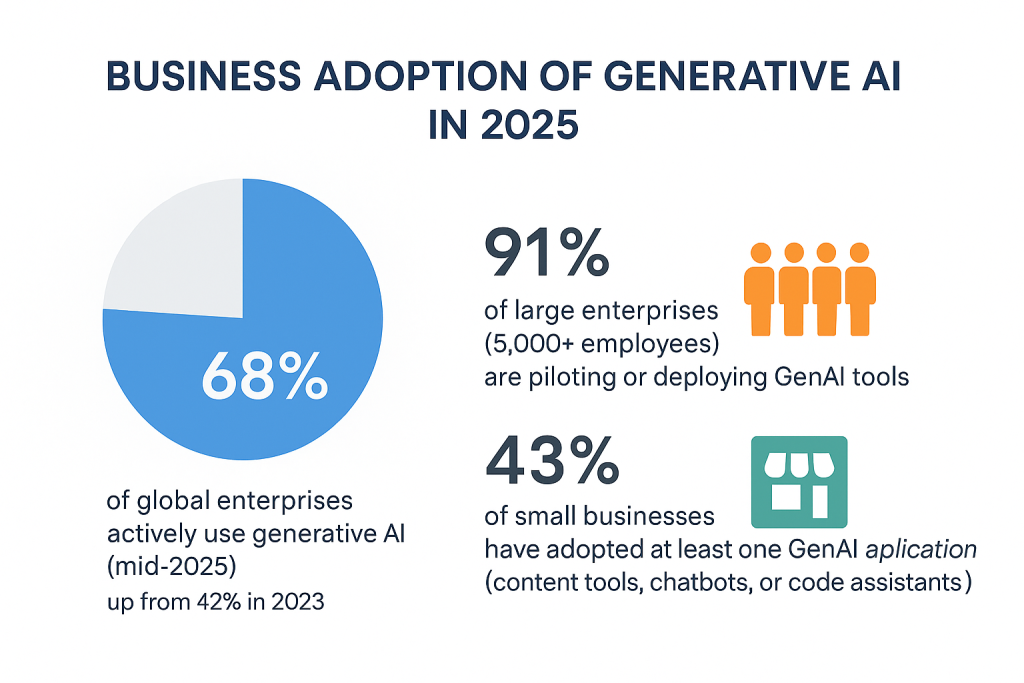
As of mid-2025, 68% of global enterprises report active use of generative AI in at least one business function, according to McKinsey. That’s up from 42% in 2023.
-
91% of large enterprises (5,000+ employees) are piloting or deploying GenAI tools
-
43% of small businesses have adopted at least one GenAI-based application (content tools, chatbots, or code assistants)
2. Time Saved in Content Creation & Marketing
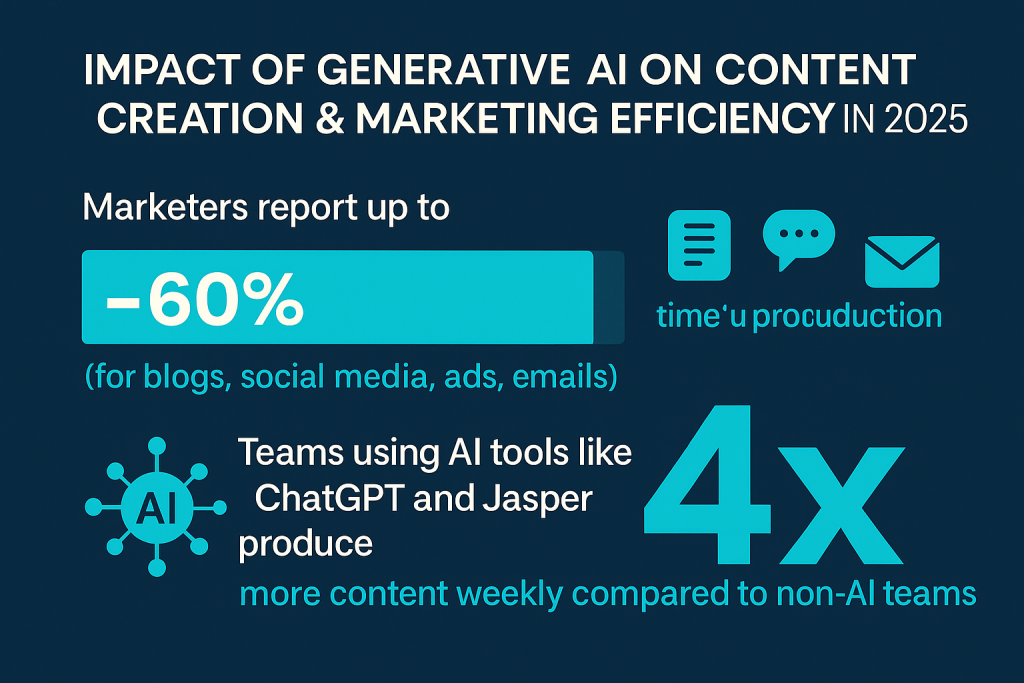
Generative AI is helping teams move faster:
-
Marketers using GenAI report up to 60% reduction in content production time, especially for blogs, social media, ad copy, and email campaigns
-
Teams using tools like ChatGPT and Jasper generate 4x more content per week compared to those without AI support
3. GenAI in Customer Service Operations
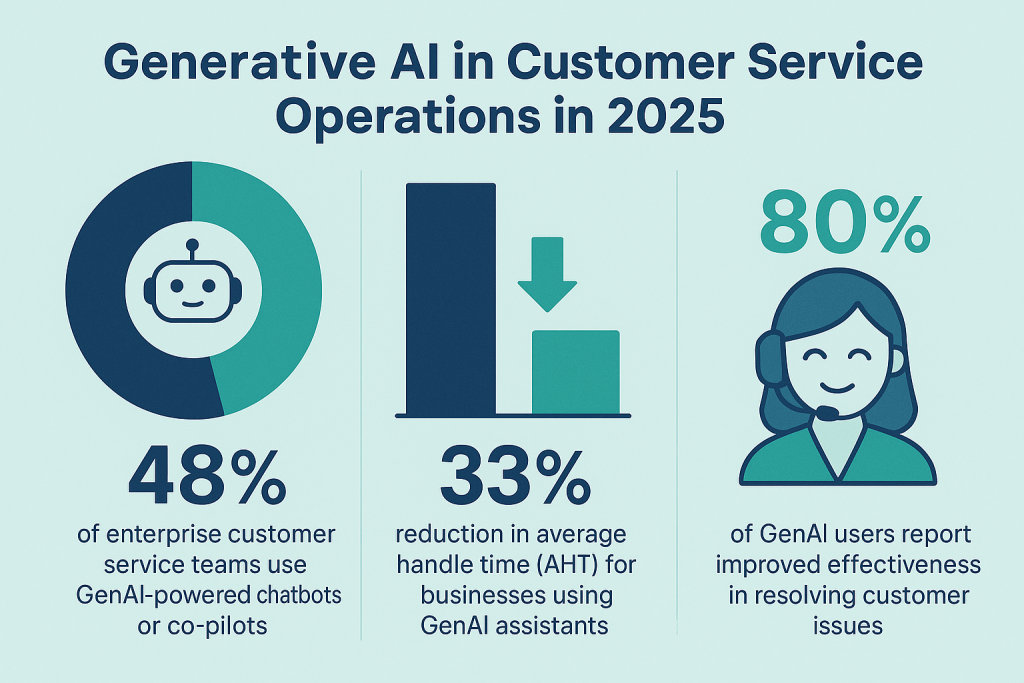
Customer-facing teams are among the early beneficiaries of GenAI:
-
48% of enterprise customer service departments now use GenAI-powered chatbots or co-pilots
-
Businesses using GenAI assistants have seen a 33% drop in average handle time (AHT)
-
80% of GenAI users in support roles say the technology helps resolve customer issues more effectively
4. ROI from Generative AI Integration
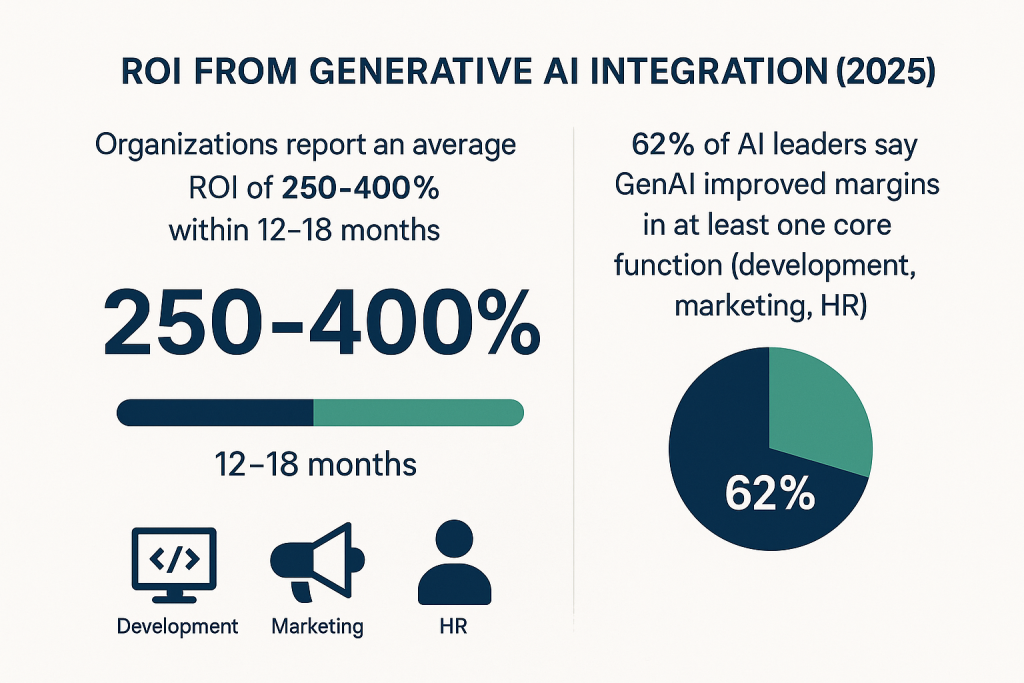
According to Accenture, organizations implementing generative AI at scale report:
-
An average ROI of 250–400% within 12–18 months
-
62% of AI leaders say GenAI improved margins in at least one core function (e.g., development, marketing, HR)
5. Operational Cost Reduction & Development Efficiency
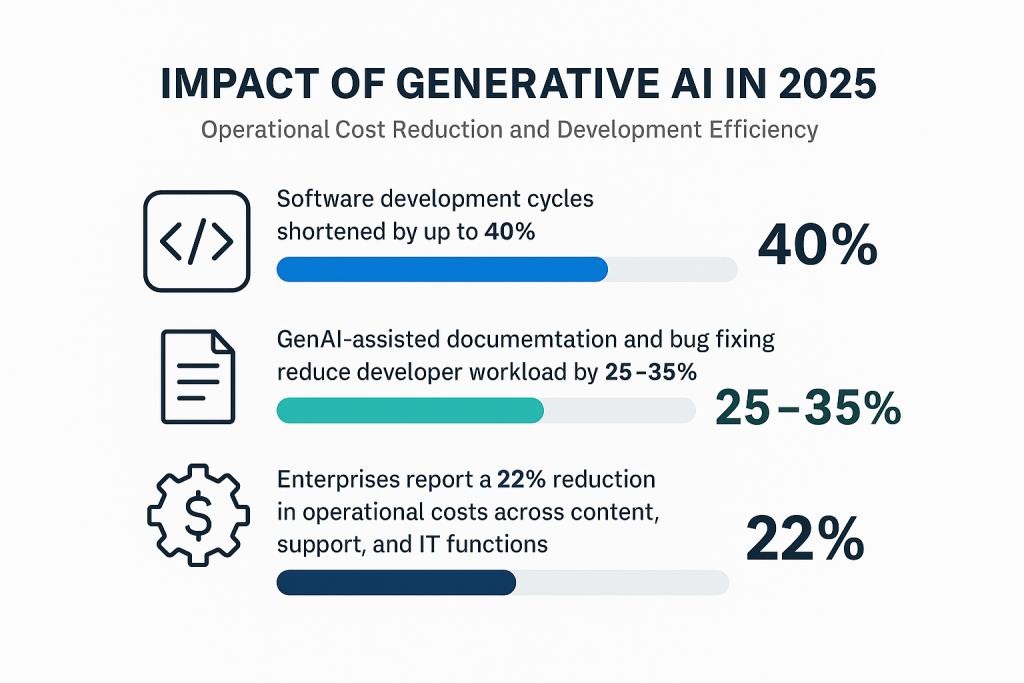
Generative AI also delivers meaningful savings on the backend:
-
Software development cycles are now up to 40% shorter thanks to AI pair programming tools like GitHub Copilot
-
GenAI-assisted documentation and bug fixing reduces developer workloads by an estimated 25–35%
-
Enterprises report a 22% reduction in operational costs when GenAI is integrated across content, support, and IT functions
6. Productivity & Workforce Augmentation
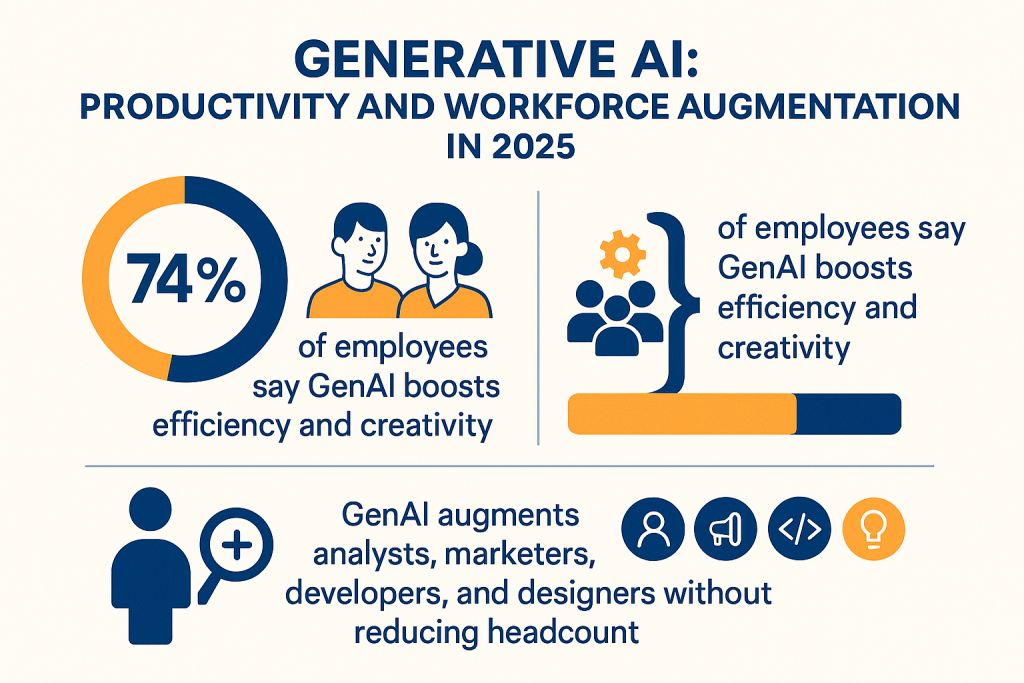
GenAI is not replacing workers—it’s amplifying them:
-
74% of employees using GenAI say it helps them perform tasks more efficiently or creatively
-
Teams that integrate GenAI tools into daily workflows see a 32% average increase in task completion speed
-
In knowledge work settings, GenAI augments the output of analysts, marketers, developers, and designers without reducing headcount
Key Insight
Generative AI isn’t just a trend—it’s a measurable driver of efficiency, speed, and competitive advantage. From frontline chatbots to backend code generation, businesses across the globe are using it to do more, faster—and smarter.
Industry-Wise Adoption of Generative AI (2025)
Generative AI adoption is expanding rapidly across sectors—not just in tech-forward industries, but also in highly regulated fields like finance, healthcare, and government.
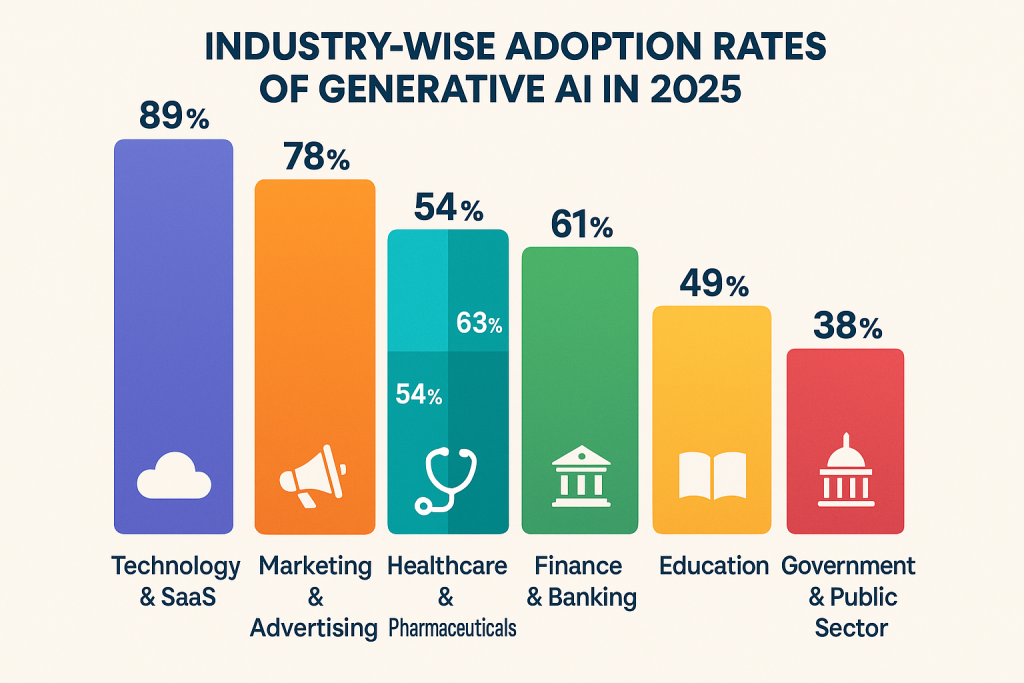
Here’s a breakdown of how different industries are leveraging GenAI in 2025 to improve efficiency, customer experience, and innovation.
1. Technology & SaaS
Adoption Rate: 89% of SaaS and tech companies report active use of generative AI tools.
Use Cases:
-
Code generation (e.g., GitHub Copilot, Tabnine)
-
Automated testing and documentation
-
Product design ideation using AI models
-
AI-assisted customer support platforms
Impact: Dev cycles are shortened by up to 40%, and teams report increased productivity in engineering, QA, and UI/UX functions.
2. Marketing & Advertising
Adoption Rate: 78% of marketing firms and departments now use GenAI tools daily.
Use Cases:
-
Content generation (blogs, ad copy, emails, landing pages)
-
A/B testing and copy variant creation
-
Visual asset design via tools like DALL·E and Midjourney
-
Campaign personalization at scale
Impact: Marketers report up to 60% faster campaign production and a 2–3x increase in content volume, without additional hires.
3. Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
Adoption Rate: 54% of healthcare organizations and 63% of pharma companies use GenAI in non-clinical operations.
Use Cases:
-
Medical documentation and transcription
-
Drug discovery modeling using large-scale AI simulations
-
Patient interaction via AI chatbots and symptom checkers
-
Training content for medical staff and patients
Impact: GenAI reduces administrative workload by up to 30% and accelerates early-stage R&D processes in pharma.
4. Finance & Banking
Adoption Rate: 61% of financial institutions report some form of GenAI integration.
Use Cases:
-
Automated customer service via chatbots and voice assistants
-
Report generation and financial analysis summaries
-
Fraud pattern recognition combined with large language models
-
Client-facing communication tools
Impact: Financial firms have cut customer service resolution times by 35%, while AI-generated reports save analysts 8–10 hours weekly.
5. Education
Adoption Rate: 49% of educational institutions and edtech companies use GenAI tools in 2025.
Use Cases:
-
AI tutors and personalized learning assistants
-
Lesson plan and curriculum creation
-
Assessment auto-grading and feedback generation
-
Language translation and accessibility tools
Impact: Educators report a 40% reduction in administrative load and more inclusive learning environments through AI-enhanced teaching tools.
6. Government & Public Sector
Adoption Rate: 38% of governments and agencies have implemented GenAI pilots or public-facing tools.
Use Cases:
-
Policy summary generation and legislative drafting support
-
Citizen service chatbots and automated response systems
-
Data insights for public health, transport, and safety
-
Multilingual support in digital portals
Impact: Governments are reducing document processing times and expanding citizen engagement through AI-driven digital assistants.
Benefits & Measurable Impacts of Generative AI
Generative AI delivers speed, accuracy, creativity, and scalability—often all at once. Whether used to write content, code software, resolve tickets, or brainstorm ideas, it is redefining how work gets done across roles and industries.
Generative AI is more than just a tech trend—it delivers real, quantifiable results across functions like content creation, coding, support, and business strategy. Here are the key benefits companies are seeing in 2025:
1. Faster Content Production at Scale
Generative AI accelerates every step of content creation—ideation, drafting, editing, and publishing.
Key Impacts:
-
60% faster content workflows for marketing teams
-
3–5x more content output per month without adding headcount
-
Improved SEO rankings due to consistent, high-volume publishing
-
Enhanced personalization in blog posts, emails, and landing pages
Example: Brands using tools like Jasper, ChatGPT, or Copy.ai can generate entire multi-channel campaigns in days instead of weeks.
2. Code Generation & Debugging Efficiency
In software development, GenAI acts as a virtual coding assistant, helping developers write, test, and fix code faster.
Key Impacts:
-
40–45% reduction in development cycles using AI pair programmers (e.g., GitHub Copilot, Replit Ghostwriter)
-
Fewer bugs at launch due to real-time code suggestions and testing
-
25–30% increase in developer productivity across teams
Example: Teams report saving up to 10 hours per week on boilerplate code, unit tests, and documentation.
3. Customer Service Automation & Personalization
Generative AI enhances both speed and quality in customer support interactions.
Key Impacts:
-
24/7 support availability via GenAI chatbots and assistants
-
33% lower average handle times (AHT) and faster resolutions
-
Improved customer satisfaction and retention
-
Real-time multi-language support for global users
Example: E-commerce brands use AI chat to resolve order issues, recommend products, and collect feedback—without human agents.
4. Creative Idea Generation & Brainstorming
GenAI serves as an intelligent brainstorming partner for product teams, marketers, writers, and designers.
Key Impacts:
-
Faster ideation cycles with high-quality idea prompts
-
Generation of variations for campaigns, product names, taglines, and visuals
-
Exploration of “what-if” concepts and market simulations
Example: Creative teams use AI to test 50+ ad headline variations or prototype new product concepts in a single afternoon.
5. Internal Knowledge Management & Automation
GenAI is transforming how organizations manage and surface internal knowledge.
Key Impacts:
-
AI-powered Q&A systems that instantly retrieve answers from internal docs
-
Automated SOPs, training materials, and onboarding guides
-
Lower reliance on siloed knowledge or manual documentation
-
Improved decision-making with summarized reports and insights
Example: Enterprises use GenAI to power internal copilots that answer employee queries about policies, tools, or historical data.
Top Use Cases of Generative AI in 2025
Generative AI has moved from experimentation to execution, playing a strategic role across industries. From automated content to advanced security applications, these are the most impactful and widely adopted use cases in 2025.
1. AI-Generated Content (Text, Image, Video)
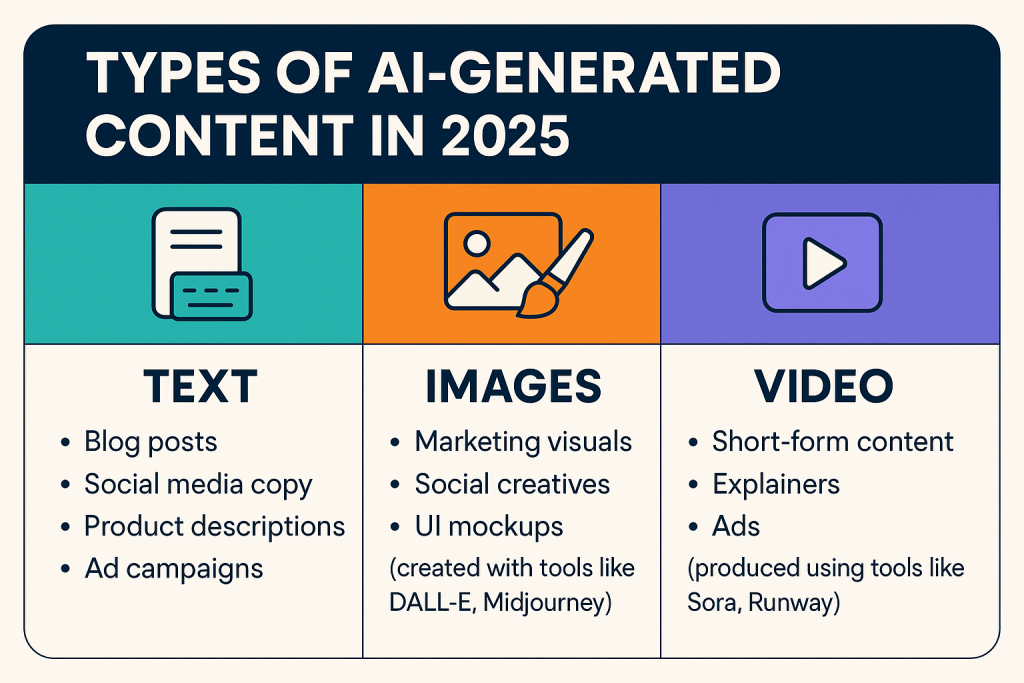
Generative AI powers a vast array of creative workflows:
-
Text: Blog posts, social media copy, product descriptions, ad campaigns
-
Images: Marketing visuals, social creatives, UI mockups (via DALL·E, Midjourney)
-
Video: Short-form content, explainers, ads using tools like Sora and Runway
Why it matters: Brands scale their content production 3–5x faster, enabling hyper-personalization and faster go-to-market strategies.
2. Automated Reporting & Documentation
GenAI tools streamline time-consuming documentation and reporting tasks in business and IT environments:
-
Financial reporting summaries
-
Business intelligence (BI) dashboards with natural language insights
-
Technical documentation, API docs, and user guides
Why it matters: Reduces manual labor by up to 50% and improves documentation consistency across teams.
3. Virtual Assistants & Chatbots
AI-powered conversational agents are improving both internal productivity and external customer service:
-
Employee co-pilots that assist with HR, IT, and compliance queries
-
Customer support bots that resolve queries and escalate intelligently
-
Voice assistants that transcribe, summarize, and automate workflows
Why it matters: GenAI virtual agents reduce support workloads while delivering 24/7 multilingual coverage.
4. Product Design & Prototyping
Generative AI tools now assist in early-stage product ideation and iteration:
-
UI/UX mockups generated from text prompts
-
Product concept testing and visual generation
-
Design collaboration platforms enhanced with GenAI suggestions
Why it matters: Teams accelerate product development by quickly validating ideas and reducing reliance on traditional design cycles.
5. Cybersecurity & Threat Detection
Security teams use GenAI to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats:
-
Anomaly detection across logs and systems
-
Threat report summaries and automated incident documentation
-
Simulated phishing attacks and training content for employee readiness
Why it matters: GenAI enhances real-time monitoring and response, reducing breach detection time and improving cyber resilience.
Key Insight
In 2025, generative AI is no longer a niche tool—it’s embedded into core business processes. From marketing to security, its use cases demonstrate a clear path to speed, intelligence, and scalable growth.
6. Rise in AI-Generated Phishing & Social Engineering
Cybercriminals now use GenAI to craft more convincing phishing emails, fake documents, and deepfake content.
Risks:
-
Higher success rates in social engineering attacks
-
Voice cloning and impersonation in vishing scams
-
Automation of large-scale phishing campaigns
Mitigation: Invest in advanced email filtering, employee training, and real-time threat detection powered by AI.
7. Regulatory Pressures & AI Ethics
Global governments are increasing scrutiny on how AI is developed, deployed, and used.
Risks:
-
Fines for non-compliance with emerging AI laws (e.g., EU AI Act)
-
Ethical concerns over bias, fairness, and discrimination
-
Reputation damage from unethical AI applications
Mitigation: Build AI ethics guidelines into your governance model, and stay updated on local and international AI regulations.
Security Spotlight: GenAI in Phishing & Deepfakes
Generative AI is transforming cybersecurity—not just for defenders, but also for attackers. In 2025, a growing number of cyber threats are AI-generated, from deepfake audio to hyper-personalized phishing emails.
AI-Generated Phishing on the Rise

According to 2025 threat intelligence reports, there’s been a 39% year-over-year increase in phishing emails created using generative AI.
Why it’s dangerous:
-
Attackers use LLMs like ChatGPT clones or custom-trained models to craft highly convincing, typo-free emails
-
Messages can impersonate executives, vendors, or IT admins with contextual precision
-
Language localization allows attackers to target victims in multiple regions more effectively
Example: In early 2025, a global bank reported a breach after employees received emails from a “CFO” requesting urgent document access—entirely generated and translated by AI tools.
Deepfakes Enter Corporate Threat Landscape
Deepfake technology has matured to the point where voice cloning and video impersonation can be executed at scale.
Real-world risks:
-
CEO voice cloning scams via WhatsApp or phone calls
-
Video messages mimicking HR personnel to trick employees
-
Synthetic identity fraud using fake KYC videos
Example: A European fintech company was defrauded of $4.3 million after a senior executive approved a fake transaction—via a deepfaked Zoom call.
Tools Used by Threat Actors
Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging:
-
Open-source text generation models trained on spear-phishing datasets
-
Voice AI tools like ElevenLabs and open-access voice cloning libraries
-
Deepfake video apps originally meant for entertainment, now used for fraud
-
PhaaS (Phishing-as-a-Service) platforms that offer ready-made AI phishing kits on the dark web
How Businesses Are Responding
Leading organizations are shifting from prevention to AI-enhanced detection and response strategies:
-
AI-based email security systems trained to spot synthetic content, inconsistencies, and prompt injection techniques
-
Real-time behavioral biometrics to verify identity beyond voice or video
-
Company-wide phishing simulations with GenAI-created scenarios
-
Clear policies prohibiting urgent fund transfers without secondary verification
-
Training employees to spot deepfake cues (lighting, lip-sync errors, audio artifacts)
Key Takeaway
Generative AI is now both a cybersecurity threat and a defense tool. Organizations must embrace adaptive threat intelligence and train teams to stay vigilant—because AI-enabled attacks don’t just scale, they evolve.
The Future of Generative AI: What’s Next?
Generative AI is evolving rapidly, pushing the boundaries of what machines can create and how businesses interact with technology. Looking beyond 2025, several key trends and challenges are set to shape the next phase of AI innovation.
1. Natural Multimodal Agents
The future lies in AI systems that seamlessly combine text, images, video, and voice—creating richer, more intuitive user experiences.
-
These multimodal agents will understand and generate multiple types of media within a single interaction.
-
Imagine asking an AI assistant to draft a report, create accompanying graphics, and even record a video summary—all in one seamless workflow.
2. AI-Personalized Experiences at Scale
Generative AI will enable mass personalization across marketing, education, entertainment, and customer service.
-
Brands will deliver unique content tailored to individual preferences in real time.
-
Education platforms will create customized lesson plans based on learner progress and style.
-
Entertainment and gaming will leverage AI to produce adaptive narratives and characters personalized for each user.
3. Enterprise-Grade AI Platforms
Businesses will demand robust, secure, and scalable AI solutions that integrate easily with existing infrastructure.
-
Expect growth in cloud-based AI platforms offering end-to-end pipelines for data ingestion, model training, deployment, and monitoring.
-
Emphasis on privacy-preserving AI, compliance, and explainability will become standard features.
4. Open vs. Closed AI Ecosystems
The AI community faces ongoing debate over open-source versus proprietary models.
-
Open AI ecosystems foster collaboration, transparency, and rapid innovation but may pose security risks.
-
Closed ecosystems offer controlled environments with better security and compliance but may limit customization and accessibility.
-
Hybrid models will likely emerge, balancing openness with governance.
5. Regulation Outlook
Regulators worldwide are stepping up efforts to govern AI development and deployment responsibly.
-
Expect stricter data privacy laws, AI ethics mandates, and transparency requirements.
-
The EU’s AI Act and similar frameworks will influence global standards.
-
Businesses must prepare for ongoing compliance challenges and incorporate ethical AI principles into their strategies.
The next frontier of generative AI promises powerful, integrated, and personalized experiences—but also demands careful stewardship. Organizations that proactively embrace innovation, ethics, and regulation will lead the way in this transformative era.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Generative AI (2025)
What is generative AI?
Generative AI is artificial intelligence that creates new content—such as text, images, videos, or code—based on patterns learned from training data.
How is generative AI different from traditional AI?
Traditional AI focuses on analyzing data and making predictions, while generative AI creates original content by generating new outputs from learned patterns.
What are the common uses of generative AI in 2025?
Generative AI is widely used for content creation, coding assistance, customer support chatbots, product design, and cybersecurity threat detection.
Which industries are adopting generative AI the fastest?
Technology, marketing, healthcare, finance, education, and government sectors lead in adopting generative AI tools and applications.
What are the main benefits of generative AI for businesses?
Generative AI helps businesses speed up content production, improve customer service, enhance creativity, automate documentation, and increase productivity.
What risks are associated with generative AI?
Key risks include AI hallucinations (factual errors), data privacy concerns, over-reliance by users, AI-powered phishing attacks, and regulatory compliance challenges.
How can organizations protect against AI-generated phishing attacks?
Organizations can use AI-powered email filtering, conduct regular employee training, implement multi-factor authentication, and adopt advanced threat detection technologies.
What is the future outlook for generative AI?
Future trends include multimodal AI agents combining text, images, and voice, personalized AI experiences at scale, enterprise-grade AI platforms, and evolving AI regulations worldwide.
The data is clear—generative AI is no longer a niche experiment but a transformative force reshaping how businesses operate and innovate. With 68% of enterprises adopting GenAI tools, time savings of up to 60% in content creation, and a reported 250–400% ROI on AI investments, the impact is measurable and accelerating.
Generative AI is evolving from a buzzword into foundational infrastructure. It’s becoming embedded across workflows—from coding and customer service to design and cybersecurity—amplifying human creativity and productivity at scale.
As adoption spreads across industries like technology, healthcare, finance, and government, organizations that harness generative AI responsibly will gain a crucial competitive edge. Embracing this AI-first future means investing in both cutting-edge tools and ethical frameworks, ensuring innovation thrives without compromising trust or security.
The future belongs to those who can seamlessly integrate generative AI into their core operations—turning data into insight, ideas into action, and AI potential into lasting value.
Disclaimer:
The content published on CompareCheapSSL is intended for general informational and educational purposes only. While we strive to keep the information accurate and up to date, we do not guarantee its completeness or reliability. Readers are advised to independently verify details before making any business, financial, or technical decisions.


