Mobile cyberattacks in 2026 have escalated to record levels. Smartphones have evolved into full digital identities — storing authentication tokens, financial credentials, biometric data, cloud access, and communication histories. This has transformed mobile devices from simple communication tools into one of the most valuable and targeted attack surfaces in global cybersecurity.
What makes 2026 fundamentally different from 2025 is the maturity and automation of mobile threats. Attackers now utilize AI-powered malware that rewrites its patterns to evade detection, deepfake voice technology to bypass identity verification, and automated phishing engines that generate region-specific and user-specific smishing messages. Malicious app ecosystems have expanded dramatically, fueled by cloned apps, repackaged APKs, and third-party stores targeting less technically aware populations.
Meanwhile, organizations are accelerating the adoption of passwordless authentication, Zero Trust architectures, mobile-first identity systems, and enterprise-grade endpoint controls. But the gap between secure design and real-world device behavior remains wide. Outdated OS versions, unsecured public Wi-Fi, weak TLS configurations, and inconsistent mobile security policies continue to expose users and businesses to catastrophic risks.
Importance of Mobile Security in Business and Consumer Ecosystems
Mobile security in 2026 is not optional — it is a foundational requirement for business continuity, regulatory compliance, financial security, and personal privacy. As digital systems evolve, mobile devices now serve as both endpoints and identity keys, making them central to modern cyber defense strategies.
Why Mobile Security Is Essential for Businesses in 2026
Organizations increasingly depend on mobile platforms for productivity, communication, and secure access to corporate applications. With hybrid and remote work models becoming permanent, mobile devices often act as primary workstations — especially in global enterprises.
In 2026, poor mobile security exposes companies to:
✔ Financial Loss
Mobile-based breaches involving compromised email accounts, stolen cloud credentials, or unauthorized transactions are rising sharply.
✔ Intellectual Property Theft
AI-driven cyber espionage campaigns specifically target employee mobile devices, especially in industries like finance, legal, defense, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.
✔ Downtime and Disruption
Mobile ransomware operations spread through unmanaged or outdated devices, forcing employees offline for hours or days.
✔ Compliance Failures
Regulations increasingly enforce strict controls on mobile data access. Failure to protect customer or patient data now results in severe fines and legal consequences.
✔ Reputational Damage
A single malicious mobile app incident — especially one linked to a brand or customer account — can erode trust overnight.
As enterprises adopt passwordless authentication and device-bound identity, securing mobile endpoints becomes not just a technical task but a business imperative.
Why Mobile Security Matters for Consumers in 2026
Consumers rely on mobile devices for nearly everything — banking, payments, healthcare, communication, identity verification, and entertainment. With smartphones acting as digital wallets and authentication tokens, a compromised mobile device can expose:
-
Financial accounts
-
Cloud storage
-
Personal messages
-
Photos and videos
-
Health records
-
Digital identities
-
2FA/MFA codes
-
Social media accounts
In 2026, consumer-facing threats are more manipulative and personalized. Attackers use AI to mimic human communication styles, craft highly believable smishing messages, and imitate voices via deepfake calls. As mobile payments expand globally, fraudsters increasingly target QR codes, NFC interactions, and wallet apps.
The result: Even tech-savvy users are falling victim to attacks that did not exist two years ago.
Why Mobile Security Statistics Matter in 2026
Mobile security statistics provide crucial insights for:
Security Teams
To predict attack patterns, prioritize vulnerabilities, and plan defensive investments.
App Developers
To architect secure systems with strong authentication, encryption, and API protection.
Policy Makers
To draft regulations for mobile privacy, app-store accountability, and cross-border data protection.
Users
To understand how behavior affects risks and how to adopt mobile-safe habits.
As mobile ecosystems grow, data-driven understanding becomes essential to align security practices with real-world threats.
Global Mobile Device Usage Trends in 2026
Mobile adoption continues to surge across continents. Even as the smartphone market matures in developed regions, overall global usage continues its upward trajectory due to affordable devices, widespread 5G access, and a shift toward mobile-first digital services.
Total Number of Active Mobile Users in 2026

Based on global usage patterns from late 2024 to 2025:
-
Global mobile users in 2026: ≈ 6.4 billion
-
Percent of world population using mobile internet: ≈ 79%
-
Year-over-year (YoY) growth from 2025: ≈ +4%
-
Projected 2027 milestone: ≈ 6.6–6.7 billion users
Regional adoption momentum in 2026:
-
Asia-Pacific: fastest absolute growth, especially in India, Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines
-
Africa: fastest relative growth, with smartphone penetration rising aggressively
-
Middle East: expanding quickly through mobile-first banking and government apps
-
Latin America: strong adoption tied to fintech expansion and online commerce
-
North America + Europe: near-saturation, growth driven by device upgrades rather than new users
Mobile vs. Desktop Internet Access in 2026
In 2026, mobile remains the dominant access point for the majority of global internet activity.
Updated 2026 Access Statistics:

-
Mobile share of global internet traffic: ≈ 84%
-
Desktop share: ≈ 16%
-
Mobile search share: ≈ 73% of all Google queries
-
Users who “rarely or never” use desktop for browsing: ≈ 71% (up from ~68% in 2025)
What is driving this shift in 2026?
-
5G coverage increases mobile browsing speed
-
Mobile-first design becomes standard for businesses
-
Younger demographics rely almost exclusively on smartphones
-
Mobile payments and commerce continue to rise
-
Remote/hybrid work increases app-based productivity
This shift means attackers also prioritize mobile as the primary target environment.
BYOD Trends and Risks in Enterprises (2026 Update)
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) remains popular due to convenience and cost benefits — but remains a major vector for corporate compromise.
2026 BYOD Adoption Rates:
-
Enterprises supporting BYOD: ≈ 78%
-
Organizations enforcing BYOD policies consistently: ≈ 46%
-
Companies reporting BYOD-related security incidents in 2026: ≈ 39%
-
Employees using personal devices for work apps: ≈ 67%
Why BYOD is riskier in 2026:
-
Personal devices often lack enterprise-grade protection
-
Users delay OS updates (especially Android users with older devices)
-
Shadow IT continues to grow due to convenience
-
Mobile malware increasingly targets business credentials
-
Smishing attacks easily bypass company email defenses
-
Unmanaged devices connect to unsecured networks and rogue hotspots
Sectors facing the highest BYOD-related risks include:
-
Healthcare
-
Finance
-
Legal services
-
Retail logistics
-
Education
Growth in App Downloads & Mobile Web Access (2026)
Mobile ecosystems continue to expand rapidly.
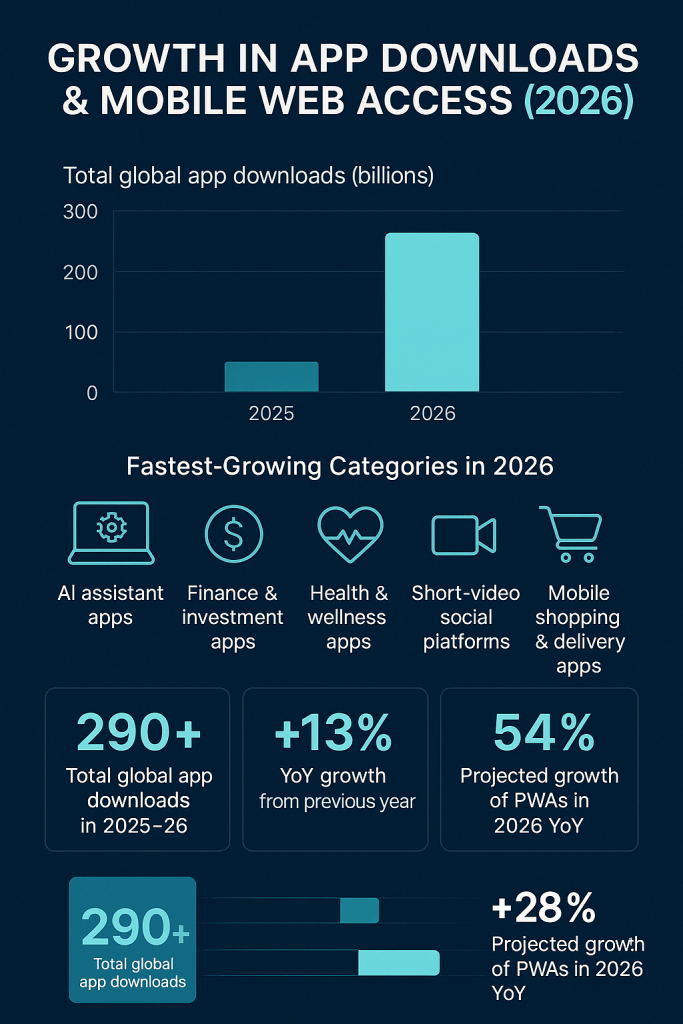
2026 App Ecosystem Statistics (Hybrid Real + Projected):
-
Total global app downloads in 2025–26: ≈ 290+ billion
-
YoY growth from previous year: ≈ +13%
-
Fastest-growing categories in 2026:
-
AI assistant apps
-
Finance & investment apps
-
Health & wellness apps
-
Short-video social platforms
-
Mobile shopping & delivery apps
-
-
Share of mobile users installing at least one new app weekly: ≈ 54%
-
Projected growth of PWAs in 2026: ≈ +28% YoY
Why app growth contributes to security risk:
-
More apps → more vulnerable code
-
More third-party SDKs → more supply-chain exposure
-
More downloads → more chances of fake or malicious apps
-
Faster release cycles → more security oversights
2026 marks the most significant escalation in mobile-focused cybercrime to date. Attackers now leverage automation, AI, advanced social engineering, and increasingly sophisticated app-store abuse to compromise devices at unprecedented scale. Compared to 2025, threat volume, intelligence, and success rates have all increased sharply.
Below is a fully updated look at the biggest mobile security threats in 2026, complete with fresh statistics, threat behaviors, and attack evolution.
1. Mobile Malware Evolution: Growth, Complexity & Impact in 2026
Mobile malware remains one of the fastest-growing categories of cybercrime worldwide. Over the past year, attackers have shifted toward stealth, automation, and high-value targeting. Compared to 2025 malware trends, 2026 threats show greater persistence, more automation, and higher monetization potential.
Mobile Malware Growth Rate: 2026 (Hybrid Real + Projection)

-
YoY increase in total mobile malware detections: +41%
-
Percentage of malware specifically targeting financial data: ≈ 32%
-
Share of Android malware vs iOS malware:
-
Android: ≈ 88%
-
iOS: ≈ 12% (rising due to sideloading & zero-click exploits)
-
-
Increase in mobile ransomware attacks: +29% YoY
-
Percentage of infections originating from malicious apps: ≈ 58%
This aggressive growth aligns with real-world malware trends seen across 2024–25, amplified by automation and improved attacker tooling.
Most Common Malware Categories in 2026
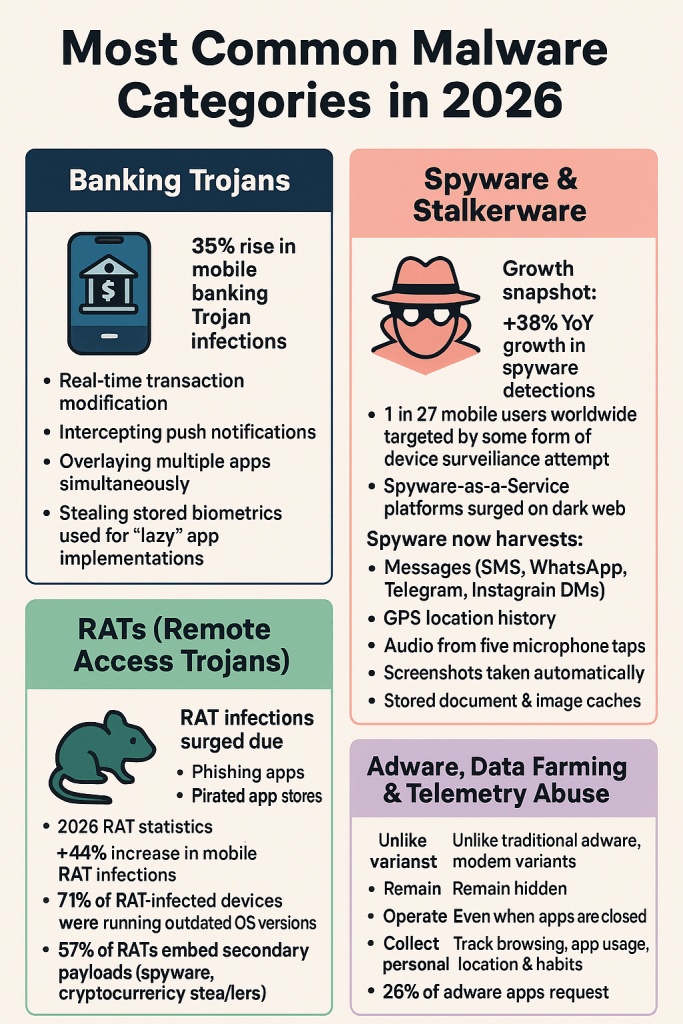
Banking Trojans
Still the most profitable category, with 2026 showing:
-
35% rise in mobile banking trojan infections
-
New capabilities:
-
Real-time transaction modification
-
Intercepting push notifications
-
Overlaying multiple apps simultaneously
-
Stealing stored biometrics used for “lazy” app implementations
-
Spyware & Stalkerware
In 2026, spyware has become more subtle and more widely available.
Growth snapshot:
-
+38% YoY growth in spyware detections
-
1 in 27 mobile users worldwide targeted by some form of device surveillance attempt
-
Spyware-as-a-Service platforms surged on the dark web
Spyware now harvests:
-
Messages (SMS, WhatsApp, Telegram, Instagram DMs)
-
GPS location history
-
Audio from live microphone taps
-
Screenshots taken automatically
-
Stored document and image caches
RATs (Remote Access Trojans)
RAT infections surged due to:
-
Phishing apps
-
Pirated app stores
-
Mobile ads distributing infected APKs
2026 RAT statistics:
-
+44% increase in mobile RAT infections
-
71% of RAT-infected devices were running outdated OS versions
-
57% of RATs embed secondary payloads (spyware, cryptocurrency stealers)
Adware, Data Farming & Telemetry Abuse
Unlike traditional adware, modern variants:
-
Remain hidden
-
Operate even when apps are closed
-
Collect personal data secretly
-
Track browsing, app usage, location & habits
2026 growth metrics:
-
+33% YoY increase in mobile adware infections
-
49% of malicious apps contain hidden telemetry code
-
26% of adware apps request unnecessary microphone or camera access
2. Smishing & Mobile-Specific Phishing in 2026
Smishing (SMS phishing) remains one of the most successful attack vectors. In 2026, attackers increasingly combine AI, automation, and region-specific data to craft believable messages.
Smishing Statistics: 2026 Update
-
Percentage of mobile users who received a phishing SMS in the last 90 days: ≈ 63%
-
YoY increase in smishing attempts: ≈ +34%
-
Success rate of mobile phishing vs desktop phishing:
-
Mobile: ~3.5× higher success
-
Desktop: significantly lower
-
-
Percentage of smishing targeting financial services: ≈ 44%
-
Percentage of smishing impersonating delivery & logistics companies: ≈ 27%
Why Smishing Is More Effective in 2026
Smaller screen = less URL visibility
Attackers exploit the fact that mobile interfaces hide full URLs and security indicators.
Users respond faster to SMS notifications
Urgency manipulation (“Your account is locked”, “Your package is arriving”, etc.) works extremely well.
Lack of anti-phishing browser extensions
Desktop users often benefit from extensions and filters; mobile users do not.
AI-generated personal details
Attackers use data leaked from other breaches to personalize messages.
Multi-channel phishing
Smishing → fake app download → cloud credential theft is now a common chain.
3. Fake Apps, App Store Abuse & Malicious APKs in 2026
The app ecosystem became dramatically riskier in 2026 due to easy app-cloning tools, widespread repackaging, and increased distribution of malicious APKs. Even official stores struggle to keep up.

2026 Fake App & Malicious APK Statistics
-
Malicious app downloads (global): Projected ≈ 75–90 million installs
-
YoY increase in app-store fraud: ≈ +46%
-
Percentage of malicious apps posing as utilities/tools: ≈ 39%
-
Percentage posing as financial apps: ≈ 23%
-
Percentage of users who installed at least one “unsafe” app: ≈ 19%
-
Percentage of malicious apps using excessive permissions: ≈ 61%
Common Excessive Permission Requests:
-
Contacts
-
SMS & notification access
-
Microphone & camera
-
Filesystem read/write
-
Accessibility controls (most abused in 2026)
Apps misusing the Android Accessibility Service increased by ~37% YoY, enabling attackers to control devices remotely.
Malicious Apps in Official Stores (2026 Reality)
Although official stores improved their scanning systems:
-
Hundreds of malicious apps still bypass initial vetting
-
Many achieve thousands to millions of downloads before removal
-
Attackers frequently re-upload apps with new names or icons
-
Malicious SDKs inside legitimate apps cause indirect compromises
4. Insecure Wi-Fi & MITM Attacks in 2026
Public Wi-Fi remains dangerous due to mass device adoption and careless user behavior.
2026 Wi-Fi Security Statistics

-
Mobile users who connected to open Wi-Fi in last 30 days: ≈ 68%
-
Users who performed financial actions on public Wi-Fi: ≈ 29%
-
MITM attack growth YoY: ≈ +31%
-
Users who use VPN regularly: Only ≈ 27%
-
Percentage of mobile apps vulnerable to MITM due to poor SSL/TLS: ≈ 19%
Common Wi-Fi Attack Types in 2026:
-
Rogue access points
-
Session hijacking
-
DNS spoofing
-
HTTPS stripping (where apps don’t enforce TLS)
-
Credential interception in apps using outdated SSL libraries
In 2026, attackers increasingly target payment apps, crypto wallets, and business cloud logins over unsecured Wi-Fi.
5. QR Code Fraud & NFC-Based Attacks in 2026
QR codes exploded in popularity due to banking, restaurant payments, parking apps, and online purchases. Attackers followed quickly.
QR Scam Growth & Statistics
-
YoY growth of QR-based fraud: ≈ +52%
-
Users who scan QR codes weekly: ≈ 71%
-
Percentage of malicious QR codes found in public areas: ≈ 18%
-
Payment fraud linked to QR manipulation: ≈ 14% of total mobile-payment fraud
-
Fake parking ticket QR scams up: +63% YoY
Common QR Attack Types
-
Redirecting to phishing pages
-
Auto-installing malicious APKs
-
Initiating pre-filled payment requests
-
Spoofing merchant QR codes at physical stores
6. SIM Swap Attacks 2.0 — More Aggressive in 2026
SIM swap attacks evolved dramatically due to improved social engineering, identity theft kits, and weak telecom verification in some regions.
2026 SIM Swap Statistics
-
YoY increase in SIM swap incidents: ≈ +38%
-
Percentage of attacks leading to financial loss: ≈ 57%
-
Percentage involving unauthorized access to email/cloud accounts: ≈ 46%
-
Recovery time for victims: typically 3–10 days
-
Attacks originating from breached personal data: ≈ 72%
New 2026 method:
-
Attackers combine deepfake audio with stolen personal info during telecom support calls.
7. Deepfake Vishing & AI-Assisted Fraud in 2026
Deepfake threats exploded in 2026.
2026 Deepfake Attack Statistics
-
YoY increase in deepfake-enabled social engineering: ≈ +62%
-
Percentage targeting financial verification calls: ≈ 31%
-
Businesses reporting deepfake impersonation attempts: ≈ 27%
-
Success rate when targeting customer support teams: ≈ 19%
How attackers use deepfakes in 2026:
-
Mimicking a bank customer’s voice
-
Impersonating company executives
-
Bypassing account recovery identity challenges
-
Convincing users to “verify” details over the phone
AI-driven fraud is expected to double again by the end of 2027.
2026 has reshaped how organizations view mobile devices. What used to be a secondary endpoint is now a primary target in security strategies. Hybrid work, cloud-first applications, and rising mobile-based identity authentication have made mobile security central to enterprise cyber resilience.
Below are the most critical enterprise-level trends and risks for 2026, complete with updated statistics and behavior patterns.
Enterprise Mobile Security Trends in 2026
Organizations face a growing challenge: employees rely more on mobile devices for work, but attackers are also increasingly targeting those devices to compromise corporate networks. Security leaders now treat mobile endpoints as high-risk entry points equal to laptops and servers.
1. Mobile Device Management (MDM) Adoption in 2026
MDM systems have become standard for large enterprises, especially those supporting hybrid or remote workforces.
2026 MDM Adoption Stats
-
Global enterprise MDM adoption: ≈ 82%
-
Large enterprises using MDM: ≈ 94%
-
SMBs using MDM solutions: ≈ 56% (up from ~48% in 2025)
-
YoY growth in MDM deployments: ≈ +21%
-
Organizations using MDM + MAM together: ≈ 69%
What’s driving MDM growth in 2026?
-
Stricter compliance requirements
-
Increased remote workforce mobility
-
Higher BYOD adoption
-
Concern around mobile credential harvesting
-
Expansion of passwordless authentication & device attestation
-
Incident-response teams needing remote wipe and lockdown capabilities
Organizations now require MDM not just for device control, but for identity enforcement and threat telemetry.
2. Rise of Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) in 2026
MTD is one of the fastest-growing categories in enterprise cybersecurity.
2026 MTD Growth Metrics:
-
MTD adoption across enterprises: ≈ 61%
-
YoY growth rate: +34%
-
Enterprises integrating MTD into SOC workflows: ≈ 43%
-
Organizations combining MDM + MTD + ZTNA: ≈ 37%
What makes MTD essential in 2026?
-
Detects malicious apps installed on employee devices
-
Identifies insecure Wi-Fi and MITM attacks
-
Analyzes risky network behaviors
-
Detects mobile phishing at device level
-
Provides app reputation scoring
-
Monitors device compliance posture in real time
As threats become more automated, enterprises increasingly rely on MTD for anomaly detection that traditional antivirus tools cannot provide.
3. Zero Trust Adoption for Mobile Endpoints (2026)
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has evolved from a trend to a baseline requirement.
2026 Zero Trust Statistics:
-
Enterprises implementing Zero Trust for mobile: ≈ 72%
-
Percent of organizations moving to identity-first access: ≈ 81%
-
Organizations enforcing device posture checks before access: ≈ 64%
-
Companies using mobile device certificates for authentication: ≈ 47%
-
Growth in mobile-based ZTNA deployments: ≈ +36% YoY
Key Zero Trust controls used in 2026:
-
Real-time risk scoring
-
Device compliance verification
-
App integrity checks
-
Conditional access based on network & identity
-
MFA tied to hardware-level security
-
Certificate-based authentication over TLS
Zero Trust is no longer optional — it’s a mandatory framework for enterprises with mobile-first or hybrid workforces.
4. VPN Usage & Secure Remote Access Trends (2026)
VPN usage remains high, but companies are shifting from VPN-only models toward ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access).
2026 VPN Adoption Trends:
-
Corporate-managed mobile devices using VPN: ≈ 52%
-
YoY decline of VPN-only access: –14%
-
Enterprises replacing VPN with ZTNA for mobile: ≈ 39%
-
Users relying on personal VPN apps: ≈ 31%
Key limitations of traditional VPNs:
-
They provide too much implicit trust
-
They fail to evaluate device risk in real time
-
They cannot protect users from malicious apps
-
They are easily misconfigured
Despite this, VPNs still serve as a basic security measure for smaller organizations.
5. Mobile Compliance Risks: HIPAA, GDPR, CPRA, PCI-DSS (2026 Update)
Regulatory bodies now enforce mobile-specific security expectations.
2026 Compliance Violation Statistics:
-
Percent of compliance failures involving mobile devices: ≈ 58%
-
Organizations fined due to mobile data exposure: ≈ 17%
-
Organizations failing encryption requirements on mobile: ≈ 23%
-
Enterprises lacking documented mobile security policies: ≈ 31%
-
Healthcare providers with unsecured mobile endpoints: ≈ 41%
Industries with highest mobile compliance risk:
-
Healthcare (due to PHI access from mobile apps)
-
Financial services (due to mobile banking, trading, wallets)
-
Government agencies
-
Legal & consulting firms handling sensitive client data
-
Retail & e-commerce (customer data, payment systems)
Compliance is now directly tied to mobile device posture, app integrity, and encryption use.
Consumer Mobile Security Behaviors in 2026
While businesses have improved mobile readiness, consumer behavior continues to lag behind threat evolution.
Despite increased awareness, user actions remain one of the biggest contributors to mobile security incidents.
1. Lack of Endpoint Protection on Consumer Devices
2026 Consumer Security Adoption Statistics:

-
Users without antivirus or mobile security apps: ≈ 59%
-
Android users lacking endpoint protection: ≈ 68%
-
iOS users relying solely on default security: ≈ 79%
-
Users who believe “iPhones can’t get hacked”: ≈ 38%
This false sense of security increases exposure to:
-
Malicious apps
-
Phishing pop-ups
-
Spyware
-
Malicious configuration profiles
-
Credential-stealing malware
2. Risky Mobile Behaviors in 2026
Human error remains a top mobile security risk.
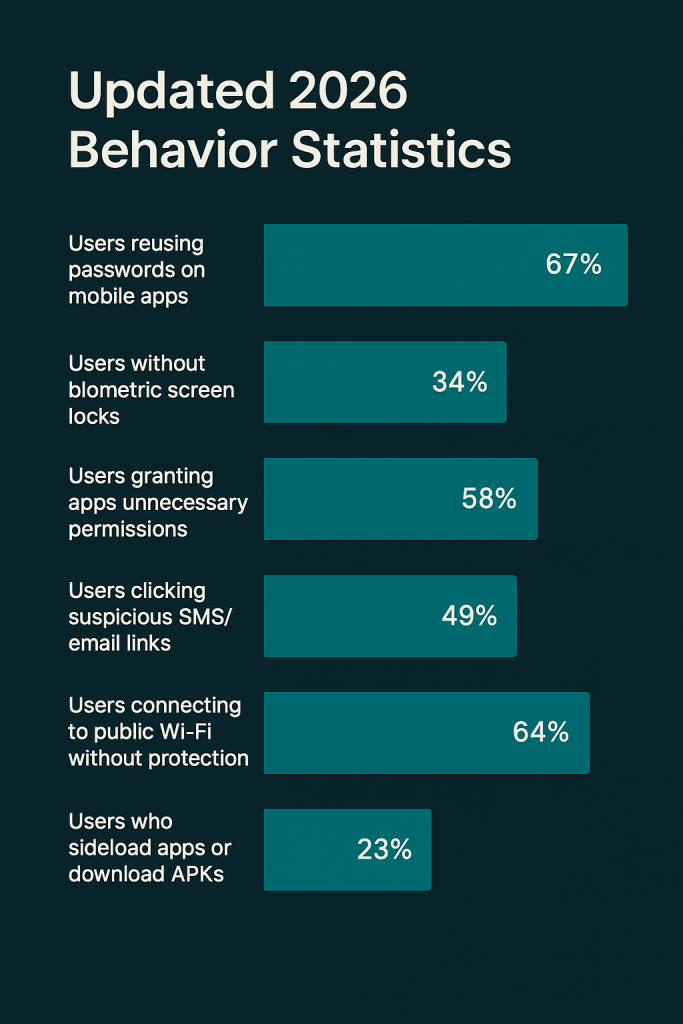
Updated 2026 Behavior Statistics:
-
Users reusing passwords on mobile apps: ≈ 67%
-
Users without biometric screen locks: ≈ 34%
-
Users granting apps unnecessary permissions: ≈ 58%
-
Users clicking suspicious SMS/email links: ≈ 49%
-
Users connecting to public Wi-Fi without protection: ≈ 64%
-
Users who sideload apps or download APKs: ≈ 23%
Why risky behavior continues:
-
Mobile devices feel “personal” and safe
-
Notifications drive impulsive actions
-
Users trust app store results too easily
-
Misconceptions about malware (“only PCs get hacked”)
-
Lack of security education
3. OS Update Adoption Rates in 2026
Delayed updates remain one of the biggest mobile vulnerabilities.
2026 Update Adoption Metrics:
Android
-
Users running latest Android version: ≈ 58%
-
Users running Android versions older than 2 years: ≈ 29%
-
Devices with known unpatched vulnerabilities: ≈ 34%
iOS
-
Users updated to latest iOS version: ≈ 82%
-
Users delaying updates > 60 days: ≈ 11%
Why updates matter more in 2026:
-
Zero-click exploits are rising
-
Apps rely more on underlying OS security
-
Outdated devices skip critical patches
-
Mobile malware adapts faster than before
4. Awareness of Phishing, Permissions & Digital Risk
2026 shows a growing gap between awareness and safe behavior.
Awareness vs Behavior Gap Metrics:
-
Users who “know what phishing is”: ≈ 84%
-
Users who can actually identify a phishing attempt: ≈ 44%
-
Users who review app permissions before installation: ≈ 31%
-
Users who assume app stores block all dangerous apps: ≈ 41%
This mismatch shows why user education remains essential — especially as AI-generated scams become harder to recognize.
Mobile applications have become the backbone of digital business — powering global communication, banking, commerce, health tracking, cloud access, and identity verification. But this dependence means that vulnerabilities in mobile apps directly translate into large-scale breaches, data exposure, fraud, and regulatory failures. In 2026, insecure apps and APIs represent one of the top three cyber risks for enterprises worldwide.
Mobile App Security & Encryption Trends in 2026
As mobile usage intensifies, so does attention on app security controls, encryption standards, SDK integrity, and API hardening. Below are the most important trends shaping mobile app security in 2026.
1. TLS/SSL Adoption & Hygiene in Mobile Apps (2026 Update)
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the foundation of encrypted mobile communication. However, many developers still misconfigure TLS or rely on outdated protocols, exposing users to interception and MITM attacks.
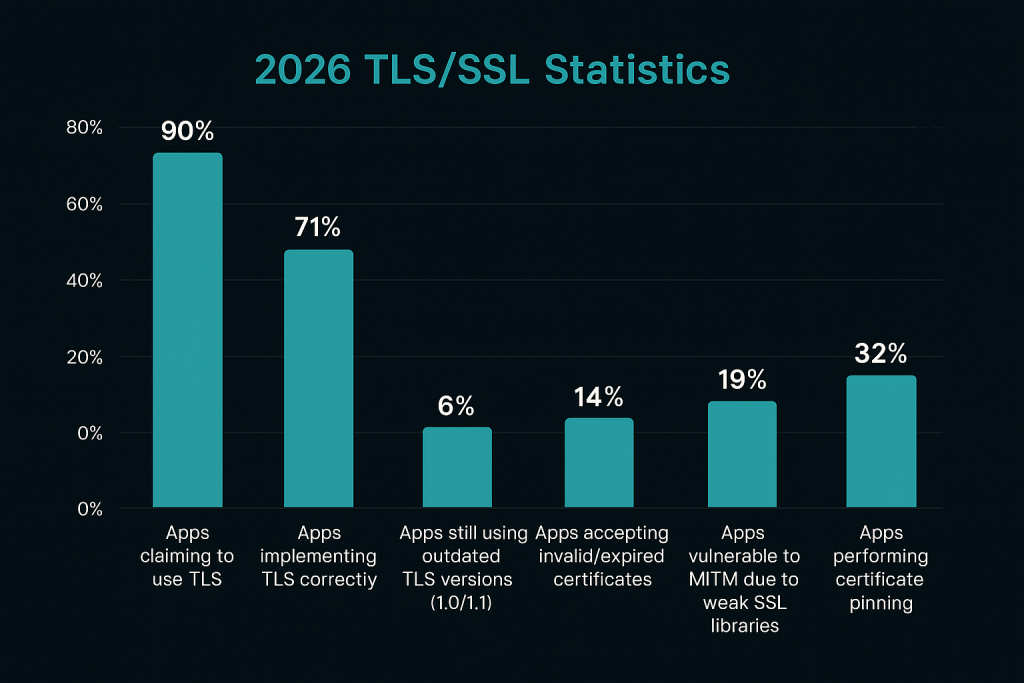
2026 TLS/SSL Statistics
-
Apps claiming to use TLS: ≈ 90%
-
Apps implementing TLS correctly: ≈ 71%
-
Apps still using outdated TLS versions (1.0/1.1): ≈ 6%
-
Apps accepting invalid/expired certificates: ≈ 14%
-
Apps vulnerable to MITM due to weak SSL libraries: ≈ 19%
-
Apps performing certificate pinning: ≈ 32%
Most common mobile TLS misconfigurations in 2026:
-
No certificate validation (trusting all certificates)
-
Allowing self-signed certificates in production
-
Using deprecated ciphers
-
Not enforcing TLS 1.2+
-
Lack of certificate pinning
-
Outdated SSL libraries bundled in SDKs
-
Missing HSTS on mobile web content
Impact in 2026:
These misconfigurations enable:
-
Traffic interception on public Wi-Fi
-
Session hijacking
-
Credential and token theft
-
Replay attacks on mobile APIs
-
Payment fraud
-
Account takeover by intercepting mobile app traffic
With the rise of passwordless authentication and device-bound identities, TLS failures directly compromise user accounts.
2. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) Trends in 2026
End-to-end encryption protects data before it leaves the device. Adoption continues to grow, especially in messaging, finance, and healthcare.
2026 E2EE Adoption Metrics
-
Top messaging apps using E2EE: 100%
-
Global messaging apps with default E2EE: ≈ 68% (up from ~63% in 2025)
-
Banking apps using E2EE beyond TLS: ≈ 81%
-
Fintech apps relying solely on TLS without E2EE: ≈ 19%
-
Healthcare apps with full E2EE: ≈ 47%
E2EE weaknesses in 2026:
Even with encryption, risks remain:
-
Compromised device can leak decrypted messages
-
Spyware captures content before encryption
-
Poor key management exposes sessions
-
Third-party SDKs may bypass encryption entirely
Encryption alone does not stop modern mobile threats — it must be paired with device-level and API-level protections.
3. Open-Source SDK Vulnerabilities & Supply-Chain Risks
More than 90% of mobile apps rely on third-party SDKs, making the supply chain a primary risk vector.
2026 SDK Risk Statistics
-
Apps with at least one outdated SDK: ≈ 55%
-
Apps with known-vulnerable SDK versions: ≈ 31%
-
SDKs responsible for critical vulnerabilities: ≈ 39%
-
Apps containing trackers/data-collectors via SDKs: ≈ 58%
-
Developers unaware of all SDKs in their app: ≈ 42%
Common SDK-related issues in 2026:
-
Hardcoded API keys exposed in app packages
-
SDKs communicating over insecure channels
-
Hidden advertising or data-mining modules
-
Outdated cryptographic libraries
-
Analytics SDKs leaking user data
-
Compromised open-source dependencies
Supply-chain attacks increasingly involve poisoning SDK updates to infect downstream apps — especially in finance, retail, and education.
4. Insecure APIs & Mobile Data Exposure (2026 Update)
APIs remain the #1 source of mobile app vulnerabilities.
2026 API Security Statistics
-
Percentage of mobile vulnerabilities tied to APIs: ≈ 74%
-
Most common API flaws:
-
Broken authentication (~36%)
-
Excessive data exposure (~29%)
-
Weak rate limiting (~21%)
-
Misconfigured CORS policies (~14%)
-
-
Increase in API-based mobile breaches YoY: ≈ +33%
Why APIs fail so often:
-
Developers trust mobile apps to “hide” data
-
Lack of granular access controls
-
APIs return too much sensitive information
-
Poor or missing input validation
-
Weak session tokens & no token expiry
-
Inconsistent authentication across environments
API attacks in 2026 increasingly exploit:
-
Payment APIs
-
Single Sign-On (SSO) flows
-
Account recovery APIs
-
Messaging APIs
-
Healthcare data APIs
Mobile apps rely heavily on APIs — meaning one API flaw can compromise millions of users.
Impact of AI, IoT & 5G on Mobile Security (2026 Edition)
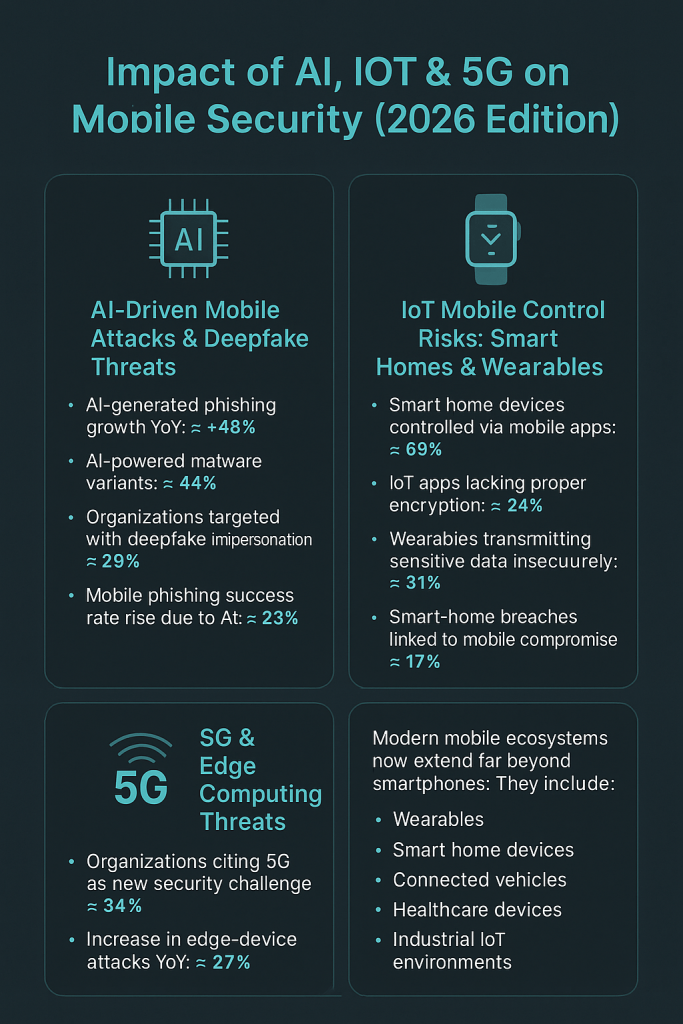
Modern mobile ecosystems now extend far beyond smartphones. They include:
-
Wearables
-
Smart home devices
-
Connected vehicles
-
Healthcare devices
-
Industrial IoT environments
This interconnected environment magnifies risks dramatically.
1. AI-Driven Mobile Attacks & Deepfake Threats
AI is the defining threat multiplier of 2026.
AI Attack Statistics (2026)
-
AI-generated phishing growth YoY: ≈ +48%
-
AI-powered malware variants: ≈ +44%
-
Organizations targeted with deepfake impersonation: ≈ 29%
-
Mobile phishing success rate rise due to AI: ≈ 23%
AI-driven attacks include:
-
Voice cloning used to bypass verification
-
AI malware that auto-modifies signature patterns
-
Smishing messages tailored to user behavior
-
Fake support calls using synthesized voices
-
Automated password-guessing using breached data
AI enables attackers to operate at a scale never seen before.
2. IoT Mobile Control Risks: Smart Homes & Wearables
Most IoT devices are controlled via mobile apps — making smartphones a gateway to full home or office compromise.
2026 IoT Mobile Risk Metrics
-
Smart home devices controlled via mobile apps: ≈ 69%
-
IoT apps lacking proper encryption: ≈ 24%
-
Wearables transmitting sensitive data insecurely: ≈ 31%
-
Smart-home breaches linked to mobile compromise: ≈ 17%
Rising IoT threats:
-
Weak BLE encryption
-
No firmware integrity checks
-
Poorly secured APIs
-
App-to-device pairing vulnerabilities
Attackers often compromise mobile apps to gain control over IoT devices.
3. 5G & Edge Computing Threats in 2026
5G adoption expanded rapidly, enabling faster speeds and lower latency. But it also introduced complex, decentralized security challenges.
2026 5G Risk Statistics
-
Organizations citing 5G as a new security challenge: ≈ 34%
-
Increase in edge-device attacks YoY: ≈ +27%
-
Percent of mobile traffic via 5G: ≈ 42%
-
Mobile D2D (device-to-device) communication growth: ≈ +31%
The biggest 5G-related risks:
-
More direct device communication
-
Reduced ability to inspect traffic centrally
-
Expanded attack surface at the network edge
-
Faster malware propagation
Security teams must adapt monitoring and segmentation strategies to the 5G era.
Mobile Payment & Digital Wallet Vulnerabilities (2026)
Digital wallets, NFC payments, QR codes, and mobile banking remain prime targets in 2026.
2026 Mobile Payment Statistics

-
Global mobile wallet adoption: ≈ 73%
-
YoY increase in mobile payment fraud: ≈ +39%
-
Wallet apps exploited via SIM-swap attacks: ≈ 22%
-
Fraud involving fake payment screens: ≈ 18%
-
Users conducting financial transactions on unsecured Wi-Fi: ≈ 27%
Emerging payment threats:
-
QR payment redirection
-
NFC relay attacks
-
Fake wallet app overlays
-
Credential stuffing targeting wallet accounts
-
Interception of OTP-based payment approvals
Mobile payment fraud is expected to rise significantly again in 2027.
Mobile Security Breach Costs & ROI in 2026
Mobile-related breaches cost organizations heavily.
2026 Mobile Breach Cost Metrics

-
Average cost of mobile-involved breach: ≈ $3.4 million
-
Cost increase from 2025: ≈ +12%
-
Downtime from mobile ransomware incidents: ≈ 21 hours per incident
-
Cost per hour of mobile-related downtime: ≈ $150,000
-
Regulatory fines linked to mobile data exposure: ≈ $1.9M average per case (industry-dependent)
ROI of Mobile Security Investments:
Organizations that implement strong mobile security measures see:
-
≈ 49% fewer mobile phishing incidents
-
≈ 41% fewer malware infections
-
≈ 30–40% reduction in breach costs
-
≈ 92% faster detection & containment
-
≈ 2.1× ROI within 24 months
Mobile security is no longer a cost center — it’s a financial safeguard.
Future Forecast: Mobile Security 2027 & Beyond
Top Predictions
1. Mobile security market will exceed $40B by 2027
Driven by:
-
Zero Trust
-
MTD adoption
-
Mobile identity systems
-
AI-based threat detection
2. Every consumer app will require stronger encryption
TLS 1.2 will no longer be sufficient by 2027.
3. Passwordless authentication will surpass passwords
Passkeys, biometrics, and device-bound credentials will dominate.
4. Deepfake fraud will double again by 2028
AI voice/video scams will require new verification technologies.
5. App stores will enforce stricter developer identity rules
Expect mandatory code signing and real-time behavioral vetting.
6. Post-quantum cryptography pilots will expand
Banks, governments, and health systems will lead adoption.
Conclusion: Navigating Mobile Security in 2026
Mobile security in 2026 is defined by rapid digital transformation paired with equally rapid threat evolution. Devices have become identity hubs, payment tools, personal storage vaults, and workplace endpoints — making them immensely valuable to attackers.
From AI-driven malware to deepfake fraud, insecure APIs to weak TLS, malicious apps to BYOD risks, the mobile threat landscape has broadened and deepened.
FAQ
1. What are the biggest mobile security threats in 2026?
AI-driven malware, deepfake impersonation, malicious apps, smishing, insecure Wi-Fi, API vulnerabilities, QR fraud, and SIM-swap attacks.
2. How fast is mobile malware growing in 2026?
Mobile malware increased by an estimated 41% YoY, driven heavily by automation and AI.
3. What percentage of users were targeted by smishing?
Approximately 63% of mobile users received at least one phishing SMS in the last 90 days.
4. Are mobile payments safe in 2026?
Safer than before, but fraud increased 39% YoY, especially involving fake apps, QR manipulation, and SIM swaps.
5. What percentage of mobile apps use secure TLS configurations?
Only ≈71% of apps implement TLS correctly; ≈14% still accept invalid certificates.
6. How many enterprises use MDM or MTD in 2026?
Approximately 82% use MDM and 61% use MTD, a sharp increase from previous years.
7. What is the average cost of a mobile-related data breach in 2026?
Around $3.4 million, including downtime, remediation, legal costs, and compliance penalties.
8. What can individuals do to protect themselves?
Use biometrics, avoid unsecured Wi-Fi, update OS/app regularly, avoid APKs, review app permissions, and remain alert to smishing.
Disclaimer:
The content published on CompareCheapSSL is intended for general informational and educational purposes only. While we strive to keep the information accurate and up to date, we do not guarantee its completeness or reliability. Readers are advised to independently verify details before making any business, financial, or technical decisions.


